![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
14 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What are the three types of blood vessels? |
Capillaries: Diffusion between blood and interstitial fluids Arteries: Carry oxygenated blood away from heart (with one exception) Veins: Return de-oxygenated blood to the heart (again, one exception) |
|
|
What are the structures of the three types of blood vessels? |
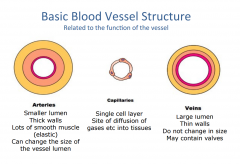
Arteries: Elastic and muscular Capillaries: Single cell thick, site of gas diffusion Veins: Thin walls as it is reservoir for blood |
|
|
What are the walls of the blood vessel? What are they made up of? |
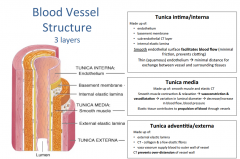
Tunica externa = outside Tunica media = middle Tunica intima = inside |
|
|
What do arteries branch off into? |
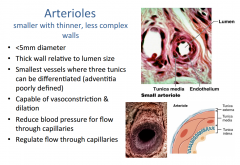
Arterioles: Smaller, contractile and somewhat elastic |
|
|
What are the details of the endothelial structure of blood vessels? |
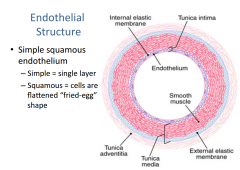
|
|
|
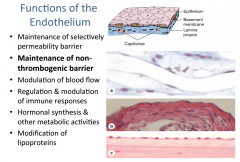
What are the functions of the endothelium? |
|
|
|
How do innervations of vessels work? (Contracting blood vessels etc to pump blood) |

|
|
|
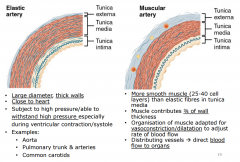
What are examples/functions of elastic and muscular arteries? |
|
|
|
What are the three types of capillaries and what do they do? |
Continuous = Barely any fenestration but allows diffusion Fenestrated = Slight gaps Sinusoidal = Large gaps |
|
|
What is the role of the venules? |
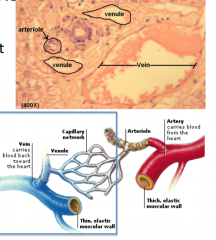
Draining the capillary network |
|
|
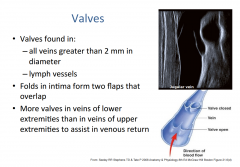
How do valves work in the veins? |
|
|
|
What are the mechanisms of venous return? |
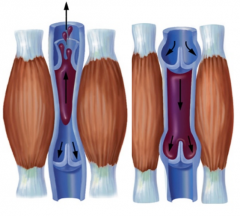
- Pressure (7-13 mmHg venous pressure towards heart) -Thoracic/respiratory pump (inhaling causes pressure changing, causing a pumping motion) - Gravity - Skeletal muscle pump (in the limbs, below heart) |
|
|
Summary of arterial and venous system |
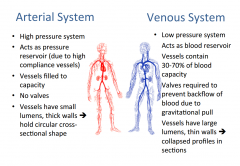
|
|
|
What are the two circuits of the heart? |
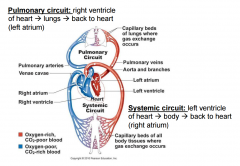
|

