![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
56 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
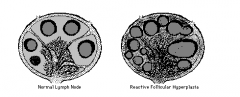
Enlargement of lymph nodes by hyperplasia of follicular (germinal) centers.
In FOLLICULAR HYPERPLASIA (increase in cell number), the hyperplastic germinal center contains a normal mixture of varibly sized lymphocytes, plasma cells, and macrophages, as well as a few dendritic reticular cells. No one lymphocyte type predominates as in lymphoma.
FOLLICULAR * rheumatoid arthritis |
|
|
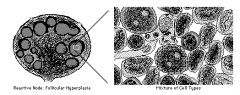
In SINUS HYPERPLASIA the sinuses become distended and filled with histiocyte/macrophages and some plasma cells.
1. **Rosai-Dorfman : 2. Kimura’s Disease: 3.** Whipple Disease: 4. Virus-Associated hemorrhagic syndrome 5. Dermatopathic lymphadenitis: 6. Autoimmune lymphproliferative syndrome: 7 . Mucocutaneous lymph node syndrome: Kawasaki’s |
|
|
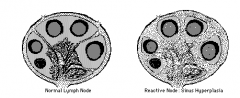
In DIFFUSE HYPERPLASIA the lymph node architecture is diffusely effaced by sheets of small lymphocytes, and a few scattered immunoblasts and macrophages. |
|
|
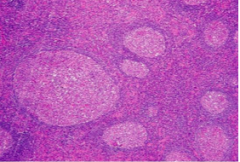
Non specific follicular hyperplasia **children and adolescents malignant NON-tender/unilateral infectious is bilateral and tender
Different sizes Regular circumscribed shape Mantle zone = lymphocyte surrounding border TINGIBLE BODY MACROPHAGES |
|
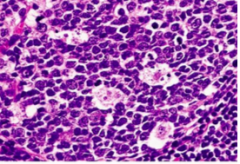
|
1. Tingible Body Macrophages: engulfed cell portions; pale cells in background
(this is a special kind of macrophage seen in follicular hyperplasia) |
|
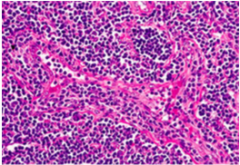
|
Paracortical Hyperplasia -caused by viral lymphadenitis 1. Post capillary venules 2. Karyolysis and karyorrhxis |
|
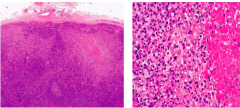
|
Necrotizing Lymphadenitis -expansion of follicles, some with necrotic dead cells at center -Necrosis in the subcapsular area (look for this as a good hint on the exam) -karyorrhexis and karyolysis on higher mag
|
|

|
Necrotizing Lymphadenitis- TB -Caseating necrosis |
|
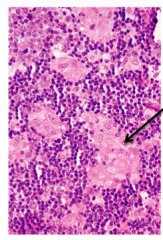
|
Necrotizing Lymphadenitis- Toxoplasmosis Lymphadenitis 1. NON-caseating necrosis 2. epitheloid histiocytes clusters 3. "monocytoid" cells that are actually B cells. 4. Toxoplasma cyst 5. in subscapsular and trabecular sinuses |
|
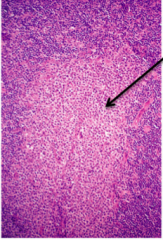
|
monocytoid B cell hyperplasia (subtype of b cells) (toxoplasmosis) |
|
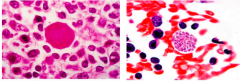
|
Toxoplasma cyst |
|
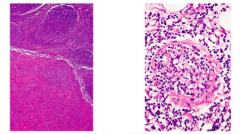
|
Follicular hyperplasia – syphilis *****plasmatic and lymphocytic infiltrate -Has periarteritis: b.v proliferation causing arthritis - spirochetes in wall of b.v |
|
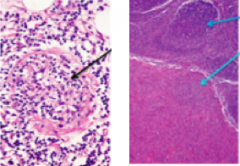
|
1. Plasmacytic and lymphocytic infiltrate*** 2. Periarteritis, spirochetesm inflammation and fibrosis
|
|
|
Granulomatous Lymphadenitis |
1. Kikuchi 2. Cat scratch 3. Lymphogranuloma verereum 4. Sarcoidosis |
|
|
Young women |
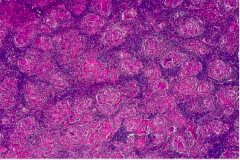
1. Kikuchi Disease ***Young women - C-shaped nuclei (maCrophages) in necrosis - fever - changes similar to SLE |
|
|
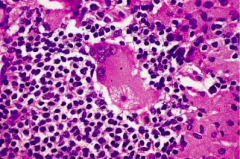
2. Sarcoidosis (Pulmonary typically 1. Asteroid bodies 2. NON-caseating dx of exclusions 3. more prominent in African Americans 4. Have discrete, well circumscribed epitheliod granulomas, 5. Schaumen bodies, Calcium oxalate crystals |
|
|
Asteroid Body |
|
|
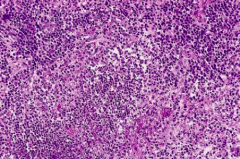
3. Cat Scratch Disease: 1. Stellate accesses with palisading macrophages 2. *Bartonella henselae: seen in early stages. The same organism but different population of infection: *Bacillary angiomatosis caused by same orgamism but in IMMUNOCOMPROMISED HOSTS** - may look like Kaposi’s sarcoma. |
|
|
Lymphogranuloma vereum NECROTIZING granuloma 1. similar to cat scratch 2. negative silver stain 3. presence of Chlamydia
|
|
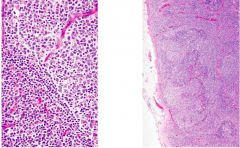
a |
HIV-related hyperplasia -geographical follicles (not round very irregular) -Extravasation o RBC in germinal centers is unique to HIV -Thinning of mantel zone -Wartthin-Finkledey - cells with multiple eosinophilic intranuclear inclusions -p24 |
|
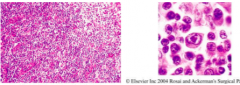
|
Infectious mononucleosis -Immunoblasts (second picture) look like Reed Sternberg Cells: prominent nucleoli, mem intact, minimal cytoplasm, ring around. -splenomegaly |
|
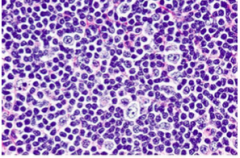
|
Post Vaccinial Lymphadenitis: used to be seen with smallpox, resembles mono, mottled vascular mixed cell infiltrate |
|
|
Allergic-like reaction |
Dilantin Hypersensitivity fever, erythematous rash, eosinophilia (THINK ALLERGIC RXN TYPE I); Immunoblasts, plasma cells |
|
|
Russel Bodies |
*Follicular Hyperplasia RA -Interfollicular plasmacytosis (similar to syphilis) -Russell Bodies -precurser lymphoma |
|
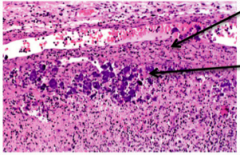
|
SLE: Lupus accumulation of basophilic staining |
|
|
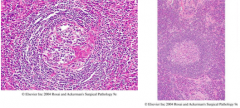
Castleman Disease* -giant lymph nodes -1. Hyaline vascularization= 'Onion skin' around germinal center represents lymphocytes -2. plasma cells = herpes 8 also linked to Kaposi’s Sarcoma (plasma cells are often asymptomatic) |
|
|
Sinus |
Sinus : non-specific pattern 1. **Rosai-Dorfman : 3.** Whipple Disease: |
|
|
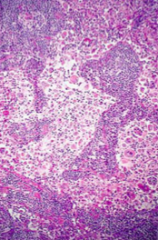
What disease is associated with macrophages with emperipolesis?* |
Rosai-Dorfman (macrophage ingested entire cell) |
|
|
1. **Rosai-Dorfman : **first two decades of life -Bilateral nontender cervical nodes -Dilated sinusitis histiocytes -S100 (stain) m -macrophages with emperipolesis: macrophage ingested entire cell. -Fevers, neutros, elevated ESR -Nodes matted together from fibrosis.
|
|
|
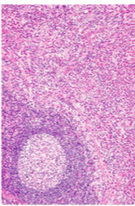
2. Kimura’s Disease:**** eosinophils*** (very pink area) -salivary glands
Kimora Lee Simmons, hello kitty
|
|
|
MIDDLE AGED MALES CNS: psych, neuro, deficits |
3.** Whipple Disease: -foamy macrophages with bacillary organism -Tropheryma whippeli -malabsorption, sickle-shaped
foamy whipped cream dirty old men
|
|
|
Younger children with pancytopenia |
4. Virus-Associated hemorrhagic syndrome Younger children with pancytopenia (low WBC, platelets) -constitutional symptoms. -bland macrophages
hemorrhagic, de=panted vampire sucks your blood and makes you pale |
|
|
Skin disease |
5. Dermatopathic lymphadenitis: associated with skin diseases especially exfoliative dermatitis; skin sloughs off; paracortical/interfollicular expansion of large cells. -Mimics lymphoma: mycosis fungoides -pigmented macrophages |
|
|
ALPS |
6. Autoimmune lymphproliferative syndrome: (ALPS) -caspase 10 -SPLENOMEGALY. -Hypergammaglobinemia.
|
|
|
Conjunctivitis, coronary artery involvement, KIDS (K's: kids, konjunctivitis, koronary artery involvement) |
7 . Mucocutaneous lymph node syndrome: Kawasaki’s Lymphoid depletion and absence of follicles. Foci necrosis and thrombi in vessels |
|
|
Wartthin-Finkledey |
HIV hyperplasia: cells with multiple eoisinophilic intranuclear inclusions. |
|
|
plasmacytic and lymphocytic infiltrate |
follicular hyperplasia- syphilis |
|
|
What age group is non-specific follicular hyperplasia common in? |
adolescents and children |
|
|
What is a key sign of follicular hyperplasia - syphilis? |
Plasmacytic and lymphocytic infiltrate |
|
|
What is a common disease in young women? |
Kikuchi Disease -C-shaped nuclei (maCrophages) -fever and looks similar to SLE |
|
|
What can be seen in immunocompromised people with Cat Scratch Fever? |
-Bartonella henselae is normal host and -BACILLIARY ANGIOMATOSIS is in immune compromised |
|
|
Herpes virus 8 is associated with.... |
1. Bacillary angiomatosis 2. Kaposi Sarcoma 3. Plasma cell: Castleman disease |
|
|
Is what checked in the serum in the first few weeks after a possible HIV exposure? |
p24 -HIV-core protein in germinal centers -useful for diagnosing very early infection when antibody levels are still low. |
|
|
1. Caseating vs 2. Non Caseating granulomas |
1. TB and 2. Toxoplasmosis |
|
|
Wartthin-Finkledey cell |
HIV- related hyperplasia, cells with multiple eosinophilic intranuclear inclusions |
|
|
Reed Sternburg Cells |
Prominent nucleoli, mem intact, minimal cytoplasm, ring around.
HL, mimics in mono |
|
|
People 20 and under |
Rosai-Dorfman syndrome |
|
|
What disease are plasma cells asymptomatic? |
Castleman's disease |
|
|
What disease do eosinophils have extensive infiltration?* |
Kimura disease |
|
|
What disease is associated with foamy macrophages? |
Whipple disease |
|
|
What mimics lymphoma, specifically mycosis fungoides? |
dermatophatic lymphadenitic |
|
|
What are Russell bodies associated with? |
RA |
|
|
What regulatory gene does HIV need to progress to AIDS? |
nef - which down regualtes cell surface expression of CD4 and MHC 1 |
|
|
what protein undergoes conformational change to fuse with CRC-5? |
gp41 |
|
|
NNRTI |
do not bind to active site do not need to be phosphorylated
|
|
|
NRTIs |
nuceoside analgoues incorporated into genome need to be phosphorylated
resistance: reverse transcriptase mutation (pol gene) |

