![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
45 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
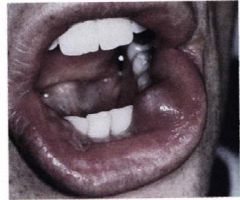
what's this?
|
Mucocele
|
|
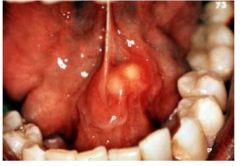
This is..
|
Sialolithiasis
|
|

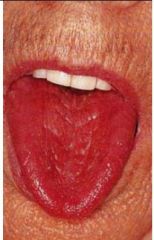
this is
|
Necrotising sialometaplasia
|
|
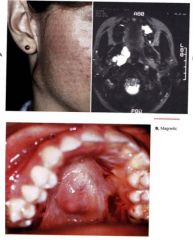
what is this condition caused by?
|
Sjögren syndrome
|
|
What's this?
|
Pleomorphic adenoma (PA)
|
|
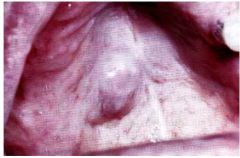
What's this?
|
Mucoepidermoid carcinoma
|
|
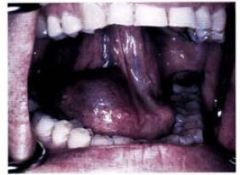
What's this?
|
Ranula
|
|
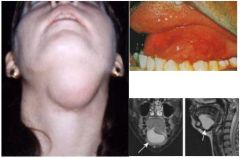
What's this?
|
Plunging ranula
|
|
|
Mucocele
Cause? |
Tissue swelling composed of pooled mucus escaped from a
severed salivary duct into the connective tissue. Continued production of the saliva even after the severed duct and pooling results |
|
|
Mucocele
locations? |
lower lip and minor salivary glands
|
|
|
Mucocele
Which is more involved? major salivary glands or minor salivary glands? |
minor salivary glands
|
|
|
Mucocele:
What's Ranula? |
If swelling appears in the floor of the mouth as a result of minor sublingual gland duct severance it's called Ranul
|
|
|
Mucocele
What's Plunging ranula or mucocele? |
Mucocele that occurs due to severance of Wharton's duct (submandibular gland)
|
|
|
Sialolithiasis
Cause? |
Due to salivary stones blocking duct
|
|
|
Sialolithiasis
Which gland is affeted? |
submandibular gland
|
|
|
Sialolithiasis
What's happens if the duct gets blocked? |
bacterial infection occurs
|
|
|
Sialolithiasis
Age and sex? |
Average age = 45 years and no sex prediliction
|
|
|
Sialolithiasis
Symptomatic? |
Yes
Pain and swelling, especialy during meal time |
|
|
Necrotising sialometaplasia
Cause? |
unknown
|
|
|
Necrotising sialometaplasia
Location? |
Hard palate
|
|
|
Necrotising sialometaplasia
Treatment? |
It will spontaneously heal
|
|
|
Sjogren's syndrome
Common? |
uncommon
|
|
|
Sjogren's syndrome
age and sex? |
elderley females
|
|
|
Sjogren's syndrome
what is it? |
Autoimmune disease where the T-lymphocytes destroy exocrine glands
|
|
|
Sjogren's syndrome
aetiologic factors? |
viral and genetic
|
|
|
Sjogren's syndrome
what r the types? |
primary and secondary
|
|
|
Sjogren's syndrome
Differentiate between primary and secondary SS |
if the disease only affects the lacrimal and salivary glands it's primary
if it is related to other autoimmune disease (eg. rheumatoid arthritis systemic, lupus erythematosus, scleroderma) it's secondary |
|
|
Sjogren's syndrome
clinical features? |
Xerostomia,
Difficulty eating Soreness Frothy viscous saliva |
|
|
What are the most popular benign lesions of the salivary glands in order?
|
1st: Pleomorphic adenoma
2nd: Papillary cystadenoma lymphamatosum |
|
|
Papillary cystadenoma lymphamatosum
is AKA? |
Warthin tumour
|
|
|
Papillary cystadenoma lymphamatosum
sex and age? |
male
6 to 7th decade |
|
|
Papillary cystadenoma lymphamatosum
lateral or bilateral? |
bilateral
|
|
|
Pleomorphic adenoma
what kind of tumour? |
Mixed tumour
Wide variation in variation in parenchymal and stromal differentiation |
|
|
Pleomorphic adenoma
Why the term "Pleomorphic" was given? Is this valid? why? |
since it was thought the
growth originated from ‘multiple’ germ layers that give rise to ‘epithelial’ and ‘mesenchymal’ components of salivary tissue. Now we know that, myoepithelial cell is present in periductal locations and has the ‘potential’ to ‘differentiate’ into “epithelial” and "connective tissue” cell types |
|
|
Pleomorphic adenoma
rate of growth? |
slow
|
|
|
Pleomorphic adenoma
age and sex? |
3 to 5th decade
female 2: male 1 |
|
|
Pleomorphic adenoma
Histology features? |
Pronounced fibrous capsule
Two dominant patterns: ‘medullary’ (diffuse sheets) and ‘trabacular’ (interlacing cords) |
|
|
Pleomorphic adenoma
Malignant transformation? |
less than 1%
|
|
|
Mucoepidermoid carcinoma
types? |
high and low grade
|
|
|
Mucoepidermoid carcinoma
age and sex? |
any age but peak 3rd 7th decade
females |
|
|
Mucoepidermoid carcinoma
which gland? |
50% in parotid
|
|
|
Mucoepidermoid carcinoma
what's the uncommon malignant feature? |
may be movable
|
|
|
Mucoepidermoid carcinoma: Histopathology
cell types? |
mucus
epidermoid intermediate |
|
|
Mucoepidermoid carcinoma
Low grade has ____ ____ potential |
limited metastastic
|
|
|
Mucoepidermoid carcinoma
What lines the cystic spaces? |
goblet mucus secreting cells
columnar ductal cells |

