![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
15 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What does chi square analysis do? |
It investigates whether there is an association between categorical variables |
|
|
What is a level of measurement? |
The abstract number that you use to separate categories. The numbers have no relevance, they are merely labels because statistics programs work in numbers. |
|
|
What is the opposite to a categorical variable? |
a continuous variable |
|
|
What are three different types of categorical variables? |
Binary (e.g. dead or alive pigeons) Nominal (e.g. meat eaters, vegetarians, vegans) Ordinal variables ( e.g. H1, H2, H3, etc) |
|
|
What are the two different types of continuous variables? |
Interval (e.g. 5 point likert scale, strongly agree to strongly disagree) Ratio (e.g. RTs- which have a true zero point, as in all scores are related back to zero) |
|
|
Is age a continuous variable or a categorical variable? |
It can be both, depending on the study |
|
|
What is meant by the count? |
It is the frequency of individual scores in a category |
|
|
What does independence mean in terms of a chi square analysis? |
that there is not association between the two variables |
|
|
When do you have evidence for an association between the two variables? |
If there is a substantial difference between the observed data and what we would expect if the variables are independent. |
|
|
If you find a difference between two categorical variables, does that mean there is an association? |
No, but whether the differences are large enough to be confident about an association? |
|
|
How do you calculate the residuals in a chi square analysis? |
Minus the Expected data from the Observed data. O - E = residual |
|
|
If you summed the residuals across categories, what would happen? |
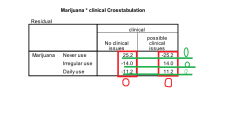
The would equal zero |
|
|
So what is the Chi Square Statistic? |
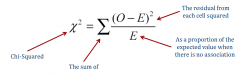
minus the expected count from the observed count, square it, and then divide it by the expected count again (to make it proportionally relevant). |
|
|
How do we calculate the degrees of freedom in a chi square statistic? |
df = (r-1)(c-1) |
|
|
Remember: The effect of adding more and more cells makes the chi square bigger before it becomes improbable that there is no association. |

|

