![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
68 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Cell Genome |
all the DNA contained in a cell |
|
|
Chromosomes |
what DNA molecules are packaged into |
|
|
Chromatin |
a complex of DNA and protein that condenses during cell division |
|
|
Somatic cells |
~non-reproductive cells ~have two sets of chromosomes ~have 23 pairs of chromosomes |
|
|
Gametes |
reproductive cells; have half as many chromosomes as somatic cells |
|
|
Heterochromatin |
a less active form of chromatin |
|
|
Euchromatin |
fully active chromatin; the genes are in use |
|
|
Sister Chromatids |
two identical copies formed by the replication of a single chromosome, with both copies joined together by a common centromere |
|
|
Mitosis |
the division of the genetic material in the nucleus |
|
|
Cytokinesis |
the division of the cytoplasm |
|
|
Interphase |
~cell growth and copying of chromosomes in preparation for cell division ~about 90% of the cell cycle |
|
|
Subphases of Interphase |
~G1 phase - first gap ~S phase - synthesis; only time when chromosomes are duplicated ~G2 phase - second gap |
|
|
G2 of Interphase |
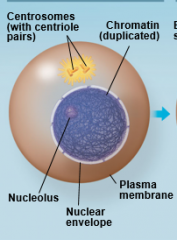
|
|
|
Prometaphase |
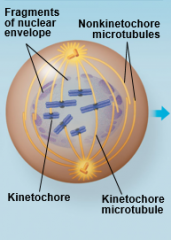
|
|
|
Prophase |
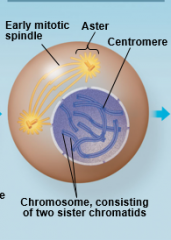
|
|
|
Metaphase |
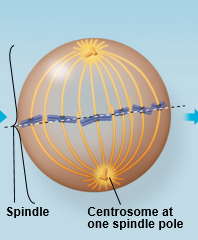
|
|
|
Anaphase |
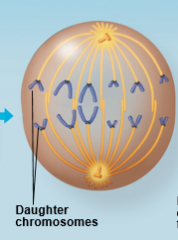
|
|
|
Telophase |
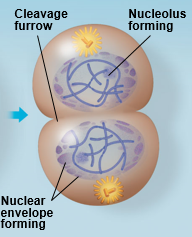
|
|
|
Mitotic Spindle |
is a structure made of microtubules that controls chromosome movement during mitosis |
|
|
Centrosome |
the microtubule organizing center |
|
|
Aster |
a radial array of short microtubules that extends from each centrosome |
|
|
Kinetochores |
protein complexes associated with centromeres |
|
|
Metaphase Plate |
an imaginary structure at the midway point between the spindle's two poles |
|
|
Binary Fission |
a reproductive process carried out by prokaryotes that involves chromosome replication, separation of sister chromatids, the inward pinching of the plasma membrane that results in cell division |
|
|
Origin of Replication |
where the chromosome begins to replicate in binary fission |
|
|
Cell Cycle Control |
how sequential events of the cell cycle are directed |
|
|
G0 Phase |
a non-dividing state reached in cells when there is no signal to begin mitosis |
|
|
Maturation-Promoting Factor (MPF) |
cyclin-Cdk complex that triggers a cell's passage past G2 phase |
|
|
Density-Dependent Inhibition |
an external signal where crowded cells stop dividing |
|
|
Anchorage Dependence |
Cells must be attached to a substratum in order to divide |
|
|
Transformation |
the process of a normal cell being converted into a cancerous cell |
|
|
Hypertrophy |
~Increase in cell size ~Normal organization
|
|
|
Hyperplasia |
~increase in cell number ~normal organization |
|
|
Dysplasia |
~disorganized cell growth |
|
|
Neoplasia |
~disorganized cell growth ~net increase in number of dividing cells |
|
|
Metastasize |
the exporting of cancer cells to other parts of the body where they may form secondary tumors |
|
|
Genetics |
the scientific study of heredity and variation |
|
|
Heredity |
the transmission of traits from one generation to the next |
|
|
Variation |
demonstrated by the differences in appearance that offspring show from parents and siblings |
|
|
Genes |
the units of heredity, made up of segments of DNA |
|
|
Locus |
the specific location of each gene on a certain chromosome |
|
|
Asexual Reproduction |
a single individual passes genes to its offspring without the fusion of gametes |
|
|
Clones |
a group of genetically identical individuals from the same parent |
|
|
Sexual Reproduction |
two parents give rise to offspring that have unique combination of genes inherited from the two parent |
|
|
Life Cycle |
the generation-to-generation sequence of stages in the reproductive history of an organism |
|
|
Karyotype |
an ordered display of the pairs of chromosomes from a cell |
|
|
Homologous Chromosomes |
the two chromosomes in each pair |
|
|
Sex Chromosomes |
determine the sex of an individual (X and Y) |
|
|
Autosomes |
the 22 pairs of chromosomes that do not determine the sex of an individual |
|
|
Diploid cell |
has 2 sets of chromosomes |
|
|
Zygote |
a fertilized egg that has one set of chromosomes from each parent |
|
|
Meiosis |
involved in the production of one set of chromosomes; a process for only sex cells |
|
|
Meiosis I |
homologs pair up and separate, resulting in two haploid daughter cells with replicated chromosomes |
|
|
Meiosis II |
sister chromatids separate |
|
|
Prophase I |
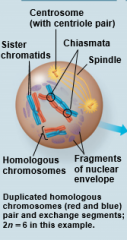
|
|
|
Metaphase I |
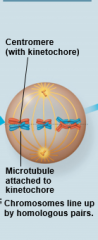
|
|
|
Anaphase I |
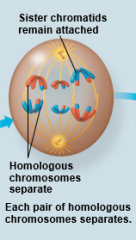
|
|
|
Telophase I |
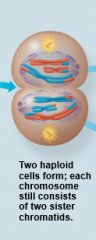
|
|
|
Synapsis |
homologous chromosomes loosely pair up, aligned gene by gene |
|
|
Crossing Over |
nonsister chromatids exchange DNA segments |
|
|
Chiasmata |
X-shaped regions where crossing over occurred |
|
|
Prophase II |

|
|
|
Metaphase II |
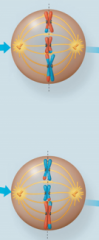
|
|
|
Anaphase II |

|
|
|
Telophase II |
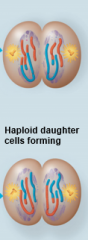
|
|
|
3 Mechanisms that Contribute to Genetic Variation |
~Independent assortment of chromosomes ~Crossing over ~Random fertilization |
|
|
Independent Assortment |
each pair of chromosomes sorts maternal and paternal homologues into daughter cells independently of the other pairs |
|
|
Recombinant Chromosome |
combines the DNA inherited from each parent |

