![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
78 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Squamous papilloma: cause?
|
HPV
|
|
|
Squamous papilloma:
Clinical Presentation? |
Sessile/peduncuated
White/pink Solitary Soft palate, uvula, tongue, gingiva, buccal mucosa |
|
|
Squamous papilloma
Histology? |
Thick papillary keratinised or non-keratinised layer
Central core of fibro-vascular CT |
|
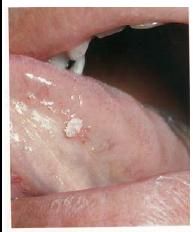
What's this?
|
Squamous Papilloma
|
|
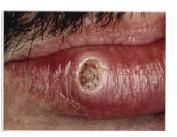
What's this?
|
Keratoacanthoma
|
|
|
Which epithelial lesion mimic SCC?
|
Keratoacanthoma
|
|
|
Keratoacanthoma:
Locations? |
Hair bearing and sun exposed skin
Cheeks, nose, eyelids, ears and lower lip |
|
|
Keratoacanthoma
Age? |
50 years or more
|
|
|
Keratoacanthoma
Sex? |
Male 2: female1
|
|
|
Keratoacanthoma:
Shape? |
Sharp circumscribed bud shaped nodule with central keratin plug/crater
|
|
|
Keratoacanthoma
Histology? |
mimics SCC
well-differentiated spinous cells Minimal nuclear pleomorphism Absence of mitotic figures CT have chronic inflammatory cells |
|
|
Ephelids
AKA |
ephelis/ freckle
|
|
|
Ephelids
Cause? |
active deposition of melanin triggered by exposure to sunlight
|
|
|
Ephelids
location? |
any surface of the skin including lip
|
|
|
Ephelids
Presentations? |
light to dark brown macule with the size unchanged
|
|
|
Ephelids
More frequent in what people? |
with fair skin
red hair |
|
what's this?
|
ephelid
|
|
|
Melanotic macule
cause? |
due to an increased production of melanin granules
|
|
|
Melanotic macule
is it due to an increase in the number of melanocytes? |
no
|
|
|
Melanotic macule
symptomatic? |
no
|
|
|
Melanotic macule
visual presentation? (color, size, shape, location) |
brown/brown-black macules
less than 1cm solitary or multiple usually on midline |
|
|
Melanotic macule
Histology |
increase in melanin granules in the basal cell layer
CT with mild lymphocytic cells |
|

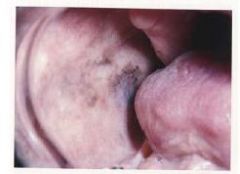
What's this?
|
melanotic macule
|
|
|
If melanotic macules are larger than 2cm it's called?
|
melanoacanthoma
|
|
|
melanoacanthoma
More frequent in which race? |
african/african-american
|
|
|
Smoker's melanosis
shape and colour? |
irregular, brown, macular pigmentation
|
|
|
Smoker's melanosis
is due to? |
Prolonged smoking of tobacco
|
|
|
Smoker's melanosis
sex? |
females
|
|
|
Smoker's melanosis
histology? |
similar to melanotic macule
|
|
What's this?
|
Smoker's melanosis
|
|
|
Nevi/nevus
cause? |
congenital
|
|
|
Nevi/nevus
common term? |
mole
|
|
|
Nevi/nevus
location? |
skin
hard palate gingiva |
|
|
Nevi/nevus
Types? |
intramucosal
junctional compound blue |
|
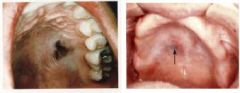
What's this?
|
Nevi
|
|
|
Seborrheic keratosis
location? |
sun exposed skin
|
|
|
Seborrheic keratosis
frequency? |
common
|
|
|
Seborrheic keratosis
age? |
middle aged or older
|
|
|
Seborrheic keratosis
shape and colour? |
well circumscribed brown papule wth stuck on appearance
|
|

What's this?
|
Seborrheic keratosis
|
|
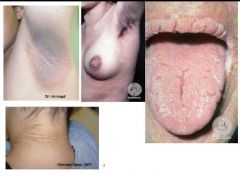
What's this?
|
Acanthosisi nigricans
|
|
|
Acanthosis nigricans
two types? |
benign
malignant |
|
|
Acanthosis nigricans
cause? |
due to endocrine disorders
sign of existing internal malignancy |
|
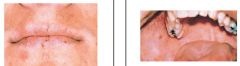
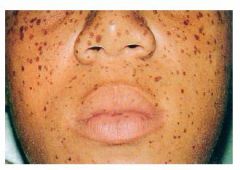
What's this?
|

Peutz-Jeghers Syndrome
|
|
|
Peutz-Jeghers Syndrome
Cause |
genetic (autosomal dominant)
|
|
|
Peutz-Jeghers Syndrome
shape? |
freckle-like pigmentations
|
|
|
Peutz-Jeghers Syndrome
location? |
skin
peri-oral peri-ocular peri-nostril peri-anal |
|
|
Peutz-Jeghers Syndrome
cause what intestinal abnormalities? |
multiple intestinal polyps
|
|
|
What are the histopathological stages in Epithelial Dysplasia
|
Mild dysplasia
Moderate dysplasia Severe dysplasia Carcinoma in situ |
|
|
What are the individual cell alterations found in epithelial dysplasia?
|
Hyperchromatism
Nuclear pleomorphism Altered N/C ratio Increased mitosis Abnormal mitosis Multinucleation |
|
|
Carcinoma in situ
Nearly always associated with erythroplakia T/F? |
True
|
|
|
Define Leukoplakia
|
A predominantly white lesion of the oral mucosa that cannot be characterised clinically or pathologically as any other disease and which is not associated with any physical or chemical causative agent except the use of tobacco
|
|
|
Leukoplakia
frequency? |
common
|
|
|
Leukoplakia
age? |
middle to late
|
|
|
Leukoplakia
cause? |
idiopathic other than tobacco
|
|
|
Spleckled Leukoplakia is called..?
|
erythroleukoplakia
|
|
|
Leukoplakia
Features associated with malignant transformation? |
female gender
duration of lesion floor of mouth non-homogenous types fungal colonisation presence of epithelial dysplasia |
|
|
What is Erythroplasia?
|
any lesion of the oral mucosa that presents as bright red velvety plaques which cannot be characterised clinically or pathologically as any other recognisable condition
|
|
|
Erythroplasia
location? |
buccal mucosa
|
|
|
Majority of Erythroplasia are cancerous
T/F? |
true
|
|
|
Actinic cheilitis
cause? |
chronic exposure to elements and actinic rays of sun
|
|
|
Actinic cheilitis
clinical presentation |
crusting
desquamation ulceration atrophy inflammation of lips |
|
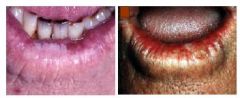
What's this?
|
Actinic cheilitis
|
|
|
Oral Submucous Fibrosis (OSMF)
freuqncy? |
uncommon
|
|
|
Oral Submucous Fibrosis (OSMF)
symptoms? |
no symptoms
|
|
|
Oral Submucous Fibrosis (OSMF)
clinical presentation? |
white erosions
tight vertical bands and trismus fibrosis of the oral submucossa |
|
|
Oral Submucous Fibrosis (OSMF)
cause? |
chewing Areca nut
|
|
|
Oral Submucous Fibrosis (OSMF)
sex? |
female
|
|
|
Oral squamous cell carcinoma (OSCC)
age? |
old patients
|
|
|
Oral squamous cell carcinoma (OSCC)
sex? |
males
|
|
|
Oral squamous cell carcinoma (OSCC)
site? |
lip (extroral)
tongue, gingiva, palate, buccal mucosa |
|
|
Oral squamous cell carcinoma (OSCC)
predisposing factors? |
In developed world:tobacco, alcohol, low SES and ethinic minority
In developing world: tobacco, alcohol, betel quid, low SES |
|
|
Oral squamous cell carcinoma (OSCC)
clinical features/ |
white/red/mixed lesion
ulcer: granular with fissuring or raised exophytic margins lump with induration lump with or without pain |
|
|
Basal Cell Carcinoma
frequency |
common
|
|
|
Basal Cell Carcinoma
clinical features? |
starts as small elevated papule
enlarge to form a large crusted ulcer spreads to adjacent skin/mucous membrane over time |
|
|
Melanoma is...
|
malignant neoplasm of melanocytes
|
|
|
Melanoma types?
|
superficial spreading
Lentigo maligna Acral lentigernous Nodular |
|
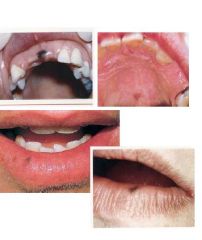
what's this?
|
melanotic macule
|

