![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
58 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
The CNS consists of ____
|
Brain and spinal cord |
|
|
The PNS consists of ____ |
Spinal and cranial nerves (everything not CNS) PNS is how CNS connects to all the muscles etc |
|
|
How many spinal nerves are there? |
31 |
|
|
How many cranial nerves are there? |
12 |
|
|
Give the name and number of vertebra in each region of the spinal cord
|
Cervical - 7 Thoracic - 12 Lumbar - 5 Sacral - 5 (fused into 1) Coccygeal - 4 (also fused with Sacral) |
|
|
Name the 12 cranial nerves, in order and with their primary function |
CNI - olfactory - smell CNII - optic - vision CNII - oculomotor - majority of ocular movement CNIV - trochlear - superior ocular movement CNV - trigeminal - facial sensory (3 branches) CNVI - abducens - lateral ocular movement CNVII - facial - facial movement CNVIII - vestibulocochlear - hearing CNIX - glossopharyngeal - tongue sense, taste CNX - vagus - rest and digest CNXI - accessory - shoulder movement CNXII - hypoglossal - tongue movement |
|
|
What are the two types of nerves (going or coming) |
Afferent - arrives Efferent - exits |
|
|
A group of neurons within the CNS with similar function, connectivity, and neurotransmitters are called _______ |
Nucleus |
|
|
A bundle of axons traveling together within the CNS are called __________ |
Tract |
|
|
A point of connection/communication between neurons is called what? |
Synapse |
|
|
A bundle of axons (plus associated CT and blood vessels) located outside the CNS is called what? |
Nerve |
|
|
A group of neurons outside of the CNS with similar function, connectivity, and neurotransmitters is called ________ |
Ganglia |
|
|
Define the somatic nervous system |
afferent and efferent systems that regular motor innervation of skeletal muscle and sensory information from the external environment |
|
|
Define the autonomic nervous system |
afferent and efferent systems that regulate motor innervation of smooth muscle and glands and sensory information from the internal environment |
|
|
What are the 3 primary functions of the nervous system? |
Sensory - detect stimuli in internal and external environments Integrative function - analyze and integrate sensory information Motor function - respond to integration decisions by initiating actions in effectors |
|
|
What is the purpose of somatic sensory neurons, and are they afferent or efferent? |
Afferent Convey information from sensory receptors |
|
|
What is the purpose of somatic motor neurons, and are they afferent or efferent? |
Efferent Convey information from the CNS to skeletal muscles |
|
|
The somatic system is (voluntary/involuntary) and (conscious/unconscious) |
The somatic system is voluntary and conscious |
|
|
The autonomic system is (voluntary/involuntary) and (conscious/unconscious) |
The autonomic system is involuntary and unconscious |
|
|
What are the two primary divisions of the autonomic nervous system and what do they control |
Sympathetic - fight or flight Parasympathetic - rest and digest |
|
|
What is the purpose of autonomic motor neurons, and are they afferent or efferent? |
Efferent Convey information from the CNS to smooth muscle, cardiac muscle, and glands |
|
|
What is the purpose of autonomic sensory neurons, and are they afferent or efferent? |
Afferent, visceral Convey information mainly from visceral organs to the CNS |
|
|
Nervous tissue is comprised of what two types of cells? |
Neurons and neuroglia |
|
|
Name the 3 specialized features of neurons |
Excitable Postmitotic (do not divide) Highly variable |
|
|
Name 2 (max 4) key notes about neuroglia |
Outnumber neurons support, nourish, and protect neurons continue to divide (mitotic) form the BBB |
|
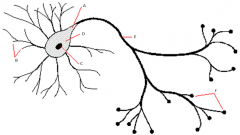
Identify Structures A-F |
A - Axon Hillock B - Dendrites C - Nucleus D - Soma E - Axon F - Terminal Buttons |
|
|
What is the name of the large stacks of rough ER responsible for high levels of protein synthesis? |
Nissl bodies |
|
|
List the components of a synapse |
Presynaptic terminal Postsynaptic terminal Synaptic cleft |
|
|
Define neuromuscular junction |
a synapse between a neuron and muscle fiber (effector) |
|
|
An axon onto dendrite is called _____ |
axodendritic |
|
|
An axon onto axon is called ____ |
axoaxonal |
|
|
An axon onto a cell body |
Axosomatic |
|
|
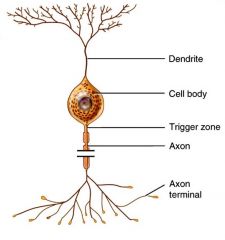
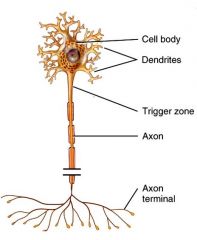
What type of neuron has 1 axon and many dendrites? (most neurons are in this category) |
Multipolar neurons |
|
|
What type of neuron has 1 axon and 1 main dendrite (example: rods/cones) |
Bipolar |
|
|
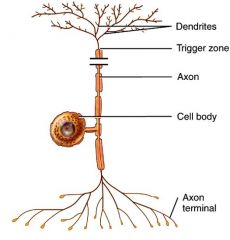
What type of neuron has 1 process exiting the soma and splits into a central and peripheral process? |
Pseudounipolar |
|
|
What type of neuron has a single process extending from the soma and exists only in invertebrates? |
Unipolar |
|
|
Bipolar |
|
|
Multipolar |
|
|
Pseudounipolar |
|
|
Give 3 (max 4) examples of neuroglia found in the CNS |
Astrocytes, oligodendrocytes, microglia, ependymal cells |
|
|
Give 2 examples of neuroglia found in the PNS |
Schwann cells Satellite cells |
|
|
What are the two types of astrocytes and where are they found (grey/white matter)? |
Protoplasmic - grey matter Fibrous - white matter |
|
|
What is the only kind of junction found in the BBB? |
Tight junctions |
|
|
What is the primary purpose of the BBB |
Protect brain from harmful substances/pathogens |
|
|
What is the BBB permeable to? |
Lipid-soluble (hydrophobic) compounds, water, a few polar substances (glucose, creatine, urea, some ions) |
|
|
What type of cell surrounds brain capillaries? |
Astrocytes |
|
|
______ help to maintain the appropriate chemical environment for the generation of nerve impulses |
Astrocytes |
|
|
What are oligodendrocytes? |
Myelinating glia of the CNS (giant octopus) |
|
|
Why is white matter white, and why is grey matter grey? |
White matter is white because of myelin sheathes (from oligodendrocytes) Grey matter is grey (not white) because of minimal myelin sheathing |
|
|
What structure makes CSF? |
Choroid plexus |
|
|
What two structures form the choroid plexus? |
Ependymal cells and choroidal capillaries |
|
|
What is the role of microglia and what makes them different from other neuroglial cells? |
Microglia originate in bone marrow and migrate to the CNS as it develps Function as phagocytes |
|
|
Name the two types of glial cells in the PNS and where the originate from in the embryo |
Schwann cells Satellite cells Both originate from the neural crest |
|
|
What are the myelinating cells of the PNS |
Schwann cells |
|
|
What are the cells that surround the cells of neurons of PNS ganglia? |
Stallite cells |
|
|
What are the myelinating cells of the CNS? |
Oligodendrocytes |
|
|
Define neurogenesis |
Formation of new neurons from stem cells, known to occur in the adult hippocampus but not elsewhere in the CNS |
|
|
Define plasticity in the context of the nervous system |
Ability to change based on experience, new synapses, new dendritic spines, etc |

