![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
22 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Chemo-
|
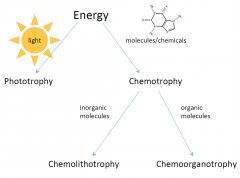
- Energy from molecules |
|
|
Litho-
|
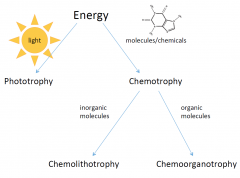
- energy from inorganic molecules (without carbon)
|
|
|
Organo-
|
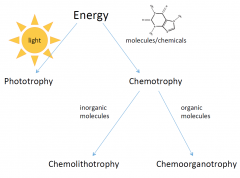
- energy from organic molecules (with carbons) |
|
|
Auto-
|
- Carbon from inorganic sources (like CO2)
|
|
|
Hetero-
|
- Carbons from organic sources |
|
|
Niche
|
environment occupied by a single species |
|
|
Habitat |
- location of mixed community of distinct niches
|
|
|
Ecosystem
|
- communities of organisms interacting among themselves and with their environment |
|
|
Roles of Microorganisms
|
typically defined in terms of nutrient cycles |
|
|
Dynamics |
Population changes in response to environment |
|
|
Primary Producers
|
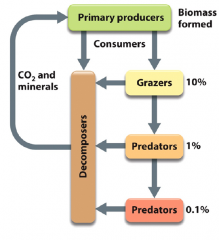
- generate reduced carbon compounds - synthesize organic matter from CO2 - Autotrophs: Phototrophs and Lithotrophs - assimilation |
|
|
Consumers
|
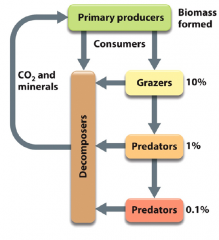
- Remove reduced compounds from the environment - generate alternative reduced carbon compounds (fermentation) or oxidized CO2 (respiration) - heterotrophs: organotrophs and phototrophs - dissimilation |
|
|
Decomposers
|
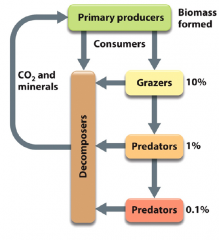
- break down complex organic matter from detritus - Organoheterotrophs - generate simple reduces carbon compounds or oxidized minerals - dissimilation |
|
|
Marine Environment
|
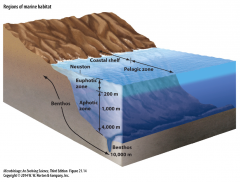
- general oligotrophic (low nutrient levels) |
|
|
Neuston/Euphotic Zone
|
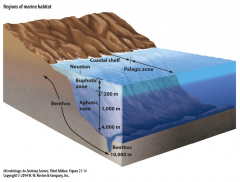
- support organoheterotrophs - most dense concentration of microbial activity |
|
|
Aphotic Zone
|
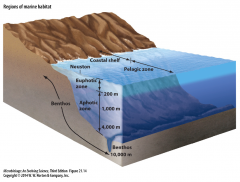
- heterotrophs & lithotrophs |
|
|
Benthos
|
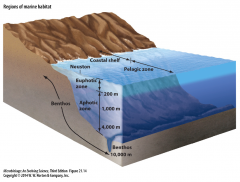
- Lithotrophic (live throughout water column but most concentrated at ocean floor) use minerals available at earth's crust |
|
|
Oxygenic Photoautotrophs
|
- can be primary producers |
|
|
Anoxygenic Photoautotrophs
|
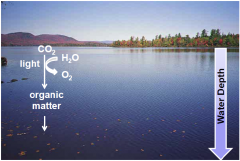
- can be primary producers |
|
|
Aerobic Heterotrophs
|
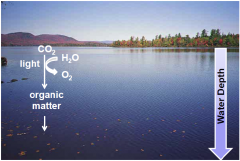
- O2 dependant respiration - consumers - associated with organic matter of primary producers - alters BOD |
|
|
Organoheterotrophs
|
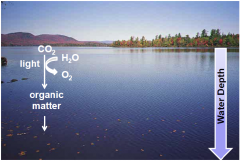
- fermentation and anaerobic respiration |
|
|
Lithoautotrophy |
- will occur wherever there are inorganic minerals that can act as electron donors and electron acceptors |

