![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
43 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
To understand and explain the mechanisms involved in pharmacological modification of reproductive hormone activity. |
. |
. |
|
|
integration of endocrine control includes what? |
Integration of Endocrine control includes The Menstrual Cycle |
|
|
|
what is menstrual cycle divided into? What does ovulation define? |
The menstrual cycle is divided into the follicular phase and the luteal phase. Ovulation defines the transition between these two phases. |
|
|
|
during folliculat phase, what do the gonadotrophe cells of anerior pituiary gland secrete in response to pulsatile GnRH stimulation? |
During the follicular phase, gonadotrophcells of the anterior pituitary gland secrete LH and FSH in response to pulsatile GnRH stimulation. |
|
|
|
what does LH and FSH promote? |
Circulating LH and FSH promote growth and maturation of ovarian follicles. |
|
|
|
Developing follicles secrete increasing amounts of what? what happens at first?
|
estrogen. At first, the estrogen has an inhibitory effect on gonadotropin release. |
|
|
|
Just before the midpoint in the menstrual cycle, however, estrogen exerts a brief positive feedback effect on LH and FSH release: what is this followed by? |
This is followed by follicular rupture and release of an egg into the fallopian tube. |
|
|
|
what happens during the second half of the menstrual cycle? |
corpus luteum secretes both estrogen and progesterone. |
|
|
|
Progesterone induces a change in the
|
Progesterone induces a change in the endometrium from a proliferative to a secretory type. |
|
|
|
If fertilization and implantation of a blastocyst do not occur within 14 days after ovulation, what happens?
|
the corpus luteum involutes, secretion of estrogen and progesterone declines, menses occurs, and a new cycle begins. |
|
|
|
Contraceptives what are the two classes of widely used oral contraceptive? |
(1) Estrogen-progestin combination (2) Progestin-only contraception" |
|
|
|
what kind of synthetic hormone is progestin? |
Progestin is a synthetic hormone which mimics the action of progesterone (pregnancy hormone which supports embryogenesis) |
|
|
|
combined estrogen-progestin birth control pills or implants prevent what?
|
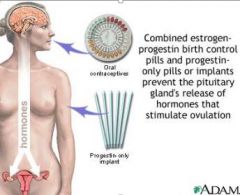
the pituitary glands release of hormones that stimulate ovulation |
|
|
|
what is the effect of Estrogen-progestin combination? |
Supresses GnRH, LH and FSH secretion and follicular development thereby inhibiting ovulation |
|
|
|
"Estrogen-progestin combination May also inhibit pregnancy by a number of different secondary mechanisms: which cause what?
|
•Alterations in tubal peristalsis •Cervical mucus secretions" •Endometrial receptivity |
|
|
|
Synthetic estrogens used in this therapy (estrogen-progestin combination) are either...
|
ethinylestradiolor mestranol
|
|
|
|
Why combination? (Estrogen-progestin combination) |
"Estrogen-progestin combination: Use of unopposed estrogenpromotes endometrial growth and risk of endometrial cancerFor this reason women with a uterus are always co-administered progestin to limit endometrial growth" |
|
|
|
Delivery methods of estrogen-progestin Contraceptives are? |
(1)Vaginal rings
(2)Transdermal patches (3)Oral tablets |
|
|
|
describe vaginal rings for contraceptive treatment |
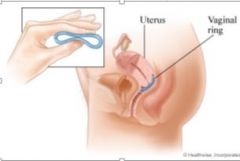
"Vaginal rings
•Silasticcylinder packed with ethinylesterdioland a progestin, etonogestrel •The steroids are release with zero order kinetics and remains in place for 21 days•After removal menses may occur (7days)" |
|
|
|
describe transdermal pathces for contraceptive |
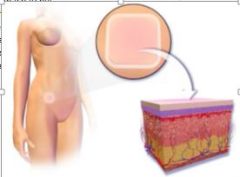
"Transdermal patches
•Matrix that continuously releases ethinylestradioland synthetic progestin, norelgestromin •Patch is changed every 3 weeks •After removal menses may occur(7days)" |
|
|
|
describe administration of oral tablets of the contraceptive |
"Oral tablets •21 day tablet of combination oral contraceptive followed by 7 day sugar pill •The 7 day placebo pill removes exogenous hormone stimulation, causing the endometrium to slough off resulting in withdrawal bleeding •Formulations include monophasic and triphasichormone schedules (progestin concincreases each week)" |
|
|
|
"Adverse effects of long term use of oral contraceptives include
|
•Increased risk of deep vein thrombosis •Increased risk of pulmonary embolism •Increased risk of gallbladder disease" |
|
|
|
"Benefits of oral contraceptives include
|
•Reduced risk of endometrial cancer (reduced endometrial growth) •Reduced risk of ovarian cancer" |
|
|
|
Progestin-only contraception involves a...
|
continuous low dose oral progestins (minipill) |
|
|
|
Progestin-only contraception Prevents ovulation 70-80% of the time by altering the.... |
frequency of GnRH pulsing and decreases pituitary gland responsiveness
|
|
|
|
what are Progestin-only contraception Secondary mechanisms? |
•Alterations in tubal peristalsis•Endometrial receptivity•Cervical mucus secretions" |
|
|
|
Progestin-only contraception Results inwhat percent effectiveness?
|
96-98% effectiveness |
|
|
|
Progestin-only contraception involves patients that typically ...
|
don't menstruate
|
|
|
|
what other prgestin contraceptive treatment is available? |
progestin-only contraception has injectable implants also available
|
|
|
|
what is the treatment for contraception? |
Morning after contraception Single dose of Potent progestin (levonorgestrel), ASAP (within 120 hours)
|
|
|
|
what does the Morning after contraception do? |
Blocks the LH surge, disrupting normal ovulation
|
|
|
|
Morning after contraception Produces...
|
endometrial changes that prevent implantation |
|
|
|
Hormone replacement therapy
Hormone Replacement involves using |
Estrogens, progestinsand androgens are used as replacement therapies in cases of hormone deficiency
|
|
|
|
"Hormone Replacement involves what?
|
Treatment of menopause to reduce•Hot flashes•Atrophy of urogenital tissues, and Treatment for hypogonadism"
|
|
|
|
"The lack of estrogenin postmenopausal women is linked to what?
|
several health problems.*estrogenhas positive effects on blood vessels and on bones. After menopause, though, women are at increased risk for heart disease and for osteoporosis, a weakening of the bones that causes them to become more vulnerable to fractures" |
|
|
|
To counteract these potential problems in women what can be done?
|
some postmenopausal women take hormone pills containing estrogento strengthen bones and help control other menopausal symptoms. But, as a consequence, such women are subjecting themselves to the harmful effects of estrogen--namely, an increased risk for invasive breast cancer and uterine cancer |
|
|
|
contraception studies carried out in the 1980s suggested that
|
adding the hormone progesterone to estrogencould offset the increased risk of uterine cancer linked to the use of estrogenby itself. For this reason, hormone replacement therapy using estrogenplus progestin (a synthetic form of progesterone) became a common way of treating women with menopausal symptoms However, a study of 16,000 menopausal women carried out by the Women’s Health Initiative was prematurely halted in 2002 when preliminary results indicated that the harm associated with this type of treatment outweighs the potential benefits. |
|
|
|
The major risks detected were? |
an increased chance of developing invasive breast cancer, as well as an increased risk of strokes, heart attacks, and blood clots. While the data also revealed that hormone replacement with estrogenplus progestin lowered the risk of osteoporosis and colon cancer, these benefits were not considered to be sufficient to outweigh the other risks. |
|
|
|
Hypogonadismis is a medical term which describes...
|
a diminished functional activity of the gonads |
|
|
|
hypogonadism is often found in aging men with...
|
•Reduced energy •Decreased libido •Decreased muscle mass decreased facial hair" |
|
|
|
Treatment for hypogonadism are?
|
Esters of testosterone administered intramuscularly or transdermal patches |
|
|
|
Oral contraceptives disrupt the...
|
cyclicity of the menstralcycle and supress ovulation |
|
|
|
Hormone replacement therapy can be used for what?
|
alleviate symptoms associated with reduced hormone synthesis
|
|

