![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
30 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
Adaptive Immunity System? |
•Pathogens responses •Develop memory for pathogens •Lymphocytes (B cells and T cells) |
|
|
|
Functions of Adaptive Immunity? |
•Generate response for infections & pathologies •Create pathogens memories for fast, accurate identification & responses •Recognize/distinguish between self & nonself antigens |
|
|
|
Adaptive immunity: what is cell mediated immune response? |
Lymphocytes |
|
|
|
Adaptive immunity: what is humoral immune response? |
mediated by antibodies & complement system |
|
|
|
Lymphatic System is a major component of? |
adaptive immune system |
|
|
|
Lymphatic System? |
•Continuous w/the circulatory system •Return interstitial fluid back into circulatory system •Site of production & maturation lymphocytes |
|
|
|
Lymphatic System: Thymus |
•Processes & maturation of T lymphocytes •Receptor variability generated through random gene shuffling •Positive & negative selection |
|
|
|
Lymphatic System: Spleen |
•Produce antibodies •Removes antibody coated cells from circulation |
|
|
|
LymphaticSystem: Lymph nodes |
•Produce antibodies |
|
|
|
Lymphatic System: other lymphoid tissues |
Tonsil,Peyer’s patches, Adenoids |
|
|
|
Antibodies |
•Immunoglobulin(Ig) •Y shaped protein recognize specific antigens •Bind & neutralize foreign material •Composedof 2 light & heavy chains |
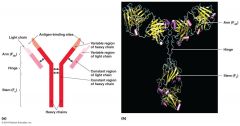
|
|
|
Antibodies highly variable regions? |
•Created through recombination & mutation •Heavy chains are encoded by VDJ segments •Light chains are encoded by the VJ segments |
|
|
|
Antibody: IgA |
In mucosal membranes, exist as a dimer |
|
|
|
Antibody: IgD |
Mostly on cell membranes of B cells |
|
|
|
Antibody: IgE |
Binds to allergens & release of histamine from mast cells & basophilin an allergic reaction |
|
|
|
Antibody: IgG |
Main type antibody binds to pathogens |
|
|
|
Antibody: IgM
|
Appear in early stages of infection, exist as a pentamer |
|
|
|
B Cells |
•Responsible for humoral immunity •Receptors (BCR) are highly specific - membrane bound antibodies •Each line recognizes 1 specific antigen |
|
|
|
Activated B cells differentiate into? |
•Plasma cells produce antibodies •Memory B cells that remain dormant in lymphoid organs |
|
|
|
B cells activated by? |
•T cell dependent activation •T cell independent activation |
|
|
|
T Cell Dependent Activation? |
•Antigens bound to BCR taken into B cells •Antigen complexed w/series of proteins (MHC) & presented on thesurface of B cell for T helper cells •T cells express CD40L, IL •Binds to B cell CD40 & activate B cell |
|
|
|
TCell Independent Activation? |
•Certain antigens activate B cells w/out T cells involvement •Foreign polysaccharide or DNA •Extensive cross-links between BCRs & components on bacterial cells causes B cells tobe activated |
|
|
|
T Cells are responsible for? |
Cell mediated immunity |
|
|
|
T cells contain TCRs on it cell surface then? |
TCRs “degenerate” - 1 TCR can recognize many antigens & 1 antigen can recognized by many TCRs |
|
|
|
T cells, TCR recognizes antigens complexed with? |
MHC |
|
|
|
T cells 2 main types? |
•Helper T cells •Cytotoxic T cells |
|
|
|
Helper T Cells |
•Contain CD4 •CD4 binds to MHC on antigen presenting cells •Cross-link w/a second signal is required for activation |
|
|
|
Helper T cells mature & differentiate into 3 what? |
•Memory •Effector •Regulatory |
|
|
|
Cytotoxic T Cells |
•ContainCD8 •Kills cells that are infected & damaged. E.g. cancer cells •TCR +CD8 recognize MHC on abnormal cells |
|
|
|
Cytotoxic T Cells activation causes the release of? |
•Various enzymes (perforin, granzyme) that activate caspases w/in the target cell •Caspase cascade causes apoptosis |
|

