![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
31 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Griffith's Transformations |
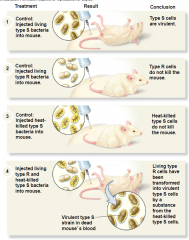
- studied two strains of Streptococcus pneumoniae, virulent and nonvirulent - Rats injected with dead virulent cells and live nonvirulent cells resulted in disease state in mice - live virulent cells can be recovered from dead mouse |
|
|
Type 'S' Bacteria |
- Virulent Streptococcus pneumoniae - contains polysaccharide capsule that protects bacterium from immune system |
|
|
Type 'R' Bacteria |
- Nonvirulent Streptococcus pneumoniae mutant - Does not contain polysaccharide capsule - does not cause disease state in host |
|
|
Transformation |
- process of importing free DNA into bacterial cells - fundamental purpose is to aquire genes that might be useful as the environment changes |
|
|
Transformasomes |
- natural transformation - import DNA fragments and plasmids released from nearby dead cells - Not all bacteria can do this |
|
|
Competentence |
- able to import free DNA fragments and incorporate them into genome |
|
|
Chemically Forced Competence |
- artificial manipulation to import DNA into cell - CaCl2 - alters the membrane, making cells chemically competent which allows DNA to pass |
|
|
Electroporation |
- artificial manipulation to import DNA into cell and force competence - brief electrical impulse shoots DNA across membrane - heat shock will suck complexes in |
|
|
Gram-Positive Transformasome Complex |
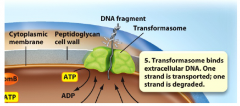
- growth phase dependent assembly - composed of binding protein, a transmembrane pore, and a nuclease - binding protein captures extracellular DNA - nuclease degrades one strand of DNA while pulling the other strand through pore |
|
|
Conjugation |
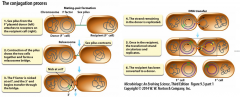
- requires cell to cell contact - tip of sex pilus attaches to a receptor on the recipient and contracts to draw cells together - Cells fuse to generate a conjugation complex - single stranded DNA passes from donor to recipient - requires the presence of special transferable plasmids |
|
|
Sex Pilus |
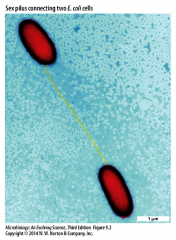
- specialized pilus - tip attached to a receptor on recipient cell - contracts to draw cells together |
|
|
ssDNA |
- single stranded DNA |
|
|
Plasmid |
- extrachromosomal genetic element, present in some cells |
|
|
F Factor |
- fertility factor - studied in E. coli - can transfer itself to another recipient cell - two replication origins - oriV (replicate and maintain the plasmid in nonconjugating cells) - and oriT (used only to replicate DNA during DNA transfer) |
|
|
Relaxosome |
- unwinds donor double stranded DNA - begins transfer process |
|
|
Phage Transduction |
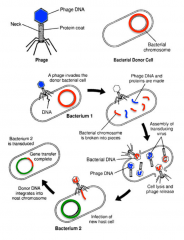
- process in which bacteriophages carry payloads of host DNA from one cell to another - bacteriophages can't distinguish host DNA from their own - so, pieces of host DNA becomes package in phage capsid instead of phage DNA - Host DNA is injected into new cell, where DNA can recombine or exchange with new cell DNA |
|
|
Bacteriophage |
- viruses that specifically infect bacteria |
|
|
Restriction Endonuclease |

- restriction enzymes - recognizes specific short DNA sequences (recognition site) - cleaves DNA at or near that sequence |
|
|
Methylase |

- enzyme - adds methyl group on adenines - makes sequence invisible restriction enzyme, protecting DNA - only 1 strand must be methylated to work, so newly formed DNA is protected |
|
|
CRISPR |
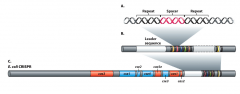
- Clustered Regulatory Interspaced Short Palindromic Repeats - host cell captures a piece of phage genome and integrated into host DNA becoming spacers between repeat DNA in CRISPR locus - does not encode proteins, RNA is produced of all spacer and is process into single spacer sequences (crRNA) - crRNA binds to homologous sequence of infecting phage and marks it for degradation - sequences encoding proteins associated with CRISPR system are located upstream of spacers |
|
|
Spacer Acquisition |
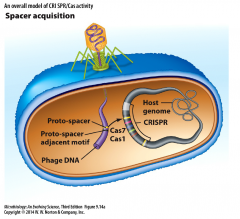
- process by which invading phage DNA is integrated by bacterial host - assisted by Cas proteins |
|
|
crRNA processing |
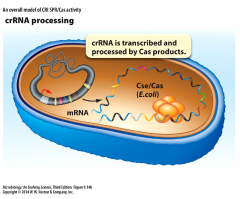
- transcription of spacers occur upstream of leader sequence - crRNA is processed by Cas proteins into singe spacer sequences |
|
|
Effector Stage |
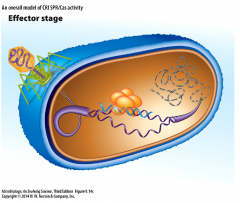
- crRNA in complex with Cas proteins binds to homologous sequence and lead to degradation of invader DNA - may limit transfer of genetic materials between cells via tranduction |
|
|
Effect of CRISPR on Biofilm Formation |
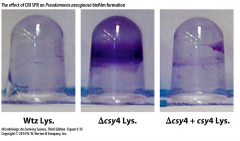
- infection of phage banishes cell from biofilm - disruption of CRISPR locus allows infected cell to form biofilm, so CRISPR is essential for this self-exclusion process - protects other cells of biofilm from infection after infected cell lyses |
|
|
Transposable Elements |
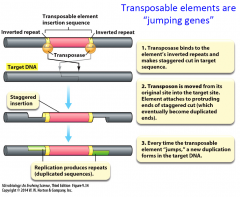
- segment of DNA that can move from one DNA region to another |
|
|
Transposase |
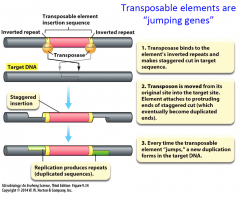
- gene for this enzyme is included in all transposable elements - enzyme that catalyzes the transfer or copying of the element from one DNA molecule into another |
|
|
Transposon |
- transposable DNA element that contains genes in addition for those required for transposition - 2 insertion sequences that flank other genes (antibiotic resistant genes) |
|
|
Nonreplicative Transposition |
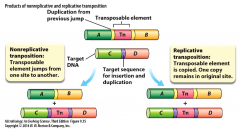
- transposable element jumps from one site to another |
|
|
Replicative Transposition |
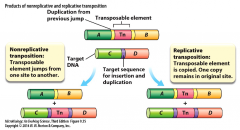
- transposable element is copied. one copy remains in original site |
|
|
Restriction and Modification System |
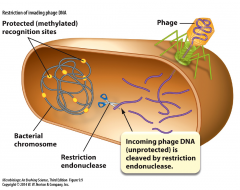
- bacterial cell defense against phage - enzymatic cleavage (restriction) of alien DNA by restriction endonucleases - protective methylation (modification) of self-DNA by modification enzymes that protects host cell DNA from restriction nucleases
|
|
|
Transposition |
- process of moving a transposable element within or between DNA molecules - short sequence on target DNA molecule is duplicated so that one copy of the sequence will flank each end of the element |

