![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
28 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
what is the main route of Phase I metabolism of drugs?
|
oxidation by CYP450
|
|
|
what is the most important function of CYP450 ?
|
is its ability to “activate” molecular oxygen, bringing oxygen and the substrate together to permit oxidation of the substrate.
|
|
|
Approximately one-third of the total CYP450 is found where?
and two-thirds of CYP 3A4 is found where? |
The liver
The intestine |
|
|
What is responsible for the metabolism of more than one-third of the clinically important drugs.
|
Isoform
|
|
|
more than one-third of all the drugs are metabolized by one isoform which is what? What does this increase?
|
CYP3A4, increasing the potential for drug–drug interactions.
|
|
|
When two drugs are metabolized by the same isoform what happens? What is increased? One drug has a lower what?
|
only one drug can serve as a substrate at one time, increasing the likelihood of a drug–drug interaction, especially if one drug has a lower therapeutic threshold
|
|
|
What are the two major pathways of Xenobiotic Metabolism?
|
Biotransformations and conjugation
|
|
|
Phase 1 reactions include what 4 reactions?
|
Include oxidation, hydroxylation, reduction, and hydrolysis.
|
|
|
In these phase 1 enzymatic reactions, what is introduced? What is modified? What is exposed?
|
a new functional group is introduced into the substrate molecule, an existing functional group is modified, or a functional group or acceptor site for Phase 2 transfer reactions is exposed
|
|
|
Phase 1 reactions are largely catalyzed by what?
|
Largely catalyzed by Cytochrome P450 Enzymes (CYP450).
|
|
|
What does CYP450 make the xenobiotic do?
|
Makes the xenobiotic more polar and, therefore, more readily excreted.
|
|
|
During Phase 2 reactions what functional groups are involved? what happens to them?
|
A functional group, such as alcohol, phenol, or amine, is masked by the addition of a new group, such as acetyl, sulfate, glucuronic acid, or certain amino acid
|
|
|
Phase 2 reactions increase what? Also considered what kind of reactions?
|
Further increases the polarity of the drug/xenobiotic.
Also enzymatic reactions |
|
|
Xenobiotics usually are what? Where are they well absorbed? Are they excreted fast or slow through the urine?
|
Xenobiotics usually are lipophilic, well absorbed in the blood, but slowly excreted in the urine.
|
|
|
what is added to the xenobiotic to make water solubility increased and lipid solubility decreased enough to make urinary elimination possible?
|
Only after conjugation (Phase 2) reactions have added an ionic hydrophilic moiety, such as glucuronic acid, sulfate, or glycine, to the xenobiotic
|
|
|
What is the major proportion of the administered drug dose excreted as? . Conjugation reactions may be preceded by what?
|
as conjugates into the urine and bile.
By phase 1 reactions |
|
|
For xenobiotics that already have a functional group available for conjugation, what is its fate?
|
then Phase II conjugation alone may be its fate.
|
|
|
What are the two major conjugation reactions?
|
glucuronidation and sulfation)
|
|
|
glucuronidation and sulfation were thought to terminate pharmacological activity how?
|
by transforming the parent drug or Phase 1 metabolites into readily excreted ionic polar products.
|
|
|
minoxidil sulfate is the active metabolite for what?
|
antihypertensive minoxidil.
|
|
|
What are 5 other Phase 2 reactions?
|
Conjugation with amino acids
Conjugation with Coenzyme A (CoA) Acetylation Glutathione Conjugation Methylation |
|
|
Bioactivation is the processes of what? What may it lead to the formation of? Has what kind of effects? What metabolism phase does ti go through?
|
the processes of oxidation, reduction, glucuronidation, sulfation, and other enzyme-catalyzed reactions may lead to the formation of a metabolite having therapeutic or toxic effects. Phase I or Phase II Metabolism.
|
|
|
What are 7 electrophiles from metabolism/bioactivation?
|

|
|
|
What are 4 ecamplesof activated double bonds?
What are 5 reactive intermediates from drugs that form activated double bonds? |

|
|
|
What are 3 radicals from metabolism/bioactivation?
|

|
|
|
What are 6 examples of bioactivation drugs?
|
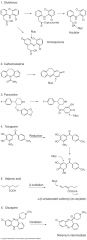
|
|
|
Structural modification can reduce what?
|
Drug-Induced Hepatotoxicity
|
|
|
Tripelennamine goes through what 4 pathways?
|
para-hydroxylation
benzylic C-hydroxylation N-depyridinylation N-debenzylation |

