![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
156 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Sternberg’s triarchic theory of intelligence
|
focuses on what leader DOES when solving problems
3 types of intelligence: analytical, practical, creative |
|
|
Three domains of intelligence
|
Analytical
Practical Creative |
|
|
Analytical Intelligence
|
general problem-solving ability, IQ
|
|
|
Practical Intelligence
|
“street smarts”, knowing how to get things done
• Domain-specific, limited to the situation • Grows with experience and reflection • May compensate for lower analytical intelligence |
|
|
Creative Intelligence
|
produce work that is novel and useful, not perfectly correlated with analytical intelligence
|
|
|
7 components of creative intelligence
|
Synthetic, Analytic, Practical, Thinking style, Personality, Intrinsic motivation, Environmental factors
|
|
|
Synthetic ability
|
see things in new ways or make novel connections between seemingly unrelated issues or concepts
|
|
|
Analytic intelligence
|
evaluate usefulness of potential solutions
|
|
|
Practical intelligence
|
apply relevant knowledge and experience
|
|
|
Thinking style
|
prefer to use what already exists or start anew
|
|
|
Personality
|
lower prudence, higher openness to experience, higher surgency equals higher creativity
|
|
|
Intrinsic motivation
|
people are more creative when they are personally interested
|
|
|
Environmental factors
|
supportive leadership, lack of time pressure, team stability, weaker social ties
|
|
|
Divergent thinking
|
creative thinking
|
|
|
Convergent thinking
|
for tests with single best answer
|
|
|
Relationship between intelligence and leadership effectiveness
|
Intelligent leaders are fast learners, make better assumptions, deductions, and inferences. They are better at creating, developing strategies, and problem-solving.
Analytical intelligence is highly correlated with leadership ability in the literature, but we all know very smart people who could not lead lemmings over a cliff. Leaders with high practical intelligence often have a lot of relevant experience and know how to get things done. And because of this experience base, practical intelligence becomes very important when leaders are under stress or face a crisis. Creative intelligence is the ability to create novel and useful solutions to problems. There are seven components to creative intelligence, and leaders need to understand how their behavior can either foster or stifle followers’ creativity. Like personality traits, analytic and creative intelligence are fairly “hard wired”, but practical intelligence does improve with experience and reflection. |
|
|
Emotional intelligence
|
the ability to monitor personal and other's feelings and use them for your own thinking and behavior
|
|
|
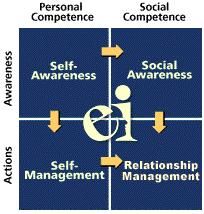
Development of EQ
|
filling in the matrix from self awareness to self management and from self awareness to social awareness
once this is done, you have the foundation for effective relationship management |
|
|
Self Awareness
|
Emotional self-awareness: Reading one’s emotions and recognizing their impact
using “gut sense” to guide decisions Accurate self-assessment: Knowing one’s strengths and limits Self-confidence: A sound sense of one’s self-worth and capabilities |
|
|
Self-Management
|
"Emotional self-control: Keeping disruptive emotions and impulses under control
Transparency: Displaying honestly and integrity, trustworthiness Adaptability: Flexibility in adapting to changing situations or overcoming obstacles Achievement: The drive to improve performance to meet inner standards of excellence Initiative: Readiness to act and seize opportunities Optimism: Seeing the upside in events |
|
|
Social Awareness
|
"Empathy: Sensing others’ emotions, understanding their perspective, and taking active interest in their concerns
Organizational awareness: Reading the currents, decision networks, and politics at the organizational level Service: recognizing and meeting follower, client, or customer needs |
|
|
Relationship Management
|
"Inspirational leadership: Guiding and motivating with a compelling vision
Influence: Wielding a range of tactics for persuasion Developing others: Bolstering others’ abilities through feedback and guidance Change catalyst: Initiating, managing, and leading in a new direction Conflict management: Resolving disagreements Teamwork and collaboration: Cooperation and team-building |
|
|
Impact of emotional intelligence on leadership ability
|
Goleman calls EQ “Maturity.”
Emotional Intelligence has a lot to do with self-leadership, self-awareness, and the awareness of others. The emotional state of a leader affects the entire group High EQ means long term growth and effectiveness Emotional Intelligence can be developed Leaders build emotional intelligence of teams by creating positive norms that support development and emotional growth, not by stifling or ignoring it. Emotionally intelligent leaders help followers grow and develop, see and enhance their self-worth, meet and achieve goals and needs. |
|
|
4 Domains of Emotional Intelligence
|
Self-Awareness
Self-Management Social awareness Relationship Management |
|
|
Can EQ be developed?
|
Yes
|
|
|
Personality traits in weak situations
|
play an important role in determining behavior in unfamiliar, ambiguous, WEAK situations
|
|
|
Personality traits in strong situations
|
are minimized in situations governed by clearly specified rules, demands, or policies, STONG situations
|
|
|
5 Factor Model Dimension (Bright-Side Traits)
|
1.Surgency
2.Agreeableness 3.Dependability 4.Adjustment 5.Openness to Experience, Inquisitiveness, Curiosity |
|
|
Surgency
|
self-confidence, need for power
Often appears when an individual is trying to influence or control others |
|
|
Agreeableness
|
empathy, friendliness
Concerns how one gets along with others |
|
|
Dependability
|
conscientiousness
Concerns how one approaches work |
|
|
Adjustment
|
emotional stability or self control
Concerned with how people react to stress, failure, or personal criticism |
|
|
Openness to Experience
|
inquisitiveness, curiosity
Concerns how one deals with problems and reacts to new experiences |
|
|
Dark Side Personality Traits
|
Excitable
Skeptical Cautious Reserved Leisurely Bold Mischievious Colorful Imaginative Diligent Dutiful |
|
|
How do dark-side traits relate to the Five Factor Model?
|
Everyone has at least one dark-side trait
Dark-side traits usually emerge in crisis or high stress as coping mechanism Dark-side traits have bigger influence on performance for leaders than followers Dark-side traits usually only apparent when leaders are not attending to public image Dark-side traits co-vary with social skills and are difficult to detect in formal settings (interviews, short-term interactions) Dark-side traits are associated with extreme FFM (Bright-side) scores Diligence is associated with extremely high Dependability Excitable is associated with extremely low Adjustment Dark-side traits occur at any leadership level |
|
|
What are the inter-relationships between perception, observation, reflection and action?
|
Perception affects all three phases of the AOR model.
Both perception and observation deal with attending to events around us. We are selective in what we attend to and perceive. Perception is related to reflection in that reflection has to do with the interpretation of our experiences and perception is an interpretive activity. Perception is related to action in that our actions result from perceptions and biases we hold. |
|
|
Self-fulfilling prophecy
|
occurs when our expectations/predictions play a causal role in bringing about the events we predict
|
|
|
Perceptual set
|
tendency or bias to perceive one thing and not another
can influence any of our senses |
|
|
Actor/Observer difference
|
People who are observing an action are much more likely than the actor to make the fundamental attribution error
|
|
|
Attributions
|
the explanations we develop for the behaviours or actions we attend to
|
|
|
Fundamental Attribution Error
|
tendency to overestimate the dispositional causes of behaviour and underestimate the environmental causes when others fail
|
|
|
Self-serving bias
|
tendency to make external attributions for one’s own failure, yet make internal attributions for one’s successes
|
|
|
Single-loop learning
|
a kind of learning between the individual and the environment in which learners seek relatively little feedback that may significantly confront their fundamental ideas/actions
criticize idea only |
|
|
Double-loop learning
|
involves a willingness to confront one’s own views and an invitation to others to do so, too
challenges foundation and fundamental assumptions of idea broader sense |
|
|
Four ways that a leader's values impact her leadership
|
They are a primary determinant in what data are reviewed by leaders and how they define problems.
Values also affect the solutions generated and the decisions made about problems. Values help leaders choose right from wrong and between ethical and unethical behavior. Values affect the choices leaders make about direct reports leaders tend to like followers with similar values and dislike those with dissimilar values. |
|
|
What are 4 ideal characteristics that leaders can have that engender trust with their followers?
|
Vision
Empathy Consistency Integrity |
|
|
Theory X
|
pessimistic
coercive/external control methods need to be used to motivate workers assumes that ppl are not naturally industrious/motivated |
|
|
Theory Y
|
assumes ppl are intrinsically motivated by their work
leader’s job is to provide resources, guidance, and opportunity to followers |
|
|
What is the relationship between followership and leadership?
|
Followers are subject to value differences, with implications for what motivates them
Exemplary followers are typically those who become exemplary leaders Followers are a critical part of the leadership equation. The followers’ expectations, personality traits, maturity levels, levels of competence, and motivation affect the leadership process. Leadership must be understood in terms of both leader variables and follower variables, as well as interactions among them. |
|
|
What are the 5 types of followers under Kelley's followership model?
|
Alienated
Conformist Pragmatist Passive Exemplary |
|
|
What is an alienated follower?
|
Cynical and negative
Acts with a “chip on the shoulder” Headstrong Not a team player Adversarial to the point of being hostile Root causes: Broken trust, Unmet expectations |
|
|
What is a conformist follower?
|
Accept assignment easily and gladly
Team player Averse to conflict Compromise to please others Lack of own ideas Root causes: Society encourages this type of followership, Domineering leaders, Rigid rules and procedures |
|
|
What is a passive follower?
|
Require an inordinate amount of supervision
Follow the crowd without considering why Put in their time Look to the leader to do their thinking Root causes: Laziness, Treated like sheep—act like sheep |
|
|
What is a pragmatist follower?
|
Play political games
Avoid risk Carry out the letter of the law rather than the spirit Hug the middle of the road Carry out assignments with middling enthusiasm and in a mediocre fashion Root causes: Uncertainty about the leader and/or environment, Risk adverse |
|
|
What is an exemplary follower?
|
"enthusiastic, intelligent, and self-reliant participation in pursuit of an organizational goal
|
|
|
What is motivation?
|
Anything that provides direction, intensity and persistence to behavior
The likelihood an individual will initiate and continue exhibiting certain behaviours |
|
|
What is performance?
|
Those behaviours directed towards the organization’s mission or goals or the products and services resulting from those behaviours
Factors such as intelligence, skill and the availability of key resources can affect a followers behaviour in accomplishing organizational goals (performance) independently of that person’s level of motivation |
|
|
What is job satisfaction?
|
Not how hard one works or how well one works, but rather how much one likes a specific kind of job or work activity
Deals with one’s attitudes or feelings about the job itself, pay promotion or educational opportunities Organizational citizenship behaviours: behaviours not directly related to one’s job that are helpful to others at work Higher motivation will usually only affect performance if followers already have the abilities, skills and resources to get the job done |
|
|
What is effectiveness?
|
involves making judgments about the adequacy of behaviour with respect to certain criteria such as work-group or organizational goals
|
|
|
What are needs?
|
refer to internal states of tension or arousal, or uncomfortable states of deficiency people are motivated to change
Leaders can motivate followers by helping them satisfy their needs. In order to get people to do things, you have to appeal to their needs. |
|
|
What is Maslow's Hierarchy of Needs (bottom to top)?
|
Physiological
Security Belongingness Esteem Self-Actualization |
|
|
What is an exemplary follower?
|
enthusiastic, intelligent, and self-reliant participation in pursuit of an organizational goal
Take the initiative Assume ownership Manage themselves well Buy into the organization’s purpose, vision, and values Know and understand their leader Build competence and focus efforts Display flexibility and adaptability Work well on a team Act with courage, honesty, humility and credibility |
|
|
What is the relationship between leadership and the ability to motivate followers according to Maslow?
|
Leaders may need to satisfy basic needs before appealing to higher motivation level are effective in motivating ppl
|
|
|
What is Alderfer's ERG theory and explain the practical implications for motivating followers?
|
You don't have to fill the lower level needs first
you can satisfy multiple needs simultaneously |
|
|
What are the 3 cognitive theories of motivation?
|
Goal setting
Equity Expectancy theory |
|
|
What is the relationship between the cognitives theories of motivation and leadership?
|
thinking differently about rewards, cognitive theories focus on “playing the hand you’re dealt” by recognizing, will workers exert more effort toward group goals when the expectations for performance and the links between the level of effort and desired outcomes are clear
|
|
|
What is the overjustification effect?
|
external rewards can result in a decrease in intrinsic motivation when they are perceived as being to controlling, considered more myth than reality
|
|
|
What is achievement orientation
|
the strength of the intrinsic motive to achieve success
|
|
|
What are the 2 fundamental assumptions of the expectancy theory?
|
motivated performance is the results of conscious choice
people will do what they believe will provide them the highest/surest rewards |
|
|
What are the 3 components of Expectancy theory?
|
1.effort-to-performance
2.performance-to-outcome 3.valence-how much the reward is valued |
|
|
What is the Equity theory?
|
concerned with fairness of inputs relative to outputs
|
|
|
What is self-efficacy?
|
Concerned with one’s core beliefs about being able to successfully perform a task
Positive self-efficacy is used to note beliefs where people feel confident that they have the power to create desired effects Negative self-efficacy is used to note self debilitating beliefs Varies depending on task To boost self-efficacy, leaders can provide relevant work experience and tie it to training, coaching, encouragement, and support, and ensuring followers get the resources they need to be successful |
|
|
What is the Pygmalion Effect?
|
occurs when leaders articulate high expectations for followers, which often times lead to higher performing followers and teams
|
|
|
What is the Golem Effect?
|
Leaders who have little faith in their followers' ability to accomplish a goal are rarely disappointed
|
|
|
Describe the process of leadership using the Interactional Framework of Leadership
|
Leadership is the result of a complex set of interactions among 3 elements: the leader, the followers, and the situation. Elements are mutually influential.
|
|
|
What is the distinction between leaders and managers?
|
Leaders are more personal in their orientation to group members than managers
leaders are more global in their thinking leaders focus on values, expectations, and context Managers focus on control and results differences in interactions with others |
|
|
What is the distinction between adaptive and technical problems?
|
technical problems are solved by assistance from an expert
adaptive problems are onces that are difficult to define in themselves and are only solved by changing the system itself |
|
|
What are 8 power and influence tactics?
|
Rational persuasion – logical argument and factual evidence
Inspirational appeals – arouse enthusiasm or emotions Consultation – ask targets to participate Ingratiation – flattery to achieve an advantage Personal appeals – asking for favors as a result of friendship Coalition – teaming up on Pressure – threats or persistent reminders Legitimizing – marshaled by proper authority |
|
|
What are the 5 bases of power?
|
Expert, Referent, Legitimate, Reward, Coercive (opposite of reward)
Referent power often means greater access to influence tactics |
|
|
What is the relationship between power, influence, and influence tactics?
|
Effective leaders use all sources of power
Strong leaders acknowledge and are open to followers influencing them Leaders vary with the extent they share power Hard tactics (legit/pressure) when have the upper hand, when resistance expected, or when other violates norms Soft tactics (ingratiation) when at disadvantage, when they expect resistance Rational tactics The right tactic not enough – must also be skillfully executed, positive tactics more effective than negative tactics (in general) |
|
|
What is the operant approach to motivation?
|
motivating others through the use of rewards and punishments
|
|
|
What is a contingent award?
|
"involves the process of leaders rewarding followers whose performance meets previously agreed upon goals
Rewards: material (money)/non-material (praise |
|
|
What is a non-contingent reward?
|
Not associated with particular behaviors
|
|
|
What is extinction (with regard to motivation and rewarding)?
|
the elimination of behaviors due to lack of rewards
|
|
|
How do you improve follower motivation using the Operant Approach?
|
Specify what behaviors are important
Determine if those behaviors are currently being punished or ignored Find out exactly what followers find rewarding and punishing Beware feelings of inequity Don’t limit to institutional sanctions and rewards Use contingent rewards and punishment |
|
|
What is empowerment?
|
the process of motivating employees by giving them authority to make decisions about the delegated tasks equipping them with the skills needed to perform these tasks.
|
|
|
What are 2 components of empowerment?
|
Delegate leadership and decision making to lowest possible level
Equipping with resources, knowledge, and skills |
|
|
Empowerment principles:
|
Delegate leadership and decision-making to lowest level possible.
Equip followers with resources they need. Macro-psychological components: Motivation, Learning, Stress Micro-psychological components – measures of whether employees are empowered: Self-determination, Meaning, Competence, Influence Pitfalls: Overdelegation becomes abandonment, Underdelegation becomes micro-management |
|
|
What are two primary components of Transaction Leadership?
|
Contingent Reward
Management by Exception |
|
|
What is management by exception?
|
“catching people doing something wrong” or “if it ain’t broke don’t fix it”
Active – patrolling/looking for errors and correcting/punishing (room/zone inspections, Quality Assurance audits). Passive – sitting back and waiting for errors to occur, then correcting/punishing (8-Oclock Reports) |
|
|
When is transaction leadership appropriate to use?
|
When not enough time for transformational leadership
When followers are unwilling “Default” option for leading people – we must be skilled transactional leaders in the military Can be conceived as the foundation from which transformational styles can be employed. Short-term operations |
|
|
What are the drawbacks of solely employing transactional leadership?
|
requires heavy supervision
no buy-in from followers subordinates not developed/transformed intrinsically motivated followers may not perform well more reactive than proactive emphasis on “bottom line”, could lead to unethical practices produces “yes men” |
|
|
What are the 4 Components of Transformational Leadership? (4 I's)
|
Idealized influence
Inspirational motivation Individual consideration Intellectual Stimulation |
|
|
What is idealized influence
|
role model for followers which elicits followers’ admiration, respect, and trust. Followers want to emulate leaders who provide this idealized influence.
Considers needs of others Shares risk Consistent High ethical and moral standards and conduct Never uses power for personal gain |
|
|
What is Inspirational motivation?
|
emotional component of transformational leadership
Charisma and “charismatic leadership” Leader sees what is currently important and has vision to anticipate the future Linked to pre-existing values and attitude of the followers Has been defined as a followers reaction to and identification with a certain leader (shared values, shared vision, shared goals) |
|
|
What is individualized consideration?
|
Reflects leader’s concerns for followers and their development
Understands that different followers have different needs Interact on personal basis Attentive to ALL subordinates Tailor behavior to different subordinates |
|
|
What is intellectual stimulation?
|
Encourage innovation and creativity
Allows for re-thinking of ideas and re-evaluation of procedures |
|
|
What is the 4-step process of of transformation in a follower?
|
1. Personal identification
2. Social identification 3. Internalization 4. Increase in self-efficacy |
|
|
What are six guidelines for effective feedback and counseling?
|
Be helpful
Be descriptive Be timely Be flexible Give +/- feedback avoid blame or embarrassment |
|
|
How does group size impact group development?
|
Cliques, span of control, process loss, social loafing, social facilitation
|
|
|
What are the 4 stages of group development?
|
Forming
Storming Norming Performing |
|
|
What is intrasender role conflict?
|
Mixed signals from same person
|
|
|
What is intersender role conflict?
|
Mixed signals from several others
|
|
|
What is interrole conflict?
|
Can't satisfy both bosses and subordinates
|
|
|
What is person-role conflict?
|
Role violates someone's personal values
|
|
|
What is role ambiguity?
|
Lack of clarity on expectations
|
|
|
What are group norms and what are their impact on performance?
|
Informal rules to regulate and regularize group behavior, and only that behavior the group feels important; Norms are more important if they: Facilitate group survival, Simplify what behavior is expected of the group, Help avoid embarrassing interpersonal problems within the group, Express the group’s central values
|
|
|
What is the relationship between group cohesion, norms, performance and leadership?
|
Highly cohesive groups generally have better job satisfaction and less turnover;;Too high in cohesion can lead to “overbounding” (shutting out other groups or individuals) or “groupthink” (creativity/thinking constrained by group habits and norms) that tends to suppress dissent.;In general, cohesion within the group and performance of the group is positively correlated, though highly cohesive groups can also perform poorly.
|
|
|
What is intrasender role conflict?
|
Mixed signals from same person
|
|
|
What is intersender role conflict?
|
Mixed signals from several others
|
|
|
What is interrole conflict?
|
Can't satisfy both bosses and subordinates
|
|
|
What is person-role conflict?
|
Role violates someone's personal values
|
|
|
What is role ambiguity?
|
Lack of clarity on expectations
|
|
|
What are group norms and what are their impact on performance?
|
Informal rules to regulate and regularize group behavior, and only that behavior the group feels important
Norms are more important if they: Facilitate group survival, Simplify what behavior is expected of the group, Help avoid embarrassing interpersonal problems within the group, Express the group’s central values |
|
|
What is the relationship between group cohesion, norms, performance and leadership?
|
Highly cohesive groups generally have better job satisfaction and less turnover
Too high in cohesion can lead to “overbounding” (shutting out other groups or individuals) or “groupthink” (creativity/thinking constrained by group habits and norms) that tends to suppress dissent. In general, cohesion within the group and performance of the group is positively correlated, though highly cohesive groups can also perform poorly. |
|
|
Dark side personality traits
|
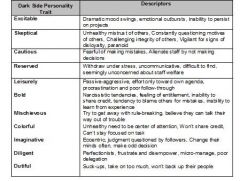
|
|
|
4 domains of EQ
|
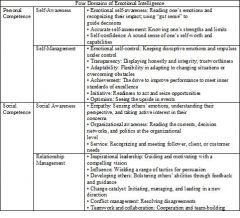
|
|
|
Emotional Intell table
|
|
|
|
5 Factor Dimensions
|
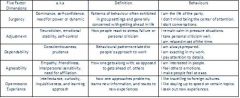
|
|
|
Maslow's Hierarchy of Needs
|
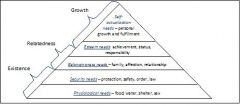
|
|
|
Relationship between leadership, job satisfaction, and performance
|
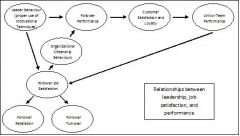
|
|
|
Followership styles
|
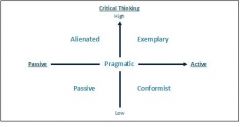
|
|
|
Leader
Follower Situation Venn Diagram |
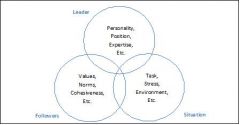
|
|
|
What is the importance of task structure to team effectiveness?
|
Task structure – knowledge of task, consistent with team mission and unambiguous
|
|
|
What is the importance of group boundaries to team effectiveness?
|
Group boundaries – are team members fit to the work, sufficient knowledge and skills, size of team okay, team members get along
|
|
|
What is the importance of norms to team effectiveness?
|
Norms – is teamwork valued? Are norms fit to the task? How were they formed?
|
|
|
What is the importance of authority to team effectiveness?
|
Authority – does leader share authority? Should she? Can leader be questioned?
|
|
|
What are the six common indicators of in-group dynamic?
|
High degree of communication of information
Greater influence in decisions Higher priority of task assignment Greater job latititude More support More attention |
|
|
What is empowerment?
|
Empowerment: the process of motivating employees by giving them authority to make decisions about the delegated tasks equipping them with the skills needed to perform these tasks.
Two components:Delegate leadership and decision making to lowest possible level Equipping with resources, knowledge, and skills |
|
|
What are the principles of empowerment?
|
Delegate leadership and decision-making to lowest level possible.
Equip followers with resources they need. Macro-psychological components:Motivation,Learning,Stress Micro-psychological components – measures of whether employees are empowered:Self-determination,Meaning,Competence,Influence Pitfalls :Overdelegation becomes abandonment,Underdelegation becomes micro-management |
|
|
What is the impact of conflict on a unit?
|
Conflict resolution a major topic in leadership effectiveness studies, many practical application for the skill
Some conflict over task items may actually enhance performance Interpersonal conflict is usually dysfunctional and should be avoided |
|
|
What are the 5 conflict resolution strategies?
|
Competition (Dominate) – win/lose, quick action is vital (emergencies)
Accommodation (Appease) – lose/win, when you know you’re wrong (and they’re right), build social credit, when outcome not important to you Sharing (Compromise) – draw, each side gives in interest of resolution, under time crunch, achieve short-term fix Collaboration (Integrate) – win/win, both sides have concerns too important to compromise, creativity wanted! Avoidance (Neglect) – lose/lose, issue is trivial or less important than others, parties need to cool off |
|
|
What is the difficulty in changing organizational culture?
|
Basically it’s due to a fear of loss and a lack of understanding as to why the change is needed.
Loss of power (gained over time in the old structure) Loss of rewards (or unclear rewards) Loss of identity (the old way was inadequate or you are not important) Loss of competence (my skills are not valid anymore) Loss of relationships (new teams, new groups, new peers and bosses) Fear due to bad past experiences with change |
|
|
What is Beer's Rational Approach to organizational change?
|
C = D x M x P > R
D: the level of dissatisfaction with the status quo M: the model of the future and the systems and goals needed to support this vision P: a change plan or process to implement needed changes R: the level of resistance to the new vision of the future. This formula states that the more people are dissatisfied with the current situation the clearer the vision, goals, and change plan and the better the leader is able to counter resistance, the greater the potential for organizational change. Leaders can also use this change formula to determine where an organizational change initiative is failing and what to do to increase the odds of success. |
|
|
What is the effect of resistance on change initiatives using the SARA model.
|
Shock, Anger, Resistance, Acceptance
Leaders looking to enact change need to anticipate the sequence of normal human reactions. When the situation permits, leaders must also provide support and time for followers to progress through the stages. Leaders should directly address the fears created by change Loss of power: listen, empathize, help develop new ways to build power Loss of rewards: clearly design and communicate new reward system based on the changes Loss of identity: emphasize the value of the new roles and the changes…changing identity does not mean getting rid of the old one completely. Loss of competence: ensure processes are in place to train, coach, mentor and build new competencies. Loss of relationships: allow new relationship to occur before the change takes place, then support and drive new interactions. Do not allow isolation. |
|
|
What is the relationship between Team Effectiveness and Leadership?
|
Clear mission
High performance standards Stock-taking of equipment Assess technical skills of team members Secure resources Plan and organize Establish high level of communication Minimize interpersonal conflict |
|
|
What are methods and techniques to learn and improve decision-making skills
|
More than any single activity leaders make decisions. There are basically two ways to make decisions: analytically or intuitively.
Time and experience are critical factor in deciding which method to apply. If you have the time (and especially if you lack experience) you should apply a more analytical process. The OODA loop is a method for making better analytical decisions. The ability to quickly complete the OODA loop can also help you make better intuitive decisions. |
|
|
What are the two types of decision making?
|
Intuitive – based on a leader’s ability to quickly recognize patterns and viable solutions given a specific situation. Intuitive decisions are made by quickly scanning the situation and comparing it to previous experiences. The real challenge of intuitive decision-making is the need for a deep and rich knowledge base.
Analytical – if they lack an experience base, leaders can make sound decisions by applying a deliberate, logical, analytical decision making process. |
|
|
What does OODA loop stand for?
|
OBSERVE
What are the facts, the assumptions and the background? How much time do you have? What don’t you know? How can you find out it? How much time should you spend gathering information? ORIENT:What assumptions, analyses, and judgments are at play? What Biases influence your analysis? What options are available? What are the consequences of these options? What does each option mean to you, the other Mids, the academy? What perceptions are created/supported by each option? DECIDE: based on the options explored above….What are your immediate actions? What are your long term actions? What alternatives to your plan will you need to consider? ACT: How will you implement your decision? What follow-up or monitoring is required? |
|
|
Explain the relationship of intelligence, experience, stress and leadership presented in Cognitive Resource Theory (CRT)
|
"Cognitive Resource Theory examines the role of intellectual and other cognitive abilities on leader performance. CRT suggests that there is an interesting relationship between leader intelligence and experience levels and group performance in stressful vs. non-stressful conditions.
Intelligence and experience are two key concepts in the theory. Intelligence is one's overall effectiveness in activities directed by thought as typically measured by standard IQ tests. Experience includes learned behaviors and skills that are acquired over the years by performing various tasks. These two variables can impact a teams performance depending on the level of stress present. Stress is defined as the level of interpersonal conflict and concerns about performance with superiors or the apprehension associated with performance evaluation. CRT provides the following hypotheses: |
|
|
Explain the relationship of intelligence, experience, stress and leadership presented in Cognitive Resource Theory (CRT)
|
"Cognitive Resource Theory examines the role of intellectual and other cognitive abilities on leader performance. CRT suggests that there is an interesting relationship between leader intelligence and experience levels and group performance in stressful vs. non-stressful conditions.
Intelligence and experience are two key concepts in the theory. Intelligence is one's overall effectiveness in activities directed by thought as typically measured by standard IQ tests. Experience includes learned behaviors and skills that are acquired over the years by performing various tasks. These two variables can impact a teams performance depending on the level of stress present. Stress is defined as the level of interpersonal conflict and concerns about performance with superiors or the apprehension associated with performance evaluation. CRT provides the following hypotheses: Leader experience is related positively to performance in high-stress situations but not in low-stress ones. That is, under high stress a leader can fall back on tried-and-true experiences they have acquired, and thereby help group performance. In low stress situations, they may rely too much on past experience. Stress moderates the relationship between IQ and performance. That is, intelligence is an asset in low and moderate stress situations under high stress, intellectual skills can become impaired and detract from or have no effect on a group's performance. |
|
|
"
|
|
|
|
• Explain how to effectively treat CSD and PTSD
|
• CSD treatment:
– Best people to treat it: Front-line supervisors (small-unit leaders) – Rest – Nutrition – P-I-E • Proximity • Immediacy • Expectancy • PTSD Treatment – Trained Professional |
|
|
• CSD/PTSD Prevention:
|
Small unit identity / cohesion
– Competent, Ethical, Supported Leadership – Training – Early treatment (i.e. properly treating CSD/ASD) |
|
|
• Describe the possible symptoms of CSD
|
CSD symptoms include, but not limited to:
– Excessive fatigue – Slow, indecisive behaviors – “1000-yard” stare – Feelings of guilt, incompetence – Mild confusion re: time, events, location – Nausea, vomiting, increased pulse & breathing – Crying, anxiety, forgetfulness |
|
|
• Describe the possible symptoms of PTSD
|
PTSD symptoms include, but not limited to:
– Reliving the event / flashbacks – Avoiding reminders of the event – Becoming “emotionally numb” – Feeling emotionally tense – PTSD is a debilitating disorder – it impairs an individual’s ability to function. |
|
|
• Describe guidelines for effective feedback and counseling
|
o Be Helpful
o Be Descriptive o Be Timely o Be Flexible o Give Positive and Negative Feedback o Avoid blame or embarrassment |
|
|
What is the relationship between experience, time, and effective decision-making?
|
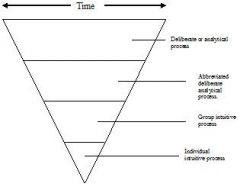
|
|
|
Describe the group and individual effects of combat / operational-related injury, death and killing
|
Sympathetic Nervous System energizes the body for fighting or fleeing…the ultimate goal being self preservation. Remember that this a natural reaction in human activity. The key is that there is a natural loss of blood to the brain as blood is directed toward other parts of the body in preparation for stesses to the rest of the body. In normal activity, 70% of the oxygen in the blood is used by the brain. During heightened times of increased stress and physical awareness, that critical oxygen is used by the body’s other life processes at a higher rate, decreasing the ability to critically think. This is where training and repetition take over to ensure the appropriate actions are taken, ie: fight or flight.
1. First time: Fear, nervousness, anxiety. This feeling can be common during a number of activities, in example: Before a big game, prior to taking the stage for a performance, doing anything in front of a crowd as it is watching you, and finally engaging in a combat environment. 2. Through repetition or TRAINING, the ability to channel that energy or fear can become a more familiar process. At this point, your mind and body can react in a voluntary or almost involuntary way as your training kicks in. |
|
|
What is Parasympathetic Backlash?
|
Parasympathetic Backlash occurs after the traumatic event or after a time of prolonged stress. Parasympathetic backlash is dangerous because in combat environments it can lead to a lack of awareness, a lessening of the senses. The “letting down of the senses” can open an opportunity for general unpreparedness or a false sense of security.
|
|
|
Explain sleep deprivation.
|
Sleep deprivation produces fatigue of the mind and contributes to a sense of fear in the person who faces uncertainty or danger. Decision-making may be aided by a growing variety of electronic information-processing technology, but it is ultimately a human brain that makes a decision. The more sleep-deprived that brain is, the more likely any decision it makes will be bad, perhaps disastrously bad. Because we all rely on our brains, each of us needs to know how much sleep we need, ways to increase sleep during periods of continuous operations, and what happens when we don’t get enough sleep.
Napping is not better than sleeping, but on continuous operations, it can help bring some relief. A nap should be no shorter than 15 minutes, but if you can get 30, do it. The closer you can get to your normal sleep requirement, the better you will perform. Before an operation, try to get as much sleep (your normal requirement) as possible, so that you do not begin your mission in a state of sleep-debt What is the importance of Circadian rhythms? Circadian rhythms are your body’s natural alarm clock. It is important that if you’re beginning operations in another time zone that you shift your work schedule prior to deployment/commencement of mission to allow your body to adjust under favorable conditions. |
|
|
How is communication affected by combat / operational-related injury, death and killing?
|
However often the importance of communication up and down the chain of command is emphasized in leadership courses, faulty communication remains one of the root causes of poor performance in units. As units prepare to fight in ever smaller and more dispersed units, effective communication throughout command levels becomes all the more important if everyone is to know what is expected of him and what is his commander’s intent. More and more missions are being influenced by political, economic, diplomatic, and sociological factors to which the individual rifleman is exposed daily. Your role, as his leader, is to explain his mission and its ground rules, especially the rules of engagement, in terms he can understand.
|
|
|
How is confidence affected by combat / operational-related injury, death and killing?
|
A person facing danger must have the confidence in himself, his peers, his leaders, and his personal weapon. No factor is more important than self-confidence in promoting combat performance and preventing combat-related psychiatric disorders. The combatant who lacks self-confidence may endanger himself and others through delay in decision-making and timidity in action. He is unlikely to dare, when daring may be necessary. When the battle is over and he thinks back on his actions, doubts about his performance will plant the seeds for later psychiatric illness. Confidence in oneself is the result of training and experience. Few factors are as important to self-confidence on the eve of battle than the realization that one has trained well for it and has the necessary physical skills and endurance to function under demanding circumstances.
|
|
|
Explain how the leader and the organization influence combat readiness / military effectiveness and resiliency in followers and mitigate the effects of combat / operational-related stress?
|
Men perform well and courageously on the battlefield primarily because of their loyalty to the men immediately around them, and not because of loyalty to any larger organizational unit. Anything that weakens this cohesion at the small-unit level will threaten the resolve of those men to perform to their maximum in battle. If a mission goes badly, is perceived to have been poorly planned, or is thought to have been unnecessary, and if casualties result, survivors will engage in scapegoating and become at risk for later psychiatric disorders as they remember their losses. Bonding, unit cohesion, and loyalty provide a different perspective on these losses: whether a mission is justified or not, or well or poorly planned and executed, men in war fight and die not for the mission but for each other. That perspective may recast the grief of survivors and help reduce their chances for later becoming psychiatric casualties.
|
|
|
Identify the enabling elements of combat killing.
|
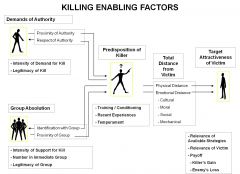
|
|
|
What are the enabling factors of killing?
|
1. The power of the leader or authority figure?
Never underestimate the power of the need to obey. If the authority is farther away or the victim is close, the willingness to fire diminishes. 2. The role of the group Man is not a killer, but the group is. Provides "mutual surveillance", "diffusion of responsibility" and a drive for "conformity," making it extremely difficult not to participate 3. The distance between killer and victim Easier to drop a bomb from high above or kill blindfolded/hooded victim than to kill an enemy up close 4.The nature of the victim and the degree to which shooting this particular target can harm the enemy and help the shooters. Enemy officers and those using key weapons become priority targets. |

