![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
55 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
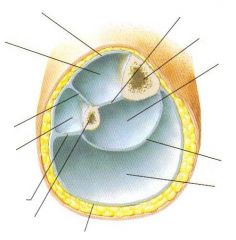
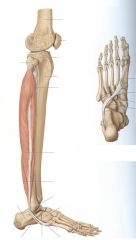
What are the three compartments of the foot?
|
Anterior
Posterior Lateral |
|
|
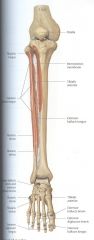
What are the:
Nerve Artery Actions of the Anterior Compartment |
N: Deep fibular
A: Anterior tibial Primary actions: dorsiflexion and extension of the digits |
|
|
What forms the compartment septae and retinaculae?
|
Deep or crural fascia
|
|
|
What "layer" contains superficial veins and cutaneous Nerves?
|
Superficial Fascia of the leg/foot
|
|
|
What are the two major parts of the extensor retinaculum?
|
Superior/Inferior
|
|
|
What are the characteristics of the supeiror and inferior extensor retinaculae?
|
Both extensor retinaculae are between the Tib/Fib
Superior is superior to the malleoli Inferior is made of three parts. -Common stem (lateral at calcaneus/talus) - Upper band - Lower band (to plantar fascia and medial cuneiform) |
|
|
What is the fascia called on the dorsum of the foot?
|
Dorsalis Pedis Fascia
|
|
|
What are the tendons included in the 1st, 2nd, and 3rd compartments of the dorsum of the foot?
|
1s- TAFT EHL/EDL
|
|
|
What muscle tendons are included in the 2nd compartment of the Deep fascial compartments of the dorsum of the foot?
|
EDB
EHB |
|
|
What is contained in the thrid compartment of the deep fascia of the dorsum of the foot?
|
Neurovascular structures
|
|
|
considering the Extensor Expansions:
What is Dorsal? What joins Laterally? What are the three slips/bands? |
Extensor expansions lie over the dorsum of the MtPJ
The EDLs are Dorsal Joined by EDB laterally (at Proximal Phalanx) Central band with two lateral bands. Terminates into terminal slip/band at the dorsal tubercle of the distal phalanx. |
|
|
Explain the function of extensor expansions-
|
Extensor expansions attach to the extensor tendons. When the tendons flex it pulls on the wing/sling and causes extension of the IPJs (not MPJs)
|
|
|
Triangular Aponerosis-
|
Helps hold the two lateral bands together (on lab practical) and terminates into the terminal slip that inserts at dorsal tubercle of distal phalanx.
|
|
|
What are the two parts of the Extensor Hood?
What is the Hood coverage? |
Sling and Wing,
Mt head to PiPjts |
|
|
What is the Extensor hood Sling?
Wing? Combined? |
Sling encircles the MTP, is proximal and interossei insert to it.
Wing is distal and lumbricals insert to it. Combined to make extensor hood. |
|
|
Where does the Central slip of the Extensor Expansion terminate?
|
dorsal tubercle of the middle phalanx.
(medial and lateral go distal, secured near distal termination by trangular aponeurosis, and insert to the dorsal tubercle of distal phalanx ) |
|
|
What muscles insert on the sling?
Wing? |
Sling is interossei
Wing is lumbricals |
|
|
What is the course of the sling?
|
From dorsum to plantar plate.
|
|
|
FDB is on the first layer of plantar MM (it is superficial). What is just deep to it at the 2nd met head?
|
FDL is deep (2nd layer of plantar mm) to FDB at met head.
|
|
|
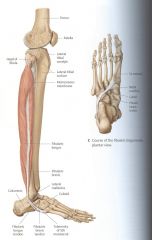
What are the MM of the lateral compartment?
What is the action? What is the real-life function? |
Superficial is Fib. longus, then Fib. brevis deep to it.
Eversion/weak plantarflexion Rolling the ankle these fire and protect from damaging ligaments. |
|
|
What holds the ligament of the Fib Long in the groove of the cuboid?
|
Superficial fibers of the long plantar ligament.
|
|
|
lateral Compartment: What NN supplies innervation?
What AA? |
Technically the superficial Fibular NN is the N to the lateral compartment. (supplies MM to longus and brevis)
AA- Perforating AA of Ant. Tibial to front and Fibular to Back. |
|
|
what holds the tendons of the fibularis long/brev in place as they course laterally and plantarly on the foot?
|
Superior and inferior fibular retinacula.
|
|
|
Proximally the fib long/brev tendon is in a singular sheath. Where does the sheath split to the fib/long tendon proper?
|
Splits at the fibular tubercle. Remember, that prominence on the lateral side of the calcaneus. like an object out in the middle of nowhere?
|
|
|
Insertion of fib brevis?
longus? |
Brevis- Styloid process
Longus- plantar foot, base of met heads |
|
|
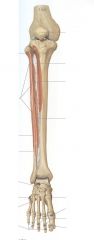
Posterior compartment of the leg
N A Action |
N: tibial N
AA: Posterior Tibial Vessels Action: Plantar flexion, inversion, Flexion of digits. |
|
|
What are the two septae that divide the Posterior compartment from the ant/lateral?
|
Interosseus ligament
Posteriro Septum |
|
|
What and were is the Kager's triangle?
|
Kagers is a fatty pad behind the achilles tendon that helps maintain space with bursa under the achilles tendon. (what?)
|
|
|
What are the contents of the superficial layer of the posterior compartment of the leg?
|
Triceps surae
Achilles tendon (w/reflex @S1) Kager's triangle Retrocalcaneal bursa |
|
|
What are the MM in the Deep portion of the Posterior Compartment?
|
Popliteus MM
Tibialus Posterior Flexor Digitorum Longus Flexor Hallucis Longus (Pop (Tom Dick an Harry)) |
|
|
Popliteus course and purpose in this world.
|
Intracapsular tendon into the medial condyle of the femur and lateral meniscus- unlock knee.
|
|
|
The flexor retinacula runs from the medial malleolus to the calcaneus. What courses deep to that, in an anterior to posterior Fashion?
|
Tibialis Posterior (T)
Flexor Digitorum Longus (D) Flexor Hallucis Longus (H) |
|
|
What is the course of the Flexor Hallucis Longus as it courses to the plantar aspect of the foot?
|
Most lateral, in the groove of posterior process of the talus, under the sustentaculum tali, to distal phalanx of hallux
|
|
|
More proximal than the flexor retinaculum what is the order of the TDH?
|
FDL (Dick)
TP (tom) (crosses inferior to FDL and ends up with tendon anterior to it) Flexor Hallucis Longus (Harry) |
|
|
What is the Porta Pedis?
|
Where vasculature and NN enter the plantar foot. Just a continuation of the tarsal tunnel onto the foot. Between the first and 2nd layers of the foot. Covered by abductor hallucis.
|
|
|
What is the "nod of henry"?
|
holds the FHL/FDL together
|
|
|
What are the two fat pads on the plantar aspect of the foot?
|
Calcaneal and metatarsal
|
|
|
What are the three sections of the "plantar fascia" or plantar aponeurosis.
|
Central- main part that comes from medial tubercle to MPJs. Wraps and encircles MPJs distally.
Lateral- dense, course, thin portion from lateral tubercle to 5th met base. Medial- unremarkable. |
|
|
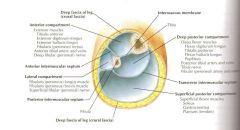
What are the four Fascial compartments of the foot called?
|
Interosseus
Lateral Medial Central |
|
|
What are the rules to the medial and lateral fascial compartments of the plantar foot?
|
Lateral has structures that attach to 5th met.
Medial has structures that attach to 1st met. |
|
|
What are the contents of the central fascial comparment of the plantar foot?
|
Lumbricals and flexor digitorum brevis MM tendons.
It is surrounded by invaginations of the central band. |
|
|
What are contained in the Interosseus compartment of the plantar foot?
|
Dorsal/ plantar interosseus MM.
|
|
|
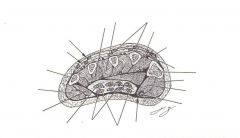
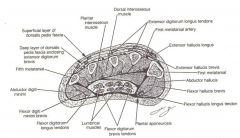
What are the MM of Layer 1 of the plantar foot MM?
|
Hallux/ digiti minimi Abductors
Flexor digitorum brevis (from medial calc tubercle) (1st Flex the Abs) |
|
|
What are the MM of layer 2 of the plantar foot?
|
FHL tendon
FDL tendon Lumbricals Quadradus Plantae (F2LQ) |
|
|
What are the MM of layer 3 of the plantar foot?
|
Medial and lateral head of FHL
Transverse and oblique head of adductor hallucis MM Flexor digiti Minimi Brevis |
|
|
What is present in the 4th MM layer of the plantar foot?
|
Dorsal and plantar interosseus MM
Deep plantar Arch AA is here, between third and 4th. PAD DAB |
|
|
What is the innervation to the plantar aspect of the foot?
|
Medial Plantar N- "3+1" Abductor Hallucis, Flexor Hallucis Brevis, Flexor Digitorum Brevis and 1st lumbrical.
Lateral Plantar= everything else. |
|
|
What are the two parts of the fibrous flexor sheaths?
|
Anular Portions
Cruciform Portions (Synovial Membrane) |
|
|
What is the relationship of the FDL and FDB tendons?
|
FDB tendons ride superficial to FDL until it splits to two lateral slips at the PIPJ.
The tendons lie in the grooves formed by the plantar plates. Connected to the bones via vincula (includes blood supply) |
|
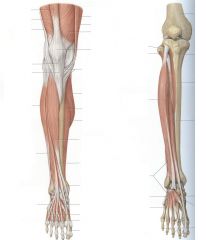
|
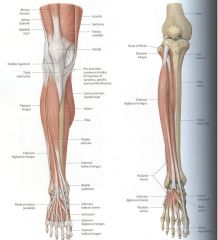
|
|
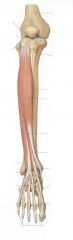
|
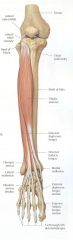
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|

