![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
48 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Stage-1-Caecilius-Where did Caecilius live? Describe town.
|
Pompeii.
1st century AD. Foot of Mt. Vesuvius. Bay of Naples. Population 10k. |
|
|
Stage-1-Caecilius-Who was Caecilius and what did he do?
|
Citizen of Pompeii.
Rich banker mainly but also auctioneers, tax collector, money lander and farmer. Dealt in slaves, cloths, property and timber. Ran a cleaning and dyeing business along with some other shops. |
|
|
Stage-1-Caecilius-Explain Latin names.
|
Lucius Caecilius Icundus.
Lucius (personal name like modern fist name ) Caecilius (shows he is member of Caecilii clan – very important in Rome; strong feeling of loyalty in them) Icundus (Name of own family and close relatives; icundus means pleasant) |
|
|
Stage-1-Caecilius-Explain rights of Roman citizens.
|
Could vote in election. Protected against unjust treatment.
Slaves had no rights and masters had full powers them. But they could not put one to death without good reasons. |
|
|
Stage-1-Metella-Explain responsibilities of Roman women.
|
Had greater freedom than other Mediterranean women.
Responsible for efficient home management. Had nearly equal freedom as men. Could shop, visit friends and run business freely. |
|
|
Stage-1-Metella-Name some jobs women had in Rome.
|
Cook, hair dresser, banker, doctor, shoe maker, silver smith.
|
|
|
Stage-1-Metella-Name one influential Pompeian woman. Her Importance?
|
Eumachia.
Wealthy business women, who gave donation that built clothe worker’s meeting hall in Pompeii. |
|
|
Stage-1-Houses-Which houses did wealthy people live in?
|
Townhouses, different from townhouses today.
|
|
|
Stage-1-Houses-Name townhouse features.
|
Came up to side walk. No garden or grass. Small windows to let light in, but maintain temperature. Houses could be one or two storied. Didn’t look inviting. Shops on sides could be rented out.
|
|
|
Stage-1-Houses-Explain usual house plan.
|
After ianua (door) was atrium (main hall). Compluvium (Open in roof) let rain water collect in the impluvium (pool to collect rain water). In the corner was lararium (god shrine). Floor of atrium was paved with marble slabs or mosaic. Walls were plastered. Pompeian liked red, orange and blue. These panels had scenes from roman stories, especially Greek myths.
Around atrium was cubicula (bed rooms), tablina (study) and triclinium (dining room). Entrances weren’t doors, but heavy curtains. From first area people walked through either study or narrow passage to second part. This was peristylium (garden court), made up of column surrounding hortus (garden). Often elaborately decorated with careful arrangements. In small fish pond in middle, a small fountain threw up a jet of water. Marble statues of heroes and gods were here and there. |
|
|
Stage-1-Houses-Explain how Pompeian thought about their houses.
|
Houses weren’t private places restricted to close family and friends. Instead much social life and business was conducted from home. Business with most visitors will be done in atrium. More important ones were invited in tablinum (study). Very close friends and high ranking officials would be able to dine in triclinium or relax in peristylium, with the family.
|
|
|
Stage-1-Houses-How did poor people live?
|
Poor shopkeepers had a room or two above their shops. In large cities like Rome, many people lived in insulae (apartment buildings), several stories high, some of them in very poor conditions.
|
|
|
Stage-2- Daily Life-What time did Caecilius and his slaves get up?
|
Caecilius at dawn, slaves even earlier to clean the house.
|
|
|
Stage-2- Daily Life-How did Caecilius dress?
|
Put on: first tunic, then a toga, then shoes, which were like modern sandals
|
|
|
Stage-2- Daily Life-How did Metella dress?
|
First stola( full length over-tunic) then in going out, a palla (large rectangular shawl)
|
|
|
Stage-2- Daily Life-What was breakfast?
|
Light, of the a cup of water and a piece of bread
|
|
|
Stage-2- Daily Life-What was Caecilius’ first duty in the day?
|
Receive greetings from poor people and former slaves. Hand out small sums of money to them. Help them as best as possible if they were in any kind of trouble. In return, they would accompany him on business trips and public appearances to show their support for him.
|
|
|
Stage-2- Daily Life-After visitors, what next?
|
If no more home business to conduct, go to forum, spend rest of day trading and banking.
|
|
|
Stage-2- Daily Life-What’s lunch for Caecilius?
|
Light meal, meat or fish followed by fruit
|
|
|
Stage-2- Daily Life-What’s after lunch for Caecilius?
|
Business ended shortly after lunch. Then was a short siesta before going to the baths.
|
|
|
Stage-2- Daily Life-What’s dinner for Caecilius?
|
Main meal of the day. During winter, inner triclinium near atrium was used. Summer used outer one looking out in the garden. Began with light dishes to prepare appetite. Eggs, fish, and vegetables were served. Then came main course, could consist of elegantly cooked foods like beef, mutton, and poultry. Desert consisted of fruits, nuts, cheese, and sweet dishes.
|
|
|
Stage-3-Town of Pompeii-Explain location and region of Pompeii.
|
Low hill of volcanic rock, 5mi from Mt. Vesuvius. One of many prosperous towns in Campania region. Outside town, many villas and estates owned by wealthy Romans attracted to region by pleasant climate and peaceful surroundings.
|
|
|
Stage-3-Town of Pompeii-What is the total area and defense of Pompeii?
|
163 acres. Surrounded by wall having 11 towers and 8 gates. Roads led out from gates to Herculaneum, Nola, Nuceria, Stabiae-, and the harbor
|
|
|
Stage-3-Town of Pompeii-How is Pompeii organized?
|
Two main streets of shops and Stabiae street, cross near the center of the town. Other streets, mostly in straight lines divided town neatly into blocks. Most streets didn’t have names.
|
|
|
Stage-3-Town of Pompeii-How were streets constructed?
|
Streets made of volcanic stones, and high paved sidewalks.
|
|
|
Stage-3-Town of Pompeii-Explain the shopping areas.
|
In main streets, bakers’ shops and bars sold drinks and snacks. Main shopping areas were forum and along Street of Shops northeast of Stabian baths. Carved/painted signs announced type of store: goat-diary, hammer and chisel-stonemason. Ads and public notices painted on whitewasher walls outside shops and houses.
|
|
|
Stage-3-Town of Pompeii-What is the forum?
|
Center for local government, business, and religion on western end of town.
|
|
|
Stage-3-Town of Pompeii-Theaters?
|
Large open air theater for large audiences (up to 5k people). Roofed smaller one for concerts and other shows. Amphitheater for gladiator fights and animal hunts. Could seat everyone in Pompeii and visitors from other towns as well
|
|
|
Stage-3-Town of Pompeii-Some nationalities in Pompeii?
|
Romans, Greeks, Spaniards, Jews, Africans, Syrians, and more
|
|
|
Stage-3-Town of Pompeii-What was the water system in Pompeii?
|
Brought by aqueducts from hills, stored on large tanks on high ground at northern side. Pressure by tank water allowed good flow through underground lead pipes to all parts of town. Fountains were on street corners where water could be drawn, but wealthy people paid to have water piped directly into their homes.
|
|
|
Stage-4-Forum-Things in forum?
|
Business, local government, religion
|
|
|
Stage-4-Forum-Statues in forum?
|
Commemorated emperor and members of family and citizens who gave distinguished service to the town
|
|
|
Stage-4-Forum-What does colonnade do?
|
Surrounded forum on 3 sides, provides corridor where people can walk, shielded from sun or rain.
|
|
|
Stage-4-Forum-Was wheeled traffic allowed?
|
No, a row of upright stones at each entrance blocked all wheeled traffic.
|
|
|
Stage-4-Forum-Who was the official responsible for policing the forum?
|
Aedile.
|
|
|
Stage-4-Forum-Sketch building around forum. Give details.
|
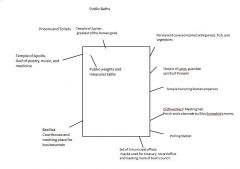
|
|
|
Stage 5-Theater at Pompeii-What is the frequency of plays?
|
Only at festivals held several times during the year.
|
|
|
Stage 5-Theater at Pompeii-Who did not hurry?
|
Council members and important citizens, due to reserved seat for them in the orchestra. Tokens told entrance and where to sit.
|
|
|
Stage 5-Theater at Pompeii-What is size in main seating areas?
|
5 k in cavea
|
|
|
Stage 5-Theater at Pompeii-What is roofed theater?
|
Odeon
|
|
|
Stage 5-Theater at Pompeii-Explain stage and adjacent buildings.
|
Scaena and scaena frons. Scaena frons had 3 or 5 doorways, entire front decorated with columns and niches.
|
|
|
Stage 5-Theater at Pompeii-What is admission?
|
Free. All expenses paid by a wealthy citizen to benefit other citizen and to gain popularity for election.
|
|
|
Stage 5-Theater at Pompeii-How did Pompeian keep cool?
|
Mainly by large canvas awning, managed by sailors. When windy, it did not work. Then, hats and sunshades were used. In between plays, attendants sprinkled scented water.
|
|
|
Stage 5-Theater at Pompeii-Explain a popular type of play.
|
Pantomine, mixture of opera and ballet plot, usually serious, taken from Greek myths.
|
|
|
Stage 5-Theater at Pompeii-Who were the actors
|
Usually Greek slaves or freedmen, admired for skill and stamina, attracts large following of friends.
|
|
|
Stage 5-Theater at Pompeii-Explain comic actors
|
Comic actors like Actius and Sorex were equally popular as the Pantomine actors. Acted in vulgar farces and one act-plays put on at the end of long performances. Packed with rude jokes and slapsticks. Familiar characters were Pappus, old fool and Manducus, greed clown.
|
|
|
Stage 5-Theater at Pompeii-Explain masks.
|
Characters were instantly recognizable from masks made of linen which was covered with plaster and painted.
|
|
|
Stage 5-Theater at Pompeii-What special plays were put on festivals?
|
Sometimes, comedies of playwright Plautus and Terence were put on had a number of familiar characters, but plots were more complicated and dialogs more witty than farces.
|

