![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
10 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Skeletal Muscle Origination
|
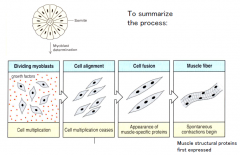
Arises from the myotome compartment of somites
Myoblasts migrate to the site of muscle formation. Single myoblast cells fuse into multinucleate myotubes. Myofibers containing contractile proteins then assemble. Muscle of the face arises from cranial somitomeres |
|
|
Smooth Muscle Origination
|
Cells do not fuse; remain Mononucleate
a. Smooth muscle of the visceral organs is derived from the splanchnic mesoderm layer. b. For most blood vessels, smooth muscle comes from the somatic mesoderm. c. Smooth muscle of the iris, sweat glands and mammary glands comes from the ectoderm. d. For the ascending aorta and carotid vessels, smooth muscle is derived from migrating neural crest cells. |
|
|
Cardiac Muscle origination
|
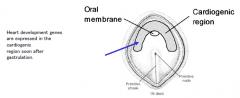
Arise from the splanchnic mesoderm in the cardiogenic region. This is sometimes called the cardiac crescent.
|
|
|
Formation of Heart
|
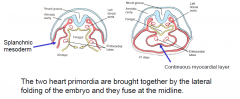
|
|
|
Vasculogenesis
|
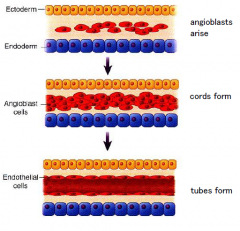
Only occurs in mesodermal tissue
Only forms the major blood vessels |
|
|
Angiogenesis
|
Blood vessel formation by branching from the primary blood vessels.
(Think VEGF) |
|
|
Liver formation
|
Dependent on the heart for signals to induce formation
|
|
|
Lateral Folding of embryo
|
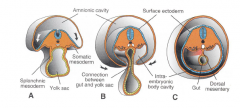
|
|
|
Sagittal folding of embryo
|
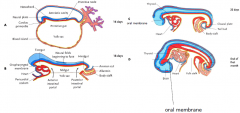
|
|
|
Meckel's Diverticulum
|
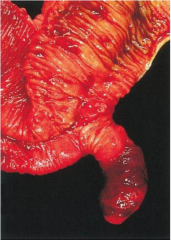
A bulge or pouch off the small intestine. Remnants of the yolk sac stalk.
Present in 1 in every 50 people. Most people show no symptoms, although intestinal blockage or bleeding may sometimes result. |

