![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
45 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What are etiologies of pregnancy loss?
|
mneumonic: MAKE ME
MECHANICAL: uterine abnormalities AUTOIMMUNE: APS KARYOTYPE: chromosomal rearrangements, aneuploidy ENDOCRINE: PCOS, DM w. hyperglycemia, thyroid w. high Ab MATERNAL INFECTION ENVIRONMENT: trauma, obesity, smoking, caffeine |
|
|
What defines recurrent spontaneous abortion?
|
3+ CONSECUTIVE spontaneous abortions
|
|
|
How do you manage a SEPTIC SA?
|
1. dilatation and curretage
2. IV broad spectrum antibiotics |
|
|
How do you manage a THREATENED SA?
|
watch and wait
note: only <5% go on to abort |
|
|
How do you manage a COMPLETE SA?
|
expectant management (NO D&C)
|
|
|
When is a fetus considered viable?
|
>/=20 weeks GA or >/=500g
|
|
|
What are pregnancy termination options <12 weeks?
|
medical: methotrexate (IM or po) + misoprostol (pv) (only if <9weeks)
surgical: dilatation + vacuum +/- curettage counselling: support, contraception (if applicable), f/u beta-hCG! Don't forget, if Rh- give RHOGAM |
|
|
What are pregnancy termination options >16 weeks?
|
medical: prostaglandins (intra-amniotically or IM)
surgical: dilatation and evacuation; early induction of labour counsel |
|
|
What is the difference b/w manual and electric vacuum aspiration?
|
MANUAL - <=10wks GA, hand-held, can be performed in office
ELECTRIC - <=13wks GA, electric pump, requires dilatation, requires consciuos sedation or general anasethetic |
|
|
What are complications of vacuum aspiration?
|
common: pain, cramping
less common: bleeding, infections/endometriosis, perforation of uterus, cervix laceration, Asherman's syndrome, infertility, retained products |
|
|
What is the management of inevitable, incomplete, or missed SA?
|
options:
1. watch and wait 2. Misoprostol 400-800 ug po/pv 3. Dilatation and curretage +/- oxytocin |
|
|
What is management of RECURRENT SA?
|
work-up cause: hypercoag w/u, karyotype parents, evaluate if uterine abnormality
manage: cervical cerclage and bed rest for next pregnancy |
|
|
IF suspicious of SA, what do you order?
|
1. U/S
2. beta-hCG 3. blood type +/-CBC |
|
|
What scoring system is used to evaluate favourability
of delivery and the probability of succeeding with an induction? |
BISHOP'S SORE
<6 cervix unfavourable >=6 cervix favourable 9-13 vaginal delivery likely |
|
|
What are the characteristics of the Bishop score?
|
Dilatation
Effacement Consistency Position Station |
|
|
In terms of cervical dilatation, what is considered the latent and active phase?
|
latent phase: 0-3cm
active phase: 4-10cm |
|
|
What are the 4 stages of labour?
|
FIRST: latent (cervix 0-3cm) and active phase (cervix 3-10cm & painful regular contractions)
SECOND: full dilatation to delivery THIRD: delivery to placenta expulsion FOURTH: 1 hour postpartum - monitor VS, repair tears |
|
|
Which stages of labour are the most dangerous to the mother?
|
3rd and 4th
d/t risk of hemorrhage |
|
|
What is the rate of dilatation for nulliparous vs. multiparous
|
nulliparous: 1.2cm/hr
multiparous: 1.5cm/hr |
|
|
How long is the course of normal labour for the nulliparous vs. multiparous?
|
Nulliparous
1st: 6-18hrs 2nd: 30mins-3hrs 3rd: 5-30mins Multiiparous 1st: 2-10hrs 2nd: 5-30mins 3rd: 5-30mins |
|
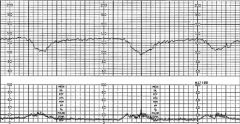
What is your interpretation of this FHR tracing?
|
EARLY deceleration: mirrors maternal contraction; benign - vagal response to head compression
|
|
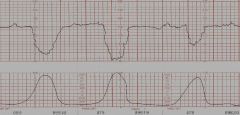
What is your interpretation of this FHR tracing?
|
VARIABLE deceleration: variable in size, onset and duration
d/t cord compression or forceful pushing |
|
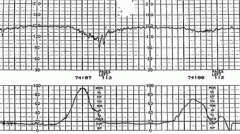
What is your interpretation of this FHR tracing?
|
LATE deceleration: nadir occurs after the peak of maternal contraction, slow return o baseline
sign of fetal hypoxia/uteroplacental insufficiency |
|
|
What is your management of early deccelerations??
|
mgmt: observe - early decels are benign
|
|
|
When do you worry about variable decelerations?
|
RULE of 60's
baseline <60 bpm deceleration nadir <60 bpm deceleration duration >60s |
|
|
How do you manage an abnormal FHR?
|
mnemonic: POISON
Position (LLDP) O2 IV fluids Scalp monitor, pH, stimulation Oxytocin stopped Notify MD Examine for cord prolapse R/O fever, dehydration |
|
|
What are risk factors for shoulder dystocia?
|
obesity
DM multiparity hx macrosomic infant prolonged 2nd stage of labour |
|
|
What is your approach to shoulder dystocia
|
1. Suprapubic pressure - Anterior shoulder disimpaction
2. McRobert's position 3. Rotate posterior shoulder anteriorly (corkscrew) 4. episiotomy 5. Rollover 6. cleidotomy 7. zavanelli (push fetus back in and C/S 8. sympyhsiotomy Note: Doing 1&2 sill resolve 90% of cases |
|
|
What are complications of shoulder dystocia
|
Hypoxia
brachial plexus injury fetal fracture maternal perineum injury |
|
|
What are possible causes of dystocia (abnormal progression of labour)
|
4 P's
Power: inadequate maternal eexpulsive efforts Passenger: fetal position, attitude Passage: pelvic structure, maternal soft tissue Psyche: stress causes release of hormones that can bring about dystocia |
|
|
What are causes of meconium in the amniotic fluid?
|
- cord compression
- undiagnosed breech - fetal distress |
|
|
light green/yellow meconium in the amniotic fluid is associated with lower APGAR scores.
T/F? |
FALSE
dark green or black meconium is associated w. lower APGAR scores |
|
|
You go assess a G1P0, GA36, who is in labour in triage. The is nurse is concerned because she has a Temp of 38.2C, HR120, and RR36. When you assess the patient, you note that she is tender when palpating the fundus of her uterus and there is a foul odour. What is most likely diagnosis?
|
Chorioamnionitis
Temperature Tachycardia Tenderness - uterine Foul discharge |
|
|
What is management of chorioamnionitis?
|
1. Deliver, despite GA
2. IV amp/gent |
|
|
What prerequisites are required for an operative vaginal delivery?
|
mnemonic: ABCDEFGHIJK
Anaesthesia Bladder empty Cervix fully dilated and effaced Determine fetal head position Eequipment ready Fontanelle (posterior) midway b/w thighs Gentle traction Handle elevated Incision Jaw visible, can remove forceps Knowledgeable operator |
|
|
what are indications for operative vaginal delivery?
|
FETAL
- atypical fetal HR - prolonged second stage of labour MATERNAL - a need to avoid pushing (cerebrovascular disease) - exhaustion - excessive analgesia |
|
|
When is vacuum extraction contraindicated?
|
1. fetus at risk for coagulation d/o
2. preterm delivery |
|
|
What are contraindications to obstetric anaelgesia?
|
refractory hypotension
maternal coagulopathy LMWH daily untreated bacteremia the usual: skin infection, inc'd ICP |
|
|
What are risk factors for prolonged ROM?
|
1. low SES
2. young maternal age 3. smoking 4. STI |
|
|
how do you determine if membranes have ruptured?
|
1. Sterile spec exam - see pooling of amniotic fluid
2. + Nitrazine paper test (blue = alkaline) 3. + Fern test - fern pattern under microscope |
|
|
What is management of premature ROM
|
1. cultures
2. If 32-36wks - consider induction of labour if <32 wks - expectant management 3. ABx - inc'd risk of chorioamnionitis 4. If <32 wks AND no infection - steroids |
|
|
Define premature labour
|
Must have all
1. regular contractions 2. concurrent cervical change 3. <37 wks GA |
|
|
Complications of prematurity
|
1. PDA - patent ducuts arteriosus
2. RDS - respiratory distress syndrome 3. bronchopulmonary d/o 4. intraventricular hemorrhage 5. retinopathy of prematurity 6. death |
|
|
What is your management of pre-term labour
|
Avoid premature birth
1. R/O infection, PROM, fetal anomalies (UA, urine culture, Cx for chlamydia and gonerrhea, sterile spec exam, U/S) 2. Tocolysis 3. Steroids 4. GBS prophylaxis |
|
|
What are types of breech presentations?
|
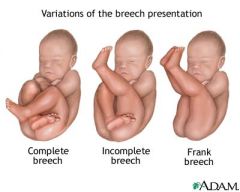
1. Frank (most common breech and most common to be delivered vaginally)
2. Footling 3. Complete |

