![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
28 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
closed circuit:
|
A circuit in which the source of emf is connected to the circuit so that current begins to flow.
|
|
|
emf: (E)
|
The work done per unit charge by a source that forces electrons to move in a direction opposite to the electrostatic field inside the source.
|
|
|
The junction rule:
|
the sum of the currents entering any junction must equal the sum of the currents leaving that junction.
|
|
|
The loop rule:
|
the sum of the potential differences across all the elements around any closed-circuit loop must be zero.
|
|
|
load resistance:
|
The external electrical resistance that the terminal voltage of a battery is hooked up to.
|
|
|
time constant: (Symbol = tRC)
|
The time required for a capacitor C in an RC circuit to charge from zero to 63.2% of its maximum value, or to discharge to 36.8% of its fully charged value.
|
|
|
Ampère's Law:
|
The law stating that the sum of the product of the magnetic field produced by a current I times a path segment Δl forming a closed path around the source of current equals the permeability of free space m0 times I.
is the component of the magnetic field that lies parallel to Δl. |
|
|
cathode ray tube: (CRT)
|
A display device consisting of an electron gun made up of a heater, a cathode, and a positively charged anode. The cathode is heated to a sufficiently high enough temperature that the electrons in the cathode material have sufficient kinetic energy to escape the cathode. The free electrons are subsequently attracted to the anode and ultimately strike a specially prepared screen that fluoresces when it is struck by the electrons.
|
|
|
dip angle:
|
The angle between the Earth's magnetic field and surface of the Earth.
|
|
|
electric motor:
|
A generator that runs in reverse taking electricity and producing mechanical torque
|
|
|
electromagnet:
|
A multiturn coil of wire that when energized with electric current produces a magnetic field around it. Sometimes referred to as a solenoid.
|
|
|
ferromagnetic:
|
Strongly magnetic materials such as iron, cobalt, and nickel whose electron spins do not cancel completely.
|
|
|
gauss:
|
The cgs unit for magnetic field. It is related to the SI unit of magnetic field, the tesla (T), by: 1 T = 10^4G
|
|
|
magnetic declination:
|
The difference in angle between magnetic north and geographic north. The magnetic declination differs from point to point on the Earth.
|
|
|
magnetic domain:
|
Large groups of atoms whose spins are aligned. The size of a magnetic domain is typically 10-4 cm to 0.1 cm.
|
|
|
magnetic field:
|
The field associated with the force surrounding magnetic materials. The direction of the magnetic field is in the direction that the north pole of a compass would point with the compass at that location.
|
|
|
permeability of free space: (Symbol = m0)
|
A magnetic proportionality constant.
4πx10-7 Hm-1 |
|
|
solenoid:
|
A multiturn coil of wire that when energized with electric current produces a magnetic field inside its core and around it.
|
|
|
Tesla (T)
|
The SI unit of magnetic field. It is related to the cgs unit of magnetic field, the gauss (G), by:
1 T = 10^4G |
|
|
Permeability of free space constant
|
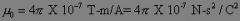
What is this?
|
|
|
back emf:
|
An induced emf appearing in electric motors that tends to reduce the applied current in the motor.
|
|
|
alternating current generator:
|
A device that converts mechanical energy to electrical energy.
|
|
|
direct electric current generator:
|
A device that takes alternating current and converts it to one polarity to produce a steady DC current.
|
|
|
Lenz's law:
|
The polarity (direction) of the induced emf is such that it produces a current whose magnetic field opposes the change in magnetic flux through the loop. That is, the induced current tends to maintain the original flux through the circuit.
|
|
|
motional emf:
|
The emf induced in a conductor moving through a magnetic field.
|
|
|
What is this equation?
|
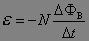
Faraday's law of induction
|
|
|
The proportionality constant that relates self-induced emf to the time rate change of the current through the circuit producing the self-induced emf.
|
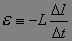
Induction
|
|
|
The product of the magnetic field perpendicular to a loop of area A.
|
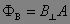
Magnetic flux
|

