![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
19 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Average age of onset?
|
63 years old
|
|
|
Most common causes of laryngeal cancer?
|
smoking + alcohol use (leads to stigma of it being the pt.'s fault)
|
|
|
60-75% or all laryngeal cancers are _________ (where do they occur?) which leads to changes in ___________
|
60-75% are glottic and change voice quality
|
|
|
Symptoms of laryngeal ca?
|
Ear pain (referred pain)
hoarse voice/vague sore throat swallowing problems coughing up blood lump in the neck |
|

|

|
|
|
Risk factors for laryngeal CA?
|
long exposure to smoke/alcohol, industrial chemicals and solvents, reflux?, HPV/other viruses, genetic predisposition
|
|
|
Stigmas surrounding laryngeal CA?
|
causation seen as pt.'s fault
race, poverty, ca, physical disfigurement, communication, issues related to gender, quality of life |
|
|
How is laryngeal CA diagnosed?
|
Examined by ENT. Direct examination of the mass and biopsy (about 3 days for biopsy to be processed)
|
|
|
staging of laryngeal cancer based on _____ and _________ of tumor
|
size + location
|
|
|
What do the T, N, and M, levels stand for in laryngeal CA staging?
|
T = tumor (graded 1-4)
N = node (has it spread to lymph nodes or not?) M - metastasis (the spread or potential to spread) |
|

|

|
|
|
Tx for laryngeal CA?
|
combo of radiation/chemo/surgery
|
|
|
Pt. diagnosed with small laryngeal tumor. Received radiation only. Will this pt need SLP services?
|
Yes, radiation therapy may have effects on voice and/or swallowing
|
|
|
Difference between partial/conservation laryngectomy and Total laryngectomy?
|
In a partial laryngectomy 10-90% of larynx is removed
Total = entire larynx from first tracheal ring to hyoid bone |
|
|
Describe a supralottic laryngectomy?
|
transverse cut of thryoid cartilage above anterior commisure and resection of tissue from ventricle up to and including the hyoid bone and pre-epiglottic space. May need to reset base of tongue. Swallowing outcomes not good as no TVFs to protect airway
|
|
|
Draw a supraglottic laryngectomy restruction
|
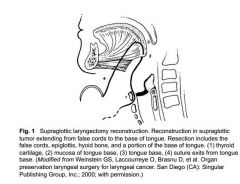
|
|

|

|
|
|
Issues to consider when determining candidacy for use of artificial larynx
|
How intact is neck tissue? May need to use an intraoral adapter
How narrow/tight is esophagus? May need an electrolarynx Any hearing impairment in pt/primary comm. partner? will this disease reoccur? Intrinsic mode may be lost (dunno what that means) |
|
|
Advantages/Disadvantages of EL speech
|
Easy to operate, can use in a variety of speech environments (telephone + noisy), no special care requirements
mechanical sounding, requires good hand control |

