![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
9 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Large animals |
Mostly livestock, can range into wildlife like elephants |
|
|
Unit conversion |
1 kg = 2.2 lbs
1 inch = 2.54 cm |
|
|
Body weight of large animals |
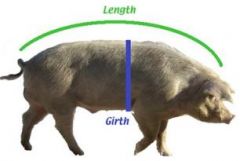
Weight (lbs) = (L x G x G) ÷ 400 (inches) or L = Length |
|
|
Body weight of cattle
|
HEART GIRTH x HEART GIRTH x BODY LENGTH / 300 = ANIMAL WEIGHT IN POUNDS. For example, if a beef cow has a heart girth equal to 70 inches and a body length equal to 78 inches, the calculation would be (70 x 70 x 78) / 300 = 1,274 lbs. |
|
|
Body weight of horse |
Adult Horse: (Heart Girth x Heart Girth x Body Length) ÷ 330 = Bodyweight in pounds |
|
|
Body weight of sheep and goats |
using the formula HEART GIRTH x HEART GIRTH x BODY LENGTH / 300 = ANIMAL WEIGHT IN POUNDS. For example, if a sheep has a heart girth equal to 35 inches and a body length equal to 30 inches, the calculation would be (35 x 35 x 30) / 300 = 122 lbs. |
|
|
Veterinarians |
Veterinarians are licensed animal health professionals who are qualified to diagnose and treat pets, livestock and exotic animals. A vet can work in a variety of environments, but will generally interact with both animal patients and human clients. |
|
|
Safety precautions |
1. Approach all animals with caution |
|
|
Veterinary associations in Malaysia |
|

