![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
162 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Elevation relief map |

Another term for topographic map. Shows change between highest and lowest points. |
|
|
What information can be studied on regional plans? |
Forest health and tree cover Transportation systems and corridors Land use allocation Urban growth patterns |
|
|
How is a region defined? |
Geographical boundaries and topographical watersheds Public service providers Political boundaries |
|
|
How far will most pedestrians walk in a ten minute time? |
0.25 mile |
|
|
What stages should budgets be prepared at? |
Implementation plan Conceptual design plan Schematic plan |
|
|
What it’s the max grade for a parking lot? |
5% |
|
|
Incompatible use setback |
25’ between incompatible uses |
|
|
Active recreation setback |
30’ on all sides avoiding tree canopy. Avoid overlapping setbacks. Pools don’t have to worry about setbacks |
|
|
Sports facility orientation |
North-south: soccer, tennis, football, basketball, volleyball East-north-east: baseball, softball |
|
|
Primary circulation route, Vehicular exceptions |
A drive solely for parking lot egress/ingress is not considered a primary circulation route Drop-off, turnaround, service, and drive through window lanes ARE considered primary circulation |
|
|
The design of parking shall never necessitate backing from a space into… |
A street, a primary circulation route, or entrance |
|
|
Min/max lane width |
11-13’ per lane |
|
|
Parking space dimensions |
9’ x 20’ 20-25’ back up and travel way space |
|
|
Double loaded parking (20 spaces) and single loaded parking (10 spaces) Area requirements |
Double: 60-65’ x 100’ (20’ row length + 20’ row length + 20-25’ backup/travelway = 60-65’ ) x (9’ space width x 10 spaces = 99’) Single: 45’ x 100’ |
|
|
Parking lot islands are required in lots with how many spaces? |
40 or more |
|
|
Drive through guidelines |
Require a by-pass lane |
|
|
How do you determine the number of accessible parking spaces needed? |
All parking lots require at least one accessible space + route to accessible building entrance (route should not require crossing a vehicular path of travel) 1-25 cars : 24 standard + 1 accessible 26+ cars: 24 standard + 2 accessible |
|
|
Accessible route width |
3’ min except at doors |
|
|
Drop off/pick up requirements |
Must be one-way, counter clockwise, single-lane, with a by-pass lane |
|
|
5 Principles of design |
Balance - (traditional, beaux-arts) can have symmetrical and symmetrical balance) Proportion - relative size and scale, relationships between objects and their context Rhythm - creates order Emphasis/dominance - focal point/s Unity/harmony - parts work together to create a wholewhole |
|
|
What’s the Max slope of an ADA Accessible walkway? |
5% (5% - 8.33% is considered a ramp) (8.33% is 1:12) |
|
|
Max slope for driveway |
15% |
|
|
Max slope for playground |
1-3% |
|
|
Max slope for lawns |
25% 3:1 or 4:1 |
|
|
Max slope for highway |
6% |
|
|
How far can a person walk in 5 minutes? |
0.25 miles |
|
|
CPTED principals |
Clear demarcation of public and private Diversity of use High pedestrian use of sidewalks Natural surveillability Sense of ownership of outdoor spaces Prompt maintenance and repair Clear wayfinding Control access to targets |
|
|
What are two types of therapeutic gardens? |
Restorative: recharge, stress reduction, thriving plant life as metaphor Enabling: support therapeutic activities like hands on interaction with plants |
|
|
How to prevent children from getting their bodies stuck in play structures? |
Make sure spaces are smaller than 3.5” or larger than 9” wide |
|
|
What’s the span for play surface cushioning? |
6’ in all directions for stationary equipment Height of slide + 4’ Height of swing hanger pivot x 2 |
|
|
What play surfacing material meets accessibility standards ? |
Engineered wood fiber (Non accessible surfaces are pea gravel, wood chips, shredded bark, sand, shredded rubber) |
|
|
Endemic plants |
Prevalent in our peculiar to a particular locality or region |
|
|
Endemic plants |
Prevalent in our peculiar to a particular locality or region |
|
|
What kindof stuff is on a management plan? |
Phasing, succession, weed abatement, establishment periods |
|
|
The clean water act |
Requires developers to avoid minimize or mitigate damages to wetlands, in that order |
|
|
What are dinner principals of urban forest management |
Diversity of tree species Age diversity Preserve heritage specimens Reduce heat island Reduce heating and cooling of buildings Manage urban soils |
|
|
Principles of sustainable design |
Use recycled materials Source locally Easy disassembly/salvage Embodied energy (sun energy required to produce) Life cycle analysis |
|
|
Ecological planning protocols |
Preserve natural resources Reduce energy use Reduce amount of land used, preserve natural features, resources and functions Allow for natural processes in urban areas |
|
|
Environmental impact statements are… |
For large projects Occurs after master plan stage Enlarge body of fact and opinion that decision makers have Expose predictions, invite scrutiny, and competing opinions |
|
|
Subsidence |
Gradual sinking of ground Can be caused by ground water depletion, oil drilling, peat oxidation |
|
|
Eutrophication |
Build up of minerals in water |
|
|
what is LOS |
level of service is a way to objectively measure the performance of transport systems. In most cases, it measures how well a system delivers a certain level of service. |
|
|
What are some lamp types ? |
Incandescent : cheap inefficient warm tone Fluorescent : cheap efficient cool tone poor in cold temps Mercury vapor : efficient low cost green/blue Induction : electromagnetic radiation Metal halide : good color rendering long life high cost High pressure sodium (HPS) : Orange/yellow high cost long life White HPS : good color rendering high cost long life Low pressure sodium : orange/yellow high cost longest life LED : very small efficient long |
|
|
What units measure light? |
Lumens measure light energy emitted from a source One Lux is equal to one lumen per square meter A footcandle is one lumen cast upon a square foot |
|
|
Efficacy vs efficiency in lighting |
Efficacy is the ability of a lamp to convert watts into light energy (lumens produced per watts consumed) Efficiency is used interchangeably with efficacy |
|
|
Photometrics |
Graphic representation of light levels produced by a light fixture usually shown as a contour interval plan |
|
|
Optics |
Describes light distribution pattern Type II is common for parts or road Type IV is for lighting a large area from its edge Type V is circular for plazas or parking lots |
|
|
IESNA |
Illuminating engineering society of North America Recommend minimum light levels for different indoor and outdoor uses |
|
|
What are rules for intersections |
Allow 100’ minimum between centerlines of intersections Allow 100’ of flat grades (3% or less) around intersections Stay 150’ away from crest of hills Provide 50’x50’ sight triangle clear of obstructions at corners Keep 50’ of straight road before starting curves |
|
|
One car lane should be how wide minimum? |
11’ |
|
|
One car lane should be how wide minimum? |
11’ |
|
|
What’s the minimum inside turning radius recommended for cars and trucks? |
18’ for cars 30’ for trucks truck |
|
|
One car lane should be how wide minimum? |
11’ |
|
|
What’s the minimum inside turning radius recommended for cars and trucks? |
18’ for cars 30’ for trucks truck |
|
|
What are the recommended light levels in lux for Building entry Roadway Residential Parking Basketball Football |

Back (Definition) |
|
|
ADT |
Average daily traffic |
|
|
Pleaching |
Interweaving of plants |
|
|
Pleaching |
Interweaving of plants |
|
|
Pollarding |
Pruning to keep trees smaller |
|
|
What pH is acidic and alkali |
Low pH 0-6 is acidic 7 is neutral High pH 8-14 is basic (alkaline) |
|
|
What are the parts of a lumber stamp |

Mill Strength grade Dried or not Certification agencies Species |
|
|
What wood is most rot resistant? |
Cedar Redwood Black locust Teak/IPE |
|
|
Hardwood vs softwood |
Hardwood comes from deciduous trees Softwood comes from coniferous trees Means nothing about actual strength of the wood |
|
|
Seasoning |
The drying of wood either by air or heat (kiln) Seasoned wood is stronger more stability and lighter Most lumber in arid climates is air-dried |
|
|
Rough vs dressed lumber |
Rough/sawn lumber hasn’t been planed |
|
|
Plain vs quarter sawn wood |
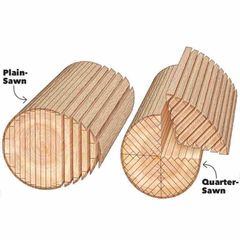
Quarter sawn is more expensive but more stable and less likely to warp |
|
|
Glu-lam vs structural-glued |
Glu-lam are beams composed of long pieces of wood glued together to meet a specific span. Can be very strong Structural glued lumber is two-or more pieces of lumber glued together to make long length pieces. |
|
|
What metals can you use with copper based wood preservatives? |
Copper, stainless steel, or galvanized/coated (Do NOT use plain steel, electro-plated steel, or aluminum) |
|
|
What are the National grading rule lumber classes? |
SLF: Structural Light Framing (1, 2, 3 highest strength) LF: Light Framing (construction, framing, utility) STUD: interior and exterior wall framing SJ&P: Structural Joists & Planks MSR: Machine Stress Rated, each piece tested mechanically |
|
|
What are the three levels of moisture content for wood? |
S-GRN: surface green, 19%+ S-DRY: surface dry, <19% MC 15: moisture content <15% |
|
|
What are the lumber grades for redwood? |
(Highest to lowest quality) Clear, all heart Clear Select heart Construction heart Select Construction common Merchantable |
|
|
What’s the equation for board for calculation? |
#pieces x thickness in inches x width in inches x length in feet / 12 |
|
|
Nominal vs dressed |
Nominal is size before seasoning and and finishing Dressed is typically 0.5” less than called out Rough sawn wood is dimensions as called out |
|
|
Bituminous concrete |
Bituminous concrete is a type of construction material used for paving roads, driveways, and parking lots. It's made from a blend of aggregate materials joined together by "bitumen" (a by-product of petroleum refining). It has a thick, sticky texture like tar when heated, then forms a dense solid surface once it dries. Bituminous concrete is also widely known as asphalt in many parts of the world. |
|
|
What are the concrete finishes? |
Float finish: rough first pass Tooled/troweled finish: too slick for outdoor Broom: light, medium, heavy. Medium is common for outdoors Top-seeded exposed aggregate: aggregate sprinkled on. Can be slippery Sandblast: Light medium or heavy Exposed aggregate: wash away top surface Salt finish: cools pavement in hot weather |
|
|
What are the qualities of type M, N, S, O mortar? |
M: below grade N: subject to exposure S: subject to severe weather exposure O: for interiors |
|
|
Frost line |
Depth at which ground water freezes |
|
|
Heat of hydration |
Heat released as concrete cures |
|
|
What are the ingredients of concrete? |
Cement (lime, silica, aluminum, gypsum), aggregate, water Water catalyze the reaction and aggregate provide the structural strength |
|
|
What are the types of portland cement? |
Type I: normal, cheap and not used much Type II: moderate sulfate resistance, most common Type III: high early strength, for speed Type IV: low heat of hydration, slow and intended for massive structures Type V: high sulfate resistance, even soil/groundwater has high sulfate content content |
|
|
How many days until concrete reaches design strength? |
28 |
|
|
Efflorescence |
Efflorescence is a crystalline deposit of salts that can form when water is present in or on brick, concrete, stone, stucco or other building surfaces. It has a white or greyish tint and consists of salt deposits that remain on the surface after water evaporates |
|
|
what’s DBH? |
Diameter at breast height (4’-6” above ground) |
|
|
What nutrients does ‘complete fertilizer’ contain? |
NPK nitrogen phosphorus potassium |
|
|
What other nutrients may be in fertilizer? |
Calcium, magnesium, sulfur Lime gypsum |
|
|
Caliper |
Diameter of tree trunk at 6” above grade (Usually for field grown nursery stock or small trees) |
|
|
Which sections of the clean water act (1972 and 1977) regulate wetlands? |
404: dredging and filling 201: point source pollution 208: non point source pollution |
|
|
What are some tidal wetlands as classified by the US Army Corps of Engineers? |
Salt marshes Brackish marshes Mangrove swamps Intertidal flatsflat |
|
|
What are the non tidal wetlands as classified by the US Army corps of engineers? |
Emergent wetlands (including potholes and verbal pools) Scrub shrub wetlands (including bogs and pocosins) Forested wetlands (including wooded swamps and bottomland hardwood forests) |
|
|
What are Estuarine wetlands as classified by the US fish and wildlife service? |
Associated with the interface between tidal and non tidal waters Tidal wetlands of coastal rivers and bays Salt tidal marshes Mangrove swamps Tidal flats |
|
|
What are Palustrine wetlands s as classified by the US Fish and Wildlife service? |
Associated with inland sites not dependent on streams (riverine), lakes (lacustrine), or oceanic (marine) water Freshwater marshes Wet meadow Fens Potholes Pocosins Bogs Swamps Small shallow ponds |
|
|
What does wetlands mitigation mean? |
Compensate for adverse impacts to wetlands Setting aside land to protect from future development Enhancing existing wetlands Creating new wetlands |
|
|
What are some wetlands mitigation strategies? |
Avoidance/minimization: avoid building in wetlands and minimize impact Restoration: manipulate site to return functions Enhancement: modify site to increase one or more functions Creation/establishment: make a new wetland Reallocation/replacement: existing wetland is converted to a different type of wetland |
|
|
What are the components of a mitigation plan? |
1 objectives 2 assessment of resources that will be lost and replaced 3 location elevation hydrology of new site 4 what will be planted when and where 5 monitoring and maintenance plan 6 contingency plan 7 guarantee work will be performed as planned and approved |
|
|
What are min and max stair treads, riser height, riser slope? |
Tread depth min 11” max 18” Riser height min 4” max 7” Riser slope min 60 max 90 degrees |
|
|
What’s the most commonly accepted equation for exterior stair proportions? |
2R + T = 24” to 26” |
|
|
How frequently should there be landings in stairs? |
Every 9-11 risers. Landing should be 5’ |
|
|
What is sociopetal vs sociofugal space? |
Sociopetal encourages fact to face communication by inclusive form Sociofugal decreases interaction by reducing eye contact and conservation |
|
|
What’s the sequence of design phases? |
Master plan Conceptual design Concept alternatives Schematic design Design development Construction documentation Implementation Post occupancy evaluation |
|
|
What are the steps of the creative process? |
Inspiration Clarification Évaluation Distillation Incubation Implementation |
|
|
Width of typical bike lane |
5’-6’ |
|
|
What is a class I, II, and III bike path? |
Class I - grade separated Class II - signage and paint marked bike lane at grade with vehicle traffic Class III - sharrow |
|
|
How long between landings in a ramp? |
200’ Max between landings for sloped walk 30’ max between landings for ramp Landings 5’ square 2% max cross slope 3’ min width of path |
|
|
When is a sloped walk a ramp? |
0-5% is a sloped walk 5-8.33% is an accessible ramp |
|
|
What’s the average end area method of calculating cut and fill? |
For use in roads paths or other linear things Cut multiple cross sections and compute the area of cut or fill at each. (Average areas) Calculate the volume by multiplying area by length between cross sections. |
|
|
When is best to use the average end area method vs grid method vs contour method of calculating cut and fill? |
Average end area for linear objects Grid method for excavations Contour method for general |
|
|
What are the different types of concrete joints? |
Expansion/isolation: completely separate slab for when new concrete meets existing structure Control/contraction joint: for cracking Construction joints: for when concrete placing stops for a time |
|
|
When does a ramp need handrails? |
When rise is greater than 6” our length longer than 72” |
|
|
How far must handrails project beyond top and bottom of ramp? |
12” parallel with ground plane |
|
|
What are the joints used in mortar? |
Concave/tooled: (recommended for high winds and heavy rains) Flush/plain cut Flush/tooled Stripped Weathered (recommended for cold regions) V-shaped (recommended for high winds and heavy rains) Extruded Talked |
|
|
What’s a grayfield? |
Abandoned retail or commercial site |
|
|
Per CPTED how tall should plants and fences and foliage be ? |
Planting < 3’ Fencing 3’-6” Foliage 10’-15’ |
|
|
What are zone A, B and C according to transit oriented development? |
Zone A - downtown transit hub 1/8 mile walking Zone B - primary area, medium density, 1/4 mile walking from transit (5-10 minutes) Zone C - secondary area, 1/2 mile or 10-20 min walking As a general rule, developments should be located no more than 1/4 mile from a transit hub |
|
|
How many ADA parking spots do you need per regular parking sort? |
1 ADA per 25 regular |
|
|
How many ADA parking spots do you need per regular parking sort? |
1 ADA per 25 regular |
|
|
What are the dimensions of a regular and ADA parking space? |
Regular 9’ x 20’ ADA 8’ or 11’ with 5’ clearance |
|
|
What setbacks are required for active recreation areas, buildings, streams and wetlands? |
Active recreation - 30’ (no ped/vehicle circulation unless providing access to recreation) Buildings - 25’ from ROW, 15’ from property lines Streams/lakes/etc - 50’ from water edge Wetlands - 100’ |
|
|
What’s the inside and outside turning radius off a car? |
18’ inside radius 25’ outside radius 30’ inside radius for truck |
|
|
How many public entrances to a building must be accessible? |
At least 50% (Public entrance is any entrance that’s not a loading dock or service entry) |
|
|
What’s the Max rise for a ramp? |
30” |
|
|
Define Framework/vision plan, Urban plan, Land use plan, site master plan |
Framework/vision plan: 20-30 years, coordinated for future growth, high level Urban plan: parts of the city, focus on public realm, shorter term, site specific Land use plan strategic implementation plan: 5 years, space utilization, stakeholder input site master plan: current development while accommodating future growth. 20-30 years. historic/cultural restoration and preservation plan parks/open space and trails master plan |
|
|
General parking guidelines |
Whenever possible, avoid dead-ends Back spaces into traffic aisles Locate ADA spaces as close to building as possible Sure drop-offs outside the main traffic flow |
|
|
What sites are most difficult to design, according to LaGro? |
Sites without significant biophysical or cultural features. “The absence Of significant site features or constraints allows a much wider range of festive options for organizing activities and structures on site. The lack of site character also makes us more challenging to create a unique sense of place” |
|
|
What material has most embodied energy? Concrete or asphalt? |
Asphalt |
|
|
What shaped bench fosters most communication? |
L |
|
|
What does the backflow preventer do? |
Protect potable water supply by preventing irrigation Easter from mixing with water meant for consumption |
|
|
What does a Master valve do? |
Turns entire irrigation system on our |
|
|
Flow sensor |
Measures flow in the irrigation system and detect leaks |
|
|
Remote control valve |
Turns a specific irrigation zone on or off within a larger system |
|
|
What are the parts of a LID treatment train? |
Green roof Permeable pavement Bio retention basin with under drain Harvest and re-use cistern |
|
|
What land use experience the most thefts? |
Schools |
|
|
According to Russ in Site Planning And Design, what are the concepts of defensible space? |
Territory (public and private space) Access Surveillance (setting and being seen) |
|
|
When do you need handrails on a slope? |
When slope is greater than 5% and cross slope is greater than 2% |
|
|
What’s the difference between site analysis and site inventory? |
Site inventory describes existing site features Site analysis finds relationships between existing site features and the proposed design |
|
|
Military crest |
Point on a hill just below the top that offers the greatest visibility of the shopper |
|
|
How are historic sites identified according to the national register of historic places? |
Associated with significant events Associated with lives of significant persons Embodies characteristics of a type, period, or method of construction Embodies characteristics that represent the work of a master or possess high artistic values Has yielded information important to history |
|
|
What are survey control points used for? |
They are used as origin points for measuring dimensions and locating things during construction |
|
|
What are the steps of problem solving? |
Problem definition Analysis Establish goals Generate Alternative solutions Analyze solutions and selection Implementation Évaluation |
|
|
What’s the difference between restorative and enabling gardens? |
Both therapeutic/healing gardens Restorative gardens are passive environments for recharge, stress reduction, well being. Depends on plant life as metaphor. Enabling gardens support therapeutic activity. |
|
|
What is acceptable play surface cushioning? |
Pea gravel Engineered wood fiber Wood chips Shredded Bark Sand Shredded rubber |
|
|
What are the principles of urban forest management? |
Promote species and age diversity Preserve heritage specimens Reduce heat island effect Use trees to reduce heating and cooling needs of buildings Manage urban soils |
|
|
What are the contents of an environmental impact statements (EIS)? |
Notice of intent Project description Purpose and need Alternatives to proposed project Affected environment Environmental consequences Comments and coordination List of preparers Record of decision |
|
|
Landfill reclamation appropriate uses include: |
Open space Play fields Sledding area Picnicking (Must be capped and methane must be vented or otherwise collected. Buildings not appropriate because settling) |
|
|
What are some key goals of LID |
Manage and tear storm water on site Decentralized interventions Reduce imperviousness Preserve vegetated areas disconnect areas from storm drain network and redirect to vegetated areas |
|
|
What’s the difference wetland restoration, re-establishment, rehabilitation, establishment, and protection/maintenance? |
restoration : return natural or historic function to degraded wetland. (The rest are sub categories of restoration) re-establishment: increase acreage rehabilitation: increase function establishment: new wetland protection/maintenance: remove threat or prevent decline |
|
|
What are station points? |
Layout points at regular intervals along road centerline to control accuracy of field layout |
|
|
How do you deal with wiring for standards vs low voltage lighting systems? |
Standard (120 V power) uses conduit pipe and pull boxes Low voltage can use direct burial (wire does not have to be in conduit) |
|
|
What materials can you use with wood treated with copper-based preservatives? |
Do use: copper, stainless steel, galvanized Do not use: steel or aluminum |
|
|
What’s galvanic corrosion? |
Dissimilar metals will corrode when placed next to each other, especially in coastal, non arid, and industrial areas |
|
|
Pozzolan |
Finely powdered material which can be added to Portland cement to increase durability. Fly ash is a type of pozzolan. Fly ash is a byproduct of coal combustion. adding it to cement gets you LEED points |
|
|
Terrazzo |
Traditionally marble chips embedded in cementitious matrix. Can be epoxy, resin, polyester, glass, porcelain |
|
|
What are the names of the different brick positions? |
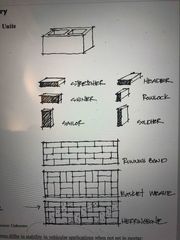
Back (Definition) |
|
|
Aggradation |
Increase in elevation Usually in streams due to deposition of sediment |
|
|
What’s the equation for rate of runoff? |
Q=ciA Q = Peak discharge (cubic ft/sec) c = runoff coefficient i = rainfall intensity (in/hr) A = drainage area (acres) |
|
|
Sanborn map |
A field survey map providing detailed historical info on building heights, footprints, pst and present uses, and construction materials |
|
|
Usgs quadrangle map |
Shows a broad range of info including township, range, new construction, wetlands, typography Does not show owns like land use or demographic info |
|
|
What are Lynch’s 5 elements of urban form? |
Edges Paths Districts Nodes Landmarks |
|
|
What can be added to increase or reduce pH of soil? |
Low pH is acidic, high pH is basic or alkaline Add sulphur to make acidic Add lime or weathered concrete to make more basic/alkaline |
|
|
Zoning ordinance |
Legally binding document to regulate growth. Can be amended. (Comprehensive master plan is guidance for future development) |
|
|
Swimming pools design guidelines |
Walkways not less than 4’ in width around entire pool Ability to drain all water Approved rates for pool water turnover Recirculating skimmers or overflow gutters |
|
|
What functions are best for type I and III brick pavers? |
Type I for high trafic areas Type III for low traffic areas |
|
|
What are four types of phytoremediation? |
Phytoextraction - plants absorb contaminants and are harvested Phytodegradation - plants absorb and break down contaminants Bioremediation - uses micro flora and fauna to break down contaminants Phytovolatization - plants absorb chemicals, break it down, and release through transpiration |

