![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
21 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
Repeating a... |
Written Word |
|
Repeating a... |
Spoken Word |
|
|
Language |
a system by which sounds (phonemes), symbols (graphemes) or gestures are used for communication |
|
|
Aphasia |
the partial or complete loss of language abilities following brain damage, often without the loss of cognitive faculties or the ability to move the muscles used in speech |
|
|
where are the Key language areas |
the left brain |
|
|
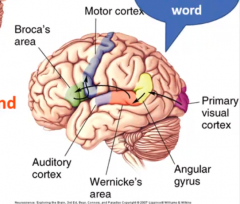
Key Language Areas |
Broca's area Wernicke's area A1 Angular Gyrus |
|
|
Broca's Area |
forms patterns --if you damage Broca's area you would have nonfluent aphasia |
|
|
Wernicke's Area |
interpretation area -gets input from A1 (Auditory Cortex) and interprets as language --if damaged can produce fluent speech but it makes no sense |
|
|
Angular gyrus |
gets input from visual cortex and sends to Wernicke's area --interprets graphemes |
|
|
Wada procedure |
confirms left hemisphere is dominant for speech |
|
|
How many people have left handed speech |
96% of right handed people and 70% of left handed people |
|
|
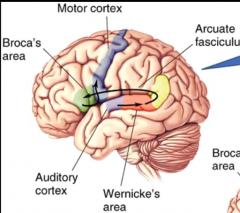
Wernicke-Geschwind Model |
connects wernicke's and Broca's area by going around the peri-sylvian fissure |
|
|
Broca's aphasia |
Motor, nonfluent aphasia --> understands what others say because Wernicke's area is intact -anomia (can't find right words) -agrammatization (mostly nouns & verbs, no transitions) -paraphasic errors (wrong or non-words) -comprehension is normal |
|
|
Wernicke's aphasia |
fluent speech, poor comprehension (can't read and write either) -mixture of clarity and gibberish -correct sounds, incorrect sequence |
|
|
Conduction Aphasia |
disruption of parietal arcuate fasicululus -can't repeat -fluent -can comprehend |
|
|
Global Aphasia |
-Stroke out both Wernicke's and Broca's area --very little speech --poor comprehension |
|
|
Aphasia's in bilinguals |
foreign languages may be in different areas of the brain |
|
|
Aphasia's in sign language |
-Similar to Broca's or Wernicke's in being non-fluent or fluent and meaningless |
|
|
Split brain people |
cut corpus collosum -minor effect for cutting 200 million axons |
|
|
There appears to be a _______ dominant assymetry near Wernicke's area |
left |
|
|
Split-Brain Patience with left language |
-right visual field, repeated easily -unable to describe anything to left of visual fixation point -if image only in left visual field, could find object in left hand but unable to describe |

