![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
31 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Mass Wasting
|
Ex: earth flows, rockfalls, avalanches
|
|
|
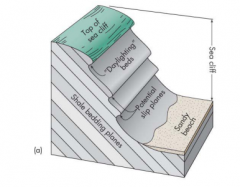
Slope Processes
|
High Cliff/free face
Talus Slope Convex Slope Straight Slope Concave Slope |
|
|
Types of Landslides- (Fall)
|
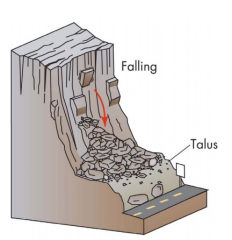
Free fall of earth
*Rockfall |
|
|
Types of Landslides- (Sliding)
|
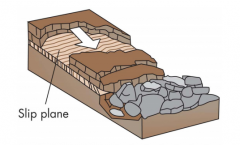
Movement of material as coherent block
*Slump (sliding along a curved plane) |
|
|
Types of Landslides- (Flows)
|
Movement of Unconsolidated material
*creep (very slow) *earth flow, debris flow, and avalanche (very fast) |
|
|
Driving Forces
|
Move materials downslope
*due to vegetation, fill material, buildings that are placed on slope |
|
|
Resisting Force
|
Oppose downslope movement
*shows strength of the material along slip planes |
|
|
Safety Factor (SF)
|
Ratio of resisting forces to driving forces
*Stable >1, unstable <1 |
|
|
Mineral Composition
|
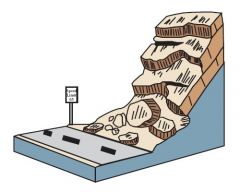
Weak pyroclastic materials produce: creep, earth flows, debris flows, and slump
When very resistant rock hangs over weak rock (pic): Rockfall |
|
|
Degree of Consolidation
|
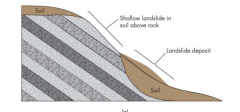
Unconsolidated material: Slumps
When unconsolidated materials are over bedrock (pic): Soil Slip |
|
|
Permeability? (seeps up water)
|
When layers have contrasts in permeability SOIL SLIPS occurs.
|
|
|
Zones of Weakness?
|
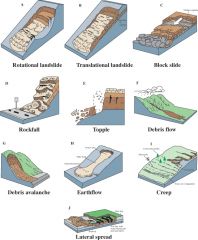
Slip planes (natural breaks in soil consistency)
Rotational slides (curved slip surfaces) Translational Slides (planar slip surfaces) (SEE PICS TO UNDERSTAND) |
|
|
Steepness of the slope or incline?
|
The steeper the slope the greater the driving force
Steep: rockfalls, avalanches, soil slips Moderate: earth flows Gentle: creep |
|
|
Topography Relief or height of hill determines what?
|
The higher up the more risk of mass wasting
|
|
|
Climate on Landslides
|
1.) Timing of WATER flow
2.) Type and amount of VEGETATION: Arid-rock falls, debris flows, soil slips Humid- landslides, earth flows, and creep |
|
|
Vegetation's Affect
|
1.) Provides protective cover, slowing surface erosion
2.) Roots at strength and cohesion to slope materials 3.) Adds weight to slopes |
|
|
Waters Affect
|
1.) Saturates soil causing soil slips and debris flows
2.) After deep infiltration of water slumps occur as well 3.) Erodes base of slope, decreasing stability 4.) Can cause spontaneous LIQUEFACTION or QUICK CLAY |
|
|
Times Affect
|
1.) Forces change
2.) DRIVING AND RESISTING FORCES CHANGE WITH SEASON DUE TO CHANGES IN MOISTURE CONTENT OR WATER TABLE 3.) Chemical erosion occurs slowly overtime as well |
|
|
Snow Avalanches
|
-Rapid downslope movement of snow and ice
-Thousands occur each year in US and Canada -Move down chutes (AVOID THESE) - Slopes >25 degrees are unstable - Stability of snowpack -Weather -Difference types: Loose-snow and slab (see other notecard) |
|

Loose-snow Avalanche
|

Widen as they move downslope
|
|

Slab Avalanches
|

-Move as a block
-Dangerous and damaging -Caused by overloaded slope or weakness in snow |
|
|
Places at risk for Landslides
(and places expected to increase risk) |
*Anywhere with significant slopes and mountains are at risk
1.) Urbanization in landslide-prone areas 2.) Cutting trees in those areas 3.) Changing global climate patterns |
|
|
Effects of Landslides?
|
1.) Can do significant damage (In US 25 people killed each year and costs >$1billion)
2.) People are buried by them 3.) Damage roads, homes, and utilities 4.) Blockage of roads, impeding travel Blockage of streams, causing floods 5.) Disease |
|
|
Links to which hazards?
|
Almost all of them!
(Earthquakes, fires, volcanoes, storms) and they can cause flooding or tsunamis |
|
|
Human Interaction
|
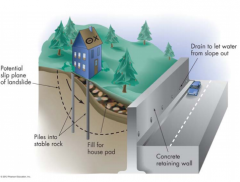
-Natural phenomenon
Humans Increase it by: Expanding in urban areas and using natural resources Humans Decrease it by: Land grading (material from upper slope moved to bottom) to increase surface instability and building stable structures and proper drainage/slope supports |
|
|
How to identify potential landslides?
|
1.) Tongue shaped masses of sediment at bottom of lope
2.) Irregular land surface at bottom of slope 3.) Refer to a hazardous map |
|
|
High cliff or free face?
|
A high, steep, or overhanging face of rock.
|
|
|
Talus Slope
|
A sloping mass of rock fragments at the foot of a cliff
|
|
|
Convex Slope
|
A slope element, and sometimes an entire slope, which gets progressively steeper downhill. (domes over)
|
|
|
Straight Slope
|
I'm guessing it's flat and straight? idk
|
|
|
Concave Slope
|
A slope which becomes progressively shallower downhill
|

