![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
66 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
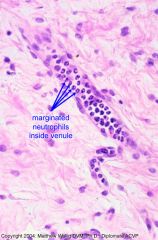
Neutrophils adhering (margination) to a vessel wall with "rounding up" of endothelial cells in an edematous/inflamed tissue section.
|
|
|
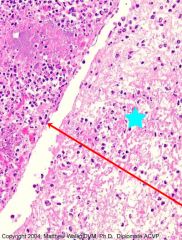
Alveolar exudate consisting of numerous degenerated and necrotic neutrophils mixed with mainly fibrinous residues. Edema and leukocyte infiltration of interlobularar connective tissue.
|
|
|
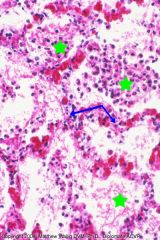
Distended lymph vessel containing fibrinous clot.
|
|
|
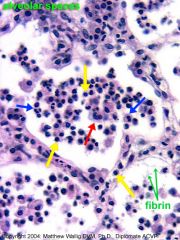
Later phase of bronchopneumonia (macrophages are present and outnumber neutros).
Yellow = lymphocyte Red = macrophage Blue = neutrophils |
|
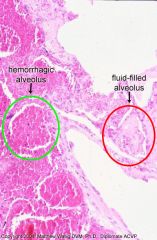
Slide 18
|
Portion of lung with edematous and hemorrhaging alveoli (caused by bact. toxins)
|
|
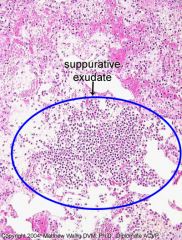
Slide 18
|
Different portion of same lung with an alveolus filled with suppurative exudate.
|
|
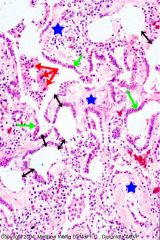
Slide 21
|
Chronic Pneumonia
Thickening of walls with fibrosis (blue=collagen), macrophages (red) outnumber neutros (yellow). Alveoli lined with Type II pneumocytes (green) -- epithelialization. |
|
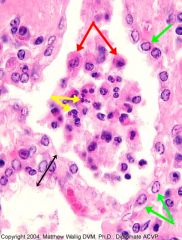
Slide 21 - Zoomed in
|
Chronic Pneumonia
Thickening of walls with fibrosis, macrophages (red) outnumber neutros (yellow). Alveoli lined with Type II pneumocytes (green) -- epithelialization. |
|
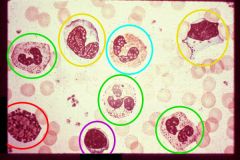
Circulating Blood Cells
|
green=neutro
purple=lympho red=basophil yellow=monocyte blue=eosinophil |
|
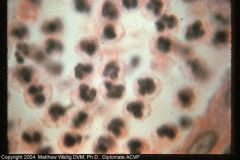
What are these?
|
Degenerating neutrophils in a suppurative exudate (pus)
|
|
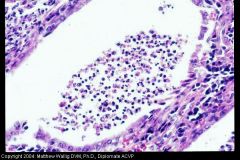
Pyometra
|
Uterine gland filled with exudate of mostly neutros with some macros
|
|
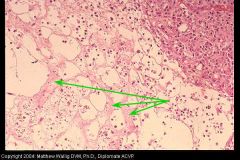
What organ is in the upper right and what is surrounding it?
|
Saponified fat next to pancreas (with necrotizing pancreatitis) stimulating neutro influx
|
|
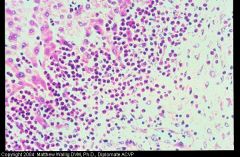
Liver
What inflam cells are most seen here? |
Eosinophilic hepatitis due to migrating ascarids.
|
|
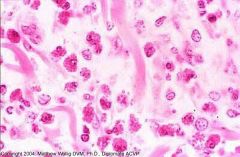
What kind of leukocyte?
|
Very intensely staining equine eosinophils in horse skin.
|
|
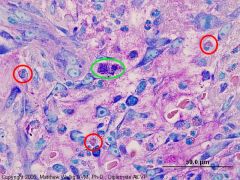
What are these? (Giemsa stain)
Dog stomach |
Red=eosinophil
Green=mast cell |
|
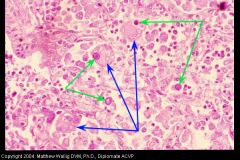
Blastomyces dermatiditis lung infection (what sort of exudate?)
|
Granulomatous pneumonia with macros filling the alveoli
|
|
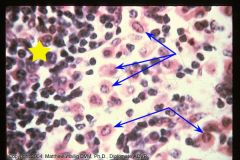
|
Yellow=lymphocytes
blue=macros |
|
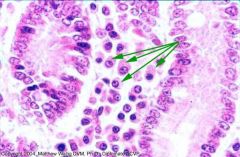
|
plasma cells in canine small intestine
|
|
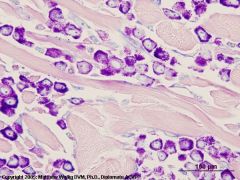
Giemsa stain
|
Mast cells and eosinophils
|
|
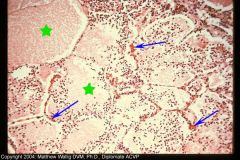
Dog Lung
What kind of exudate? How far has it progressed? |
Acute Pneumonia
Congested capillaries. Alveoli contain plasma proteinaceous fluid and neutrophils. Little stroma damage. complete regeneration possible. |
|
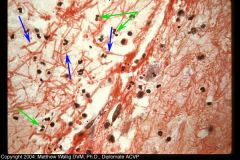
Lung
What kind of exudate? What shows that this inflam. has progressed further? |
Fibrinopurulent exudate.
Pneumonia inflammation has progressed to the point where fibrinogen has leaked out. Mix of fibrin and neutros. |
|
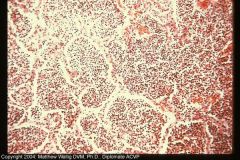
dog lung
Characterize exudate |
Consolidation: all alveoli filled with suppurative exudate. Lung would feel solid.
Lots of necrotic neutros and some fibrin. |
|
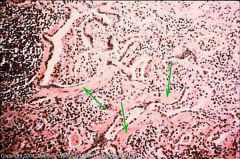
Cow lung
What stage? Why? |
Chronic pneumonia with thickened, collagenous interlobular septa. (fibrous scarring and proliferation caused by the chronic irritation)
|
|
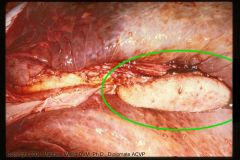
Cow
|
Enlarged lymph node (4-5x normal) from receiving lymph from inflamed lung.
|
|
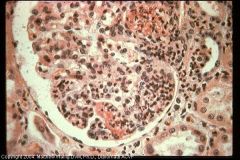
Dog kidney
|
Inflamed glomerulus
|
|
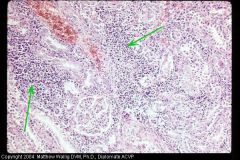
Dog kidney
|
Interstitial nephritis - leukocyte infiltration of the interstitium (lymphos, monos, plasmas) due to leptospira ---> leads to interstitial fibrosis and parenchymal atrophy
|
|
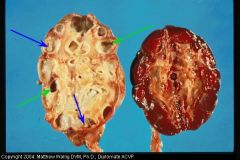
Cow kidney
|
Chronic pyelonephritis -
Thick white fibrous capsules around the dilated calyces (which contain dried pus) |
|
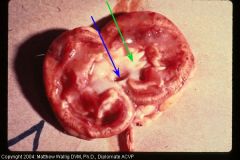
dog kidney
|
Both hydronephrosis (the dilation) and pyelonephritis (the suppurative exudate.
|
|
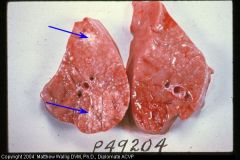
Pig Lung
|
Mycoplasma pneumonia
Bronchioles contain thick mucinous material. |
|
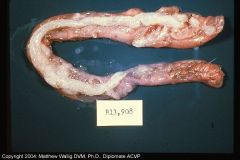
Rabbit Intestine
What sort of exudate? |
Catarrhal Enteritis
Mucous plugs from irritation of mucosa. |
|
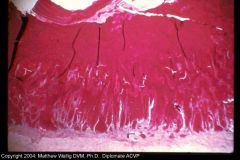
Cow intestine
PAS Stain What is this substance? |
Catarrhal Enteritis
PAS stain showing the polysaccharides in the excessive mucous. Almost the whole mucosa has been converted to mucin producing cells. |
|
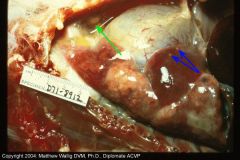
Cat thorax
Characterize exudate |
Serous exudate in chest and pericardial sac due to inflam. of pleura and pericardium.
|
|
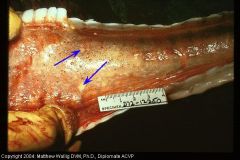
cat intestine
What is this substance on the mucosa? |
Fibrinous enteritis
(fibrinogen has leaked out of vessels due to extensive inflammation and vessel damage) - this is viral |
|
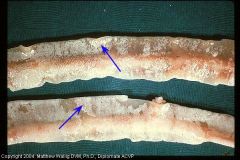
cow trachea
what is this? |
fibrinous tracheitis
caused by bact. inf |
|
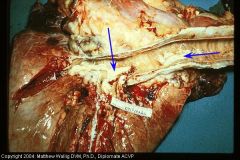
cow resp. tract
|
fibrinous bronchitis
large yellow clots may occlude the bronchi |
|
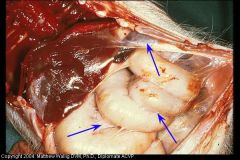
Pig abdomen
What is going on here? |
Fibrinous Peritonitis
Fibrin deposits and adhesions all over viscera. Some is being replaced by fibrous scar tissue ("organized") |
|
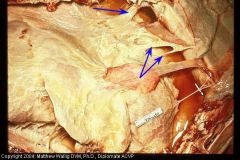
Cow thorax
|
Fibrinous pleuritis
Severe. Parially organized adhesions |
|
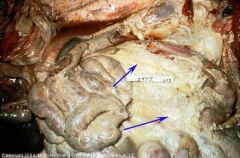
Cow abdomen
|
Fibrinopurulent exudate.
Caused by bact. inf. due to stomach penetration (foreign body) |
|
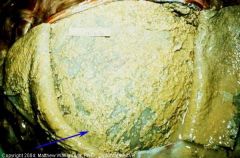
Cow heart
What kind of inflam. and for how long? |
Chronic fibrinopurulent inflam of the epicardium
Due to "hardware disease" |
|
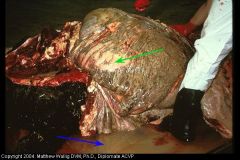
Cow abd. viscera
|
Fibrinopurulent peritonitis
Blue = fluid exudate green = fibrin covering omentum (suppurative) |
|
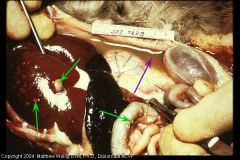
Cat abdomen
|
FIP - fibrinopurulent peritonitis
Moderate suppurative response with fibrinopurulent clumps |
|
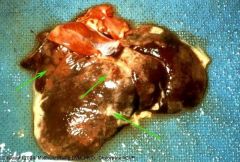
Cat liver
What has caused these changes? |
fibrinous hepatitis
due to FIP |
|
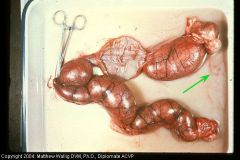
Dog uterus
Characterize exudate |
Severe purulent metritis
pan is filled with pus |
|
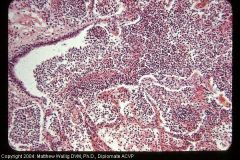
dog lung
|
Consolidation of dog lungs
Purulent bronchopneumonia with alveoli completely filled |
|
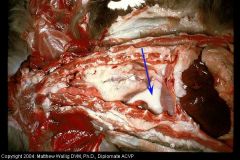
Cat thorax
What kind of exudate/inflam? |
severe suppurative pleuritis
(pyothorax) |
|
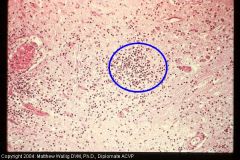
Cow brain
What kind of inflam and what cell mainly? |
Suppurative encephalitis
Micro abscesses Mostly neutrophils |
|
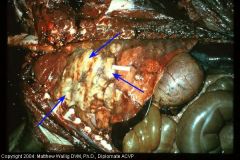
Horse lung
|
Suppurative pneumonia with many large caseous abscesses (encapsulated)
|
|
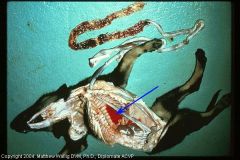
Dog intestine
|
Hemorrhagic enteritis and hemothorax due to severe hook infestation
|
|
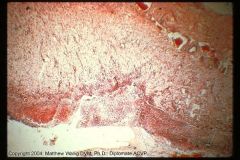
Cow bladder
|
Mucosal epithelium loss and fibrinous sanguinopurulent exudate accumulation.
"The exudate is primarily a combination of necrotic neutrophils, cell debris and red blood cells trapped within a fibrin meshwork." |
|
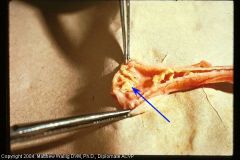
Chicken trachea
What is this change called? |
Tracheal Pseudomembrane
Viral. Necrotic portions of the mucosa are covered and enmeshed in a heavy fibrinous exudate |
|
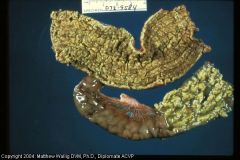
Pig intestine
|
Pseudomembranous (fibrinonecrotic) enteritis.
Caused by salmonella |
|
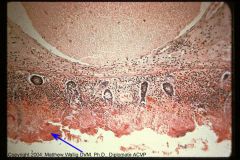
Pig colon (histologic)
|
Pseudomembranous colitis (necrotizing enteritis)
The bottom shows the necrotic layer enmeshed in fibrin from the inflam. response of the underlying living tissue. A lymph vessel is trying to drain away all the fibrin. |
|
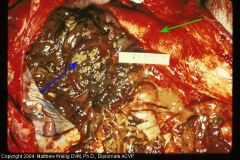
pig colon
What two sorts of change do you see here? |
some pseudomembrane has sloughed off, revealing the ulcerated hemorrhagic mucosa underneath (blue). the other parts of colon are very congested (green)
|
|
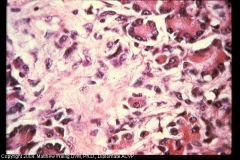
Dog pancreas
What stage of disease is this? |
Chronic pancreatitis
Mature connective tissue has replaced a lot of the parenchyma |
|
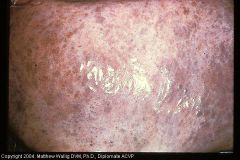
Cow liver
How long? |
Chronic hepatitis
lots of mature connective tissue (scarring) |
|
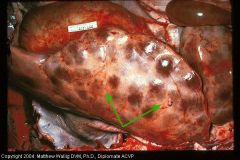
Cow liver
|
extensive loss of parenchyma with fibrous tissue replacement (hepatic fibrosis)
|
|
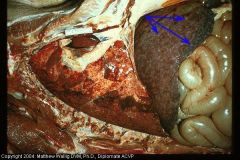
Pig liver (and lungs)
|
Fibrosis of liver due to larval migrans (eosinophilic inflam infiltrated by connective tissue)
Also, multifocal pneumonia with hemorrhage |
|
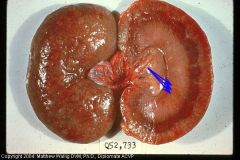
Dog Kidney
How long? Explain outward appearance of the kidney |
Chronic glomerulonephritis
Grey lines of fibrous tissue on cut surface. The uncut surface is pitted and irregular due to contraction of the scar tissue. |
|
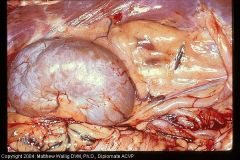
Dog kidney
|
Chronic nephritis due to pyelonephritis
Kidney is pale, irregular, and firm |
|
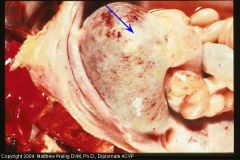
cat abdominal cavity
What happened and what is covering everything? |
Chronic peritonitis
Thick covering of fibrous tissue that has contracted, shrinking the organs |
|
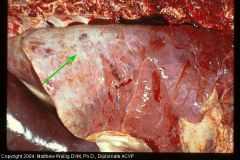
Cow - Fibrotic Lung
What could this lead to? |
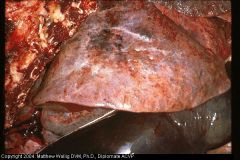
Passive congestion of liver
(beneath lung) |
|
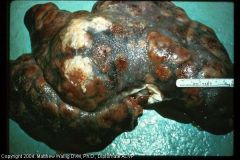
Pig liver
|
Encapsulated abscesses and diffuse fibrosis due to corynebacterium infection.
(pseudotuberculosis) |
|
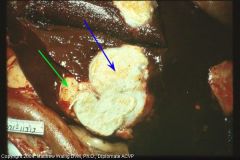
Sheep liver
|
Caseous mass with thick connective tissue capsule
(due to corynebacterium (pseudotuberculosis)) |
|
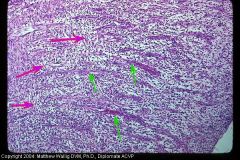
Pony
What kind of tissue is this? (healing) |
granulation tissue
see that fibroblasts (pink) are perpendicular to capillaries (green). Lots of collagen as you get deeper. |
|
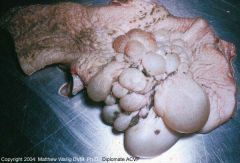
Cow rumen
|
Proliferation of connective tissue in mucosal nodules due to chronic inflammation.
|
|
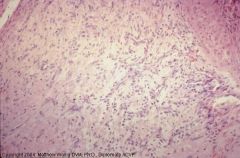
Pony
|
Deep granulation tissue
Perpendicular orientation of fibroblasts and capillaries no longer apparent. Not very cellular with a lot of collagen. |

