![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
29 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What are non wage benefits |
Supplementary Labor income - things like benefits - non wage benefits received by the EE |
|
|
What are real wages |
The quantity of goods and services that can be bought with the nominal wage Real Wage Rate = the rate of change of nominal wage - the inflation rate |
|
|
What is Functional Income Distribution |
The share of the National Income going to the owners of the factors of production. Labor & Capital |
|
|
What is the Real average labour income |
This is the total annual labour income --adjusted for inflation -- divided by average annual number of paid workers -money they earn which is made up of wages and benefits |
|
|
Two Ways to Calculate Wages |
Time Wages (time spent on job) Production/ output wages (based on piece rate) |
|
|
What happens when real wages rise? |
-if the money is worth more this year then last you can walk away with more stuff - or substitute for name brands |
|
|
What accounts for the difference between nominal wage (5 bucks, 5 bucks) and real wage (buying power) changes? |
The increase or decrease in the price level. Example - pizza $5 buying power If difference between nominal & real wage is due to price increase you have inflation. |
|
|
How to calculate the labour cost per unit of output |
Labour cost per = Wage Rate unit of output ------------------- Labour Produtivity OR Output per worker SAME AS STANDARD PIECE RATE |
|
|
What are average weekly earnings ? |
Average weekly earnings = Average weekly hourly wages X Average usual number of weekly hours worked |
|
|
Compare Average hourly wages vs. Average weekly earnings |
Average Hourly is more reliable indicator -based on average hourly rate |
|
|
What is hours polarization? |
Change in the average workweek as a standard & it means that more people are working either more OR less than the number of hours in the standard work week. |
|
|
What is a normal good? |
a good for which demand increases as ones income increases. |
|
|
What is the substitution effect (supply) |
The situation where leisure & work hours are substituted for each other as wage rate changes 1. Substitution effect (positive impact): makes person want to work more hours bc price of leisure time made more expensive due to opportunity & cost 2. The Income Effect (negative) stimulates the person to work fewer hours & buy more leisure |
|
|
Backward Bending Supply Curve for Labour |
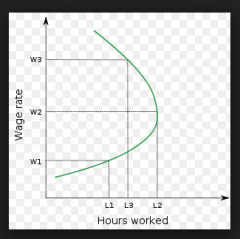
|
|
|
What is RWR? |
Reservation Wage Rate: The lowest wage rate that a person is willing to work for |
|
|
What is Economic Rent? |
The wage rate received in excess of the RWR. Ex. Your RWR is 10 - you find a job for 12 your economic rent is 2 Can be a negative number. |
|
|
The total Supply of labour |
Total supply of labour depends on: 1. the Labour force Participation Rate 2. The number of hours people are willing to work |
|
|
What is a demo grant? |
The term describes a lump sum payment to an individual based on membership in a particular demographic group |
|
|
What is the opportunity cost of work? |
Price of leisure is the wage rate for labour. or opportunity cost of not working. The opportunity cost of work is the amount of time for leisure. |
|
|
What is Human Capital? |
Term to describe Human resources when they're considered in terms of their contributions to the economy such as education, training, skills, etc. |
|
|
Marginal Revenue |
The extra revenue of selling one more unit of output |
|
|
The Scale Effect |
The change in the number of employees hired as a result of changes in the amount of product sold. Decreasing Scale Effect = diminishing returns |
|
|
Diminishing Returns |
When addition of one more worker effects productivity. One in none out nokay. Happens only in the short run. |
|
|
Formula for Marginal Revenue Product |
MRP = MR (Marginal revenue) X MPL (Marginal productivity of labour) |
|
|
Why does the demand curve for labour have a negative slope? The Scale Effect & The Substitution Effect (demand) |
SE (demand) Changes in the wage rate encourages firms to substitute capital for labour & labour for capital. Scaling back example - Ralph polo workers wage increase = increase in product price = less people buying shirt = scaling back number of workers |
|
|
What Makes labour elastic & inelastic? |
When there is no substitute for labour the demand is inelastic. When there are substitutes for labour the demand is elastic. |
|
|
Wage Rate Elasticity & Necessities |
If demand for product is elastic then consumers will respond to price increase by decreasing the quantity demanded. Necessities have inelastic demands |
|
|
Free trade elasticuty for demand for labour |
The freer the trade the more elastic the wage elasticity of demand for canadian workers and products becomes |
|
|
Quasi fixed labour costs. |
The non-wage costs of hiring workers that aren't related to the workers hours. The more the amount of production output is to be produced the more workers needed. Example hojo - job fair |

