![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
190 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)

What muscle is this? What is it’s function? |

The Buccinator. It compresses the cheeks. |
|
|

What muscle is this? What is it’s function? |

The Orbicularis Oris. It purses the lips. |
|
|

What muscle is this? What is it’s function? |
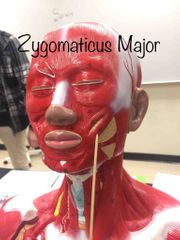
Zygomaticus major. It raises the corners of the mouth. |
|
|

What muscle is this? What is it’s action? |
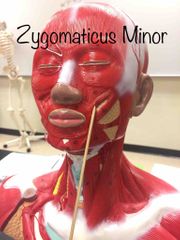
Zygomaticus minor. It raises the corners of the mouth. |
|
|

What muscle is this? What is it’s action? |
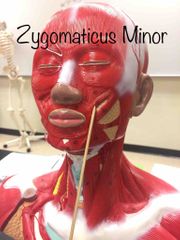
Zygomaticus minor. It raises the corners of the mouth. |
|
|

What is this muscle? What is it’s action? |
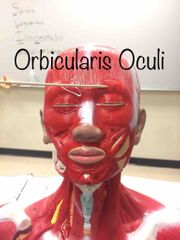
Orbicularis Oculi. It closes the eye. |
|
|

What is this muscle? What if it’s action? |
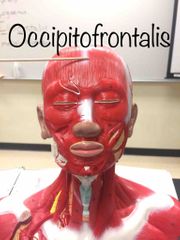
Occipitofrontalis. (Or, Epicranium.) It raises the eyebrows. |
|
|
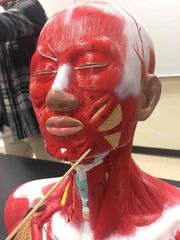
What muscle is this? What is it’s function? |

Depressor Anguli Oris. It depresses the corner of the mouth. |
|
|

What muscle is this? What is it’s function? |

Depressor Anguli Oris. It depresses the corner of the mouth. |
|
|
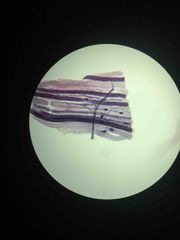
What viewed on this slide? |
The neuromuscular junction. (Or, myoneural junction.) |
|
|

What is this muscle? What is it’s action? |

Masseter. Elevated the mandible. |
|
|

What is this muscle? What is it’s action? |

Temporalis. It elevates the mandible. |
|
|

What is this muscle? What is it’s action? |

Medial pterygoid. Helps with lateral excursion & closes the jaw. |
|
|

What is this muscle? What is it’s action? |

Lateral pterygoid. Helps with lateral excursion & opens the jaw. |
|
|

What is this muscle? What is it’s function? |

Sternocleidomastoid. Neck flexion- lateral flexion, rotation away. |
|
|

What is this muscle? What is it’s action? |

Diaphragm. It moves inferiorly, allowing for more area for the lungs to expand. |
|
|

What is this muscle? What is it’s action? |

Digastric. Depresses the mandible & elevates the larynx. |
|
|

What is this muscle? What is it’s action? |

Mylohyoid. Depresses the mandible & raises (elevates) the floor of the mouth and hyoid bone. |
|
|

What muscle is this? What is it’s action? |

Anterior Scalenes. Neck flexion, lateral flexion, elevate first 3 ribs. |
|
|

What muscle is this? What is it’s action? |

Middle Scalenes. Neck flexion, lateral flexion, & elevates the first 3 ribs. |
|
|

What muscle is this? What is it’s function? |
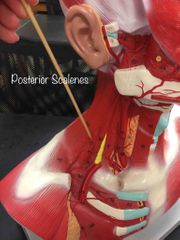
Posterior Scalenes. Neck flexion, lateral flexion, & elevates the first 3 ribs. |
|
|
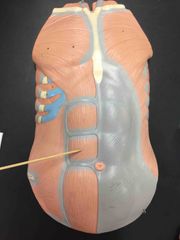
What muscle is this? What is it’s action? |

Rectus Abdominis. Trunk flexion, depresses the ribs, & compresses the abdomen. |
|
|

What is this muscle? What is it’s action? |

Internal oblique. Laterally flexing the trunk, & rotating the trunk. |
|
|
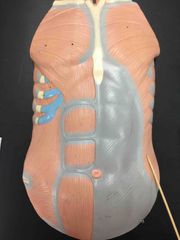
What muscle it is? What is it’s function? |

External oblique. Laterally flexes the trunk, rotates the trunk. |
|
|

What muscle is this? What is it’s action? |

Transverse Abdominis. Compresses the abdomen. |
|
|

What muscle is this? What is it’s action? |

Internal intercostals. Forceful exhalation, compresses the ribs. |
|
|

What muscle is this? What is it’s action? |
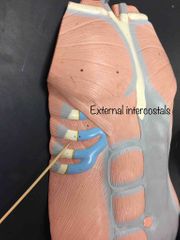
External intercostals. Elevates the ribs. |
|
|

What muscle is this? What is it’s action? |

Levator scapulae. It elevates the scapula. |
|
|

What muscle is this? What is it’s action? |

Pectoralis Minor. It depresses and protracted the scapula. |
|
|

What muscle is this? What is it’s action? |

Rhomboid Minor. Adducts the shoulders. |
|
|
|
Define “synarthrosis.” |
An immovable joint. |
|
|
|
What is abduction? |
Movement of a limb away from the midline of the body. |
|
|
|
____________ are synarthrotic joints consisting of bones joined by short, connective tissue fibers. |
Fibrous joints. |
|
|
|
A ____________ type of synovial joint allows motion in one plane only. |
Hinge. |
|
|
|
The motion called _________ involves rotating the radius around the ulna so that the palm faces posteriorly. |
Probation. |
|
|

What type of motion is this? |
Extension. |
|
|

What type of motion is this? |
Extension. |
|
|

What type of motion is this? |
Flexion. |
|
|

What type of motion is this? |
Flexion. |
|
|

What type of motion is this? |
Rotation. |
|
|

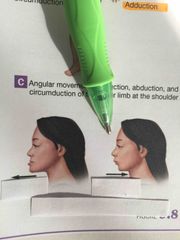
What type of motion is this? |
Circumduction. |
|
|

What type of motion is this? |
Abduction. |
|
|

What type of motion is this? |
Adduction. |
|
|

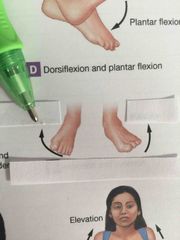
What type of motion is this? |
Dorsiflexion. |
|
|

What type of motion is this? |
Plantar flexion. |
|
|

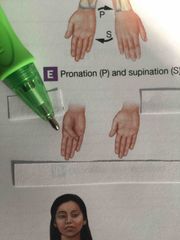
What is this motion? |
Supination. |
|
|

What is this motion? |
Pronation. |
|
|
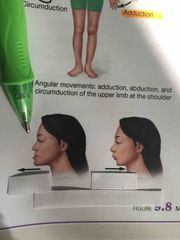
What is this motion? |
Protraction. |
|
|
What is this motion? |
Retraction. |
|
|
What is this motion? |
Inversion. |
|
|

What is this version? |
Eversion. |
|
|
What is this movement? |
Opposition. |
|
|

What is this motion? |
Reposition. |
|
|

What is this motion? |
Elevation. |
|
|

What is this motion? |
Depression. |
|
|
|
Define “pronation.” |
Rotating the radius around the ulna so that the Palms face posteriorly. |
|
|
|
_______________ is the plasma membrane of a skeletal muscle fiber. |
Sarcolemma. |
|
|
|
______________ is a group of muscle fibers surrounded by the perimysium. |
Fascicle. |
|
|
|
___________ could be defined as a rapid series of changes in the membrane potential of the muscle fiber sarcolemma. |
Action potential. |
|
|
|
_________ is a connective tissue sheath that covers a whole muscle. |
Epimysium. |
|
|
|
A(n) ______________ is a myofilament composed of the contractile protein myosin. |
Thick filament. |
|
|
|
Define “insertion.” |
The movable attachment of a muscle. |
|
|
|
Define “origin.” |
Attachment of a muscle that generally remains fixed during muscular contraction. |
|
|

What muscle is this? What is it’s action? |

Rhomboid Major. Adducts the shoulders. |
|
|

What muscle is this? What is it’s action? |

Trapezius. It elevates the clavicle, extends the neck, and elevates/depresses/retracts/rotates the scapula. |
|
|

What muscle is this? What is it’s action? |

Deltoid. It’s action is; shoulder abduction AFTER 15 degrees. |
|
|

What muscle is this? What is it’s action? |
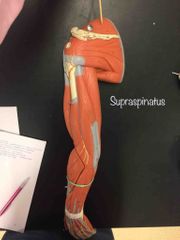
Supraspinatus. It is responsible for the first 15 degrees of shoulder abduction. |
|
|

What synovial joint is this? |

Temporomandibular. |
|
|

What synovial joint occurs here? |

Atlanto-occipital. |
|
|

What synovial joint is this? |

Atlanto-axial. |
|
|

What synovial joint is this? |

Sternoclavicular. |
|
|
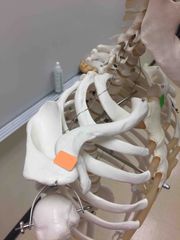
What synovial joint is this? |

Acromioclavicular. |
|
|
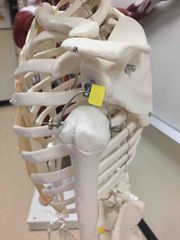
What synovial joint is this? |

Glenohumeral. |
|
|

What synovial joint is this? |

Humeroulnar. |
|
|

What synovial joint is this? |

Humeroradial. |
|
|

What synovial joint is this? |
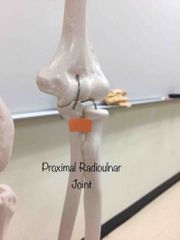
Proximal Radioulnar. |
|
|

What synovial joint is this? |

Distal Radioulnar. |
|
|

What synovial joint is this? |

Distal Radioulnar. |
|
|

What synovial joint is this? |

Radiocarpal. |
|
|

What synovial joint is this? |

Carpometacarpal. |
|
|

What synovial joint is this? |

Metacarpophalangeal. |
|
|

What synovial joint is this? |

Intervertebral. |
|
|

What synovial joint is this? |
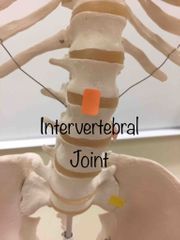
Intervertebral. |
|
|

What synovial joint is this? |

Sacroiliac. |
|
|

What synovial joint is this? |

Iliofemoral. |
|
|

What synovial joint is this? |
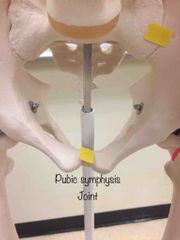
Pubic symphysis. |
|
|
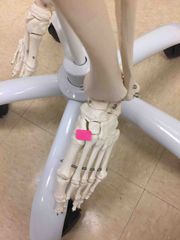
What synovial joint is this? |

Tarsometatarsal. |
|
|

What synovial joint is this? |
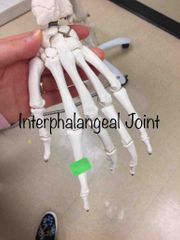
Interphalangeal. |
|
|

What synovial joint is this? |

Interphalangeal. |
|
|

What synovial joint is this? |

Interphalangeal. |
|
|

What part of the synovial tibiofemoral joint is this? |

The patellar ligament. |
|
|

What part of the synovial tibiofemoral joint is this? |

The tibial collateral ligament. |
|
|
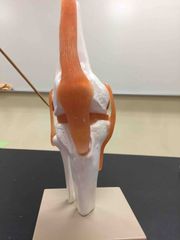
What part of the synovial tibiofemoral joint is this? |

The fibular collateral ligament. |
|
|

What part of the synovial tibiofemoral joint is this? |
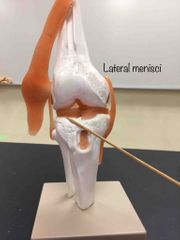
The lateral menisci. |
|
|

What part of the synovial tibiofemoral joint is this? |

The medial menisci. |
|
|
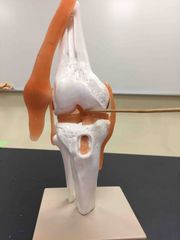
What part of the synovial tibiofemoral joint is this? |

The anterior cruciate ligament. |
|
|

What part of the synovial tibiofemoral joint is this? |

Posterior cruciate ligament. |
|
|

What is “A” pointing to? What is the structure AND what is the connective tissue covering of that structure called? (Spell the CT covering.) |

It is a muscle (as a whole) and it is covered by epimysium. |
|
|
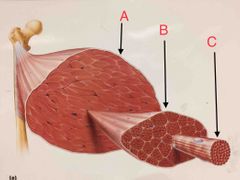
What is “B” pointing to? What is the structure AND what is the connective tissue covering of that structure called? (Spell the CT covering.) |

A muscle FASCICLE. Muscle fascicles are wrapped in Perimysium. |
|
|

What is “C” pointing to? What is the structure AND what is the connective tissue covering of that structure called? (Spell the CT covering.) |

A muscle FIBER. Muscle fibers are wrapped in Endomysium. |
|
|

What is this structure? |

Myofibrils. |
It is what muscle fibers are composed of! |
|

What structure is this? |

Myofibrils. |
What are muscle fibers composed of? |
|

What structure is being pointed to? |

Transverse tubules. |
|
|

What structure is being pointed to? |

The terminal cisterna. |
|
|

What structure is being pointed to? |
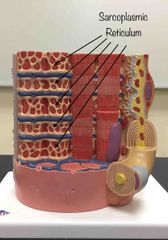
Sarcoplasmic reticulum. |
|
|

What structure is being pointed to? |

Sarcoplasmic reticulum. |
|
|

What structure is being pointed to? |
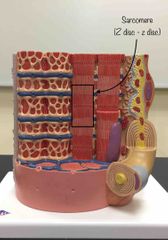
The sarcomere. |
|
|

What structure is being pointed to? |

Sarcoplasmic reticulum. |
|
|
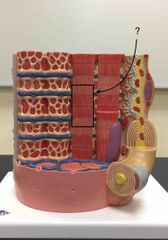
What structure is being pointed to? |

The sarcomere. |
|
|
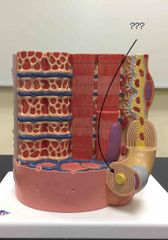
What structure is being pointed to? |

An axon. |
|
|

What structure is being pointed to? |

Sarcoplasmic reticulum. |
|
|
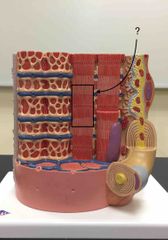
What structure is being pointed to? |

The sarcomere. |
|
|
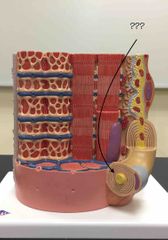
What structure is being pointed to? |

An axon. |
|
|

What structure is being pointed to? |

Endomysium. |
|
|

What structure is being pointed to? |

Sarcoplasmic reticulum. |
|
|
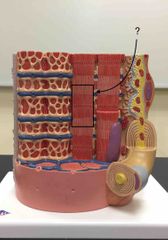
What structure is being pointed to? |
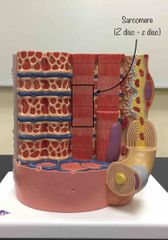
The sarcomere. |
|
|

What structure is being pointed to? |

An axon. |
|
|

What structure is being pointed to? |

Endomysium. |
|
|

What structure is being pointed to? |

Sarcoplasm. |
|
|

What structure is being pointed to? |

Sarcoplasm. |
|
|

What structure is being pointed to? |

Mitochondria. |
|
|

What structure is being pointed to? |

The sarcolemma. |
|
|

What structure is being pointed to? |

A myosin myofilament. |
|
|

What structure is being pointed to? |

An actin myofilament. |
|
|
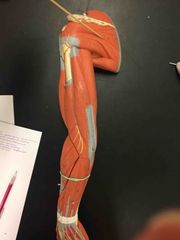
What muscle is this? What is it’s action? |

Infraspinatus. It’s action- lateral rotation of the shoulder. |
|
|

What muscle is this? What is it’s action? |

Infraspinatus. It’s action- lateral rotation of the shoulder. |
|
|
|
What are the four rotator muscles? |
Supraspinatus, infraspinatus, subscapularis, teres Minor. |
|
|

What muscle is this? What is it’s action? |

Subscapularis. It’s action- medial/internal rotation. |
|
|

What muscle is this? What is it’s action? |

Teres MINOR. It’s action- lateral rotation of the shoulder. |
|
|
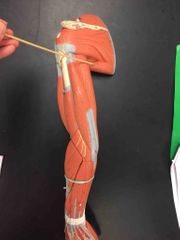
What muscle is this? What is it’s action? |

Teres MAJOR. It’s action- extension, adduction, and medial rotation. |
|
|

What muscle is this? What is it’s action? |

Coracobrachialis. It flexes and adducts the shoulder. |
|
|
What muscle is this? What is it’s action? |

Pectoralis Major. It’s action- flexion, adduction, and medial rotation. |
|
|
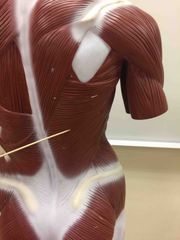
What muscle is this? What is it’s action? |

Latissimus Dorsi. It’s action- extension, adduction, and medial rotation. |
|
|

What muscle is this? What is it’s action? |

Latissimus Dorsi. It’s action- extension, adduction, and medial rotation. |
|
|

What muscle is this? What is it’s action? |
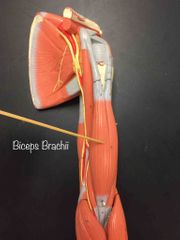
Biceps Brachii. It flexes the shoulder and elbow, it supinates the forearm. |
|
|
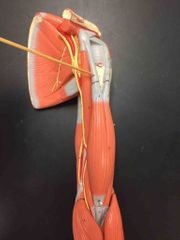
What muscle is this? What is it’s action? |
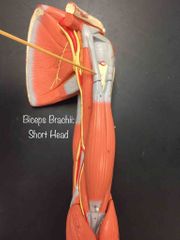
This is the Short Head of Biceps Brachii. It helps flex the shoulder and elbow, it also helps supinate the forearm. |
|
|
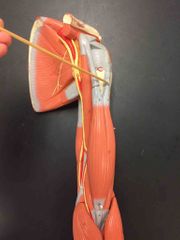
What muscle is this? What is it’s action? |

This is the Long Head of Biceps Brachii. It helps flex the shoulder and elbow, it also helps supinate the forearm. |
|
|

What muscle is this? What is it’s action? |

This is the Lateral Head of Triceps Brachii. It’s action is elbow extension. |
|
|

What muscle is this? What is it’s action? |

This is the Long Head of Triceps Brachii. It’s action is elbow extension. |
|
|

What muscle is this? What is it’s action? |
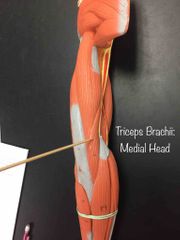
This is the Medial Head of Triceps Brachii. It’s action is elbow extension. |
|
|

What muscle is this? What is it’s action? |
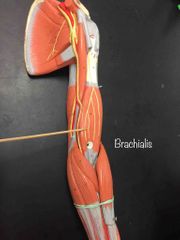
Brachialis. It is the prime mover of elbow flexion. |
|
|

What muscle is this? What is it’s action? |
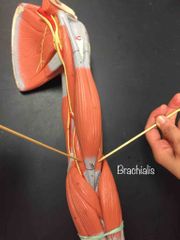
It is Brachialis. It is the prime mover of elbow flexion. |
|
|

What muscle is this? What is it’s action? |
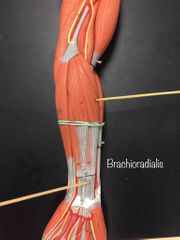
Brachioradialis. It flexes the elbow when the forearm is midway into formation. |
|
|

What muscle is this? What is it’s action? |
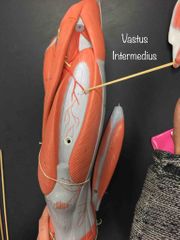
Vastus intermedius. It extends the knee. |
|
|
|
What four muscles are apart of the quadriceps femorus group? |
Rectus femoris, vastus lateralis, vastus intermedius, and vastus medialis. |
|
|
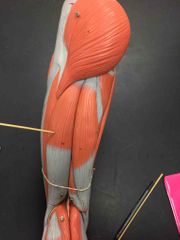
What muscle is this? What is it’s action? |

Biceps femoris. It extends and laterally rotates the hip, it also flexes the knee. |
|
|
|
What three muscles are apart of the hamstrings group? |
Biceps femoris, semitendinosus, and semimembranosus. |
|
|

What muscle is this? What is it’s action? |
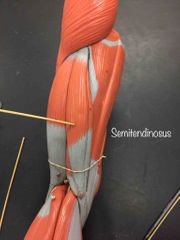
Semitendinosus. It flexes the knee. |
|
|

What muscle is this? What is it’s action? |

Semimembranosus. It flexes the knee. |
|
|
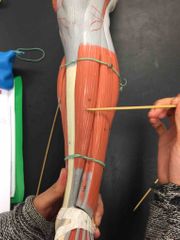
What muscle is this? What is it’s action? |
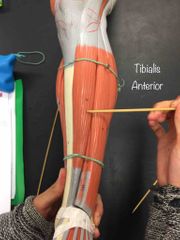
Tibialis Anterior. It causes dorsiflexion and inversion of the foot at the ankle. |
|
|

What muscle is this? What is it’s action? |

Tibialis posterior. It adducts, inverts, and plantar flexes the foot at the ankle. |
|
|

What muscle is this? What is it’s action? |
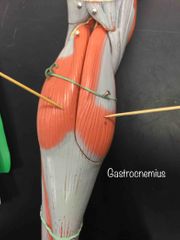
Gastrocnemius. It flexes the knee, and plantar flexion of the foot at the ankle. |
|
|
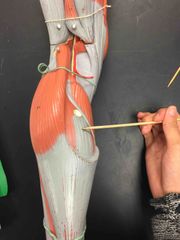
What muscle is this? What is it’s action? |
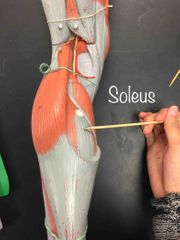
Soleus. It’s action- plantar flexion (only!) of the foot at the ankle. |
|
|

What muscle is this? What is it’s action? |

Extensor digitorum Longus. It’s action- it extends toes 2-5. |
|
|

What muscle is this? What is it’s action? |
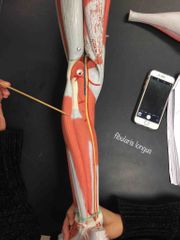
Fibularis Longus. It’s action- evertion and plantar flexion of the foot at the ankle. |
|
|
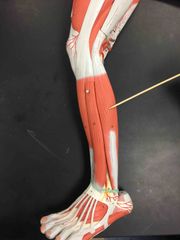
What muscle is this? What is it’s action? |

Fibularis Longus. It’s action- eversion and plantar flexion of the foot at the ankle. |
|
|
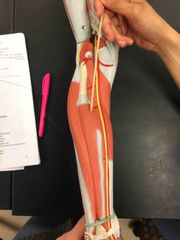
What muscle is this? What is it’s action? |

Flexor Hallucis Longus. It’s action- it flexes the big toe. |
|
|

What muscle is this? What is it’s action? |

Flexor digitorum Longus. It’s action- it flexes toes 2-5. |
|
|

What muscle is this? What is it’s action? |

Pronator Teres. It pronates the forearm. |
|
|

What muscle is this? What is it’s action? |

Supinator. It supinates the forearm. |
|
|

What muscle is this? What is it’s action? |
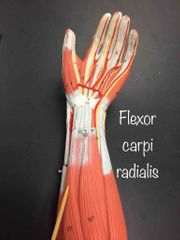
Flexor carpi radialis. It flexes the wrist and abducts the wrist. |
|
|
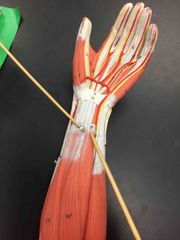
What muscle is this? What is it’s action? |

Flexor digitorum superficialis. Flexor digitorum superficialis flexes the wrist, flexes the metacarpalphalangeal joints, & flexes the proximal interphalangeal joints. |
|
|
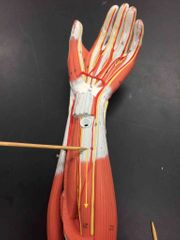
What muscle is this? What is it’s action? |

Flexor digitorum profundus. Flexor digitorum profundus flexes the distal phalangeal joints. |
|
|

What muscle is this? What is it’s action? |

Flexor carpi ulnaris. Flexor carpi ulnaris flexes the wrist, and adducts the wrist. |
|
|

What muscle is this? What is it’s action? |

Palmaris Longus. Palmaris Longus flexes the wrist. |
|
|

What muscle is this? What is it’s action? |

Flexor pollicis Longus. Flexor pollicis Longus flexes the Thumb. |
|
|
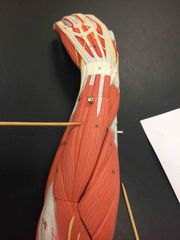
What muscle is this? What is it’s action? |
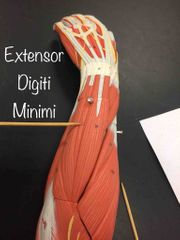
Extensor digiti minimi. Extensor digiti minimi extends the pinky. |
|
|

What muscle is this? What is it’s action? |
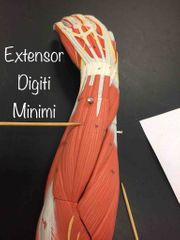
Extensor digiti minimi. Extensor digiti minimi extends the pinky. |
|
|

What muscle is this? What is it’s action? |

Extensor pollicis Longus. Extensor pollicis Longus extends the Thumb. |
|
|

What muscle is this? What is it’s action? |

Abductor pollicis Longus. Abductor pollicis Longus abducts the Thumb. |
|
|
|
What muscle is this? What is it’s action? |
Extensor carpi radialis Longus. Extensor carpi radialis Longus extends and abducts the wrist. |
|
|
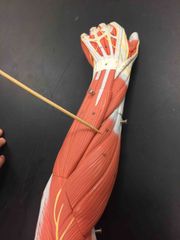
What muscle is this? What is it’s action? |

Extensor carpi radialis brevis. Extensor carpi radialis brevis extends and abducts the wrist. |
|
|

What muscle is this? What is it’s action? |

Extensor carpi ulnaris. Extensor carpi ulnaris extends and adducts. |
|
|

What muscle is this? What is it’s action? |

Extensor digitorum. Extensor digitorum extends digits 2-5. |
|
|

What muscle is this? What is it’s action? |

Gluteus Maximus. It’s action- extension and lateral rotation. |
|
|
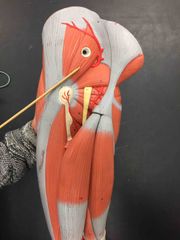
What muscle is this? What is it’s action? |

Gluteus medius. It’s action- abduction and medial rotation. |
|
|
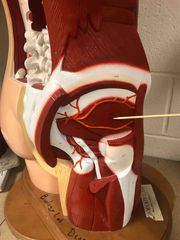
What muscle is this? What is it’s action? |
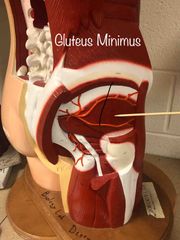
Gluteus Minimus. It’s action- abduction and medial rotation. |
|
|

What muscle is this? What is it’s action? |

Tensor Fasciae Latae. It’s action- it flexes the hip medically rotates the hip, and stabilizes the knee laterally when walking. |
|
|

What muscle is this? What is it’s action? |

Piriformis. It’s action- it abducts and laterally rotates the hip. |
|
|
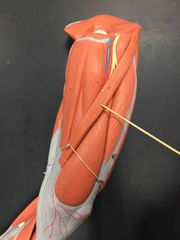
What muscle is this? What is it’s action? |
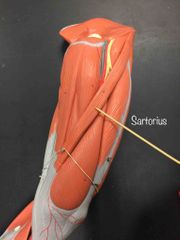
Sartorius. It’s action- it flexes the hip and knee, laterally rotates the hip. |
|
|

What muscle is this? What is it’s action? |

Adductor magnus. It’s action- flexion, adduction, and medially rotates. |
|
|

What muscle is this? What is it’s action? |

Adductor Longus. It’s action- flexion, adduction, and medial rotation. |
|
|

What muscle is this? What is it’s action? |

Gracilis. It’s action- adducts and medially rotates, flexes the knee. |
|
|
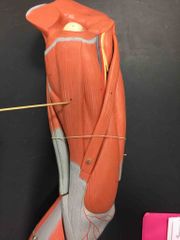
What muscle is this? What is it’s action? |

Gracilis. It’s action- adducts and medially rotates, flexes the knee. |
|
|

What muscle is this? What is it’s action? |

Iliopsoas. It’s action- it flexes the hip and lumbar spine. Composed of the Iliacus and Psoas Major. |
|
|

What muscle is this? What is it’s action? |
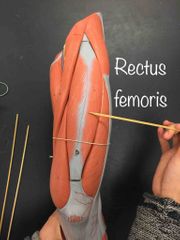
Rectus femoris. It’s action- flexes the hip and extends the knee. |
|
|

What muscle is this? What is it’s action? |
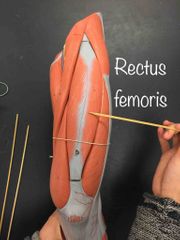
Rectus femoris. It’s action- flexes the hip and extends the knee. |
|
|

What muscle is this? What is it’s action? |

Vastus lateralis. It’s action- it extends the knee. |
|
|

What muscle is this? What is it’s action? |
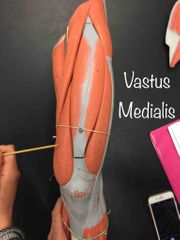
Vastus medialis. It’s action- it extends the knee. |
|
|
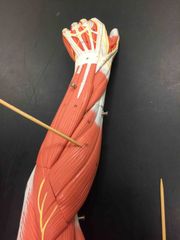
What muscle is this? What is it’s action? |
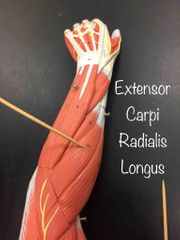
Extensor carpi radialis Longus. It’s action- it extends and abducts the wrist. |
|

