![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
39 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Class A Fire Extinguisher |
Combustibles |
|
|
Class B Fire Extinguisher |
Flammable material |
|
|
Class C Fire Extinguishers |
Electrical Fire |
|
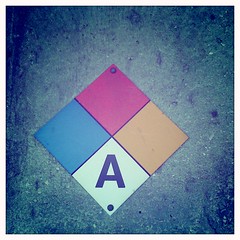
|
Red-Flammable Blue-Health Hazard Yellow-Reactivity White-Other 0-4 Risk |
|
|
Decontamination |
removal of contaminating material |
|
|
Disinfection |
elimination of pathogens |
|
|
Sterilization |
Destruction of pathogens through heat |
|
|
Responsibilities of a Safety Officer |
Orientation and training with staff Making sure labs are in compliance with existing regulations |
|
|
The 'Right to Know' Act |
Gives people information about hazardous chemicals with labels and MSDS sheets |
|
|
TLV |
Threshold Limit Values: limit of exposure to a chemical substance that a worker can be exposed to on a daily basis |
|
|
PEL |
Permissible exposure limits: regulations by OSHA on limited exposure to a chemical |
|
|
Main Classifications of Hazards in the Workplace |
Chemical Hazards Electrical Hazards Fire Hazards Glassware Hazards Infectious Waste |
|
|
SDS |
Safety Data Sheet: under the Right to Know act, provides information about hazardous chemicals |
|
|
Workplace controls |
Procedures and Rules carried out by workers |
|
|
Engineering controls |
Mechanical safety: self sheathing needles |
|
|
Blood-borne pathogen |
bacteria present in the blood |
|
|
Teratogen |
disturbs rapidly growing cells/development of embryo/fetus/Ex. Chemo |
|
|
Sensitizer |
causes allergic reaction |
|
|
Water Reactive |
reacts to water, may be explosive |
|
|
Exposure Control Plan |
identifies tasks and procedures as well as job classifications where exposure to blood occurs |
|
|
Occupational Exposure to Bloodborne Pathogens Standard |
OSHA's standards on working with infectious materials |
|
|
Scope of the Hazard Communication Standard |
working with chemicals |
|
|
Labeling requirements for purchased chemicals always in use |
Name Concentration Expiration Safety Storage |
|
|
labeling requirements for purchased chemicals in use for only 24 hours |
Name, date prepared, concentration |
|
|
labeling requirements for chemical solutions prepared in the lab |
Name Concentration Date Prepared Expiration Who made it Storage How it can hurt you |
|
|
Standard Precautions |
Treat everybody as infectious Personal Protective Equipment |
|
|
Hepatitis B |
Virus; Vaccine Available Can get from: Needle sticks, unprotected sex, and blood products |
|
|
Hepatitis C |
Virus; no vaccine Can get from: Needle sticks, unprotected sex, and blood products |
|
|
HIV |
Virus; no vaccine Can get from: needle sticks, unprotected sex, and blood products |
|
|
Tuberculosis |
Bacteria Airborne |
|
|
Flashpoint |
minimum temperature at which a liquid gives off a vapor that ignites with oxygen in the room |
|
|
Flammable Gas |
gas at room temperature that reacts with air and forms a flammable mixture |
|
|
Flammable Liquid |
any liquid with a flashpoint below 100 F |
|
|
Explosive |
chemical causes a sudden release of pressure, gas, and heat when exposed to a sudden shock, pressure, or high temp. |
|
|
Oxidizer |
chemical other than a blasting agent or explosive |
|
|
Proper containers for disposal of biohazards |
Sharps: puncture and leak proof, close able container Biobag: leak proof and close able |
|
|
OSHA's definition of a sharp |
contaminated object that can puncture the skin |
|
|
Contaminated |
exposure to microbes/dangerous substances |
|
|
parental |
other than mouth, sticking a needle into your body |

