![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
80 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
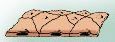
What type of tissue is this an example of?
|
Squamous
|
|
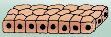
What type of tissue is this example?
|
Simple Cuboidal
|
|
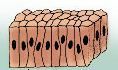
What type of tissue is this?
|
Simple Columnar
|
|

What tissue is this?
|
Transitional
|
|
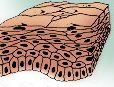
What tissue is this?
|
Stratified Squamous
|
|
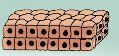
What tissue is this?
|
Stratified Cuboidal
|
|
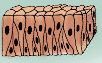
What tissue is this?
|
Pseudostratified columnar
|
|
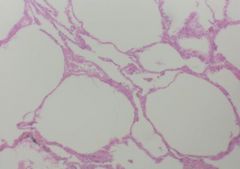
What is this?
|
Lung - Simple Squamouns
|
|
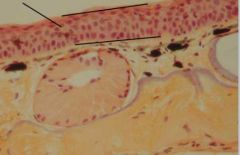
What is this?
|
Frog Skin - Stratified Squamous
|
|
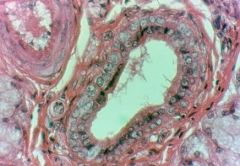
What is this?
|
Salivary Gland - Stratified Cuboidal
|
|
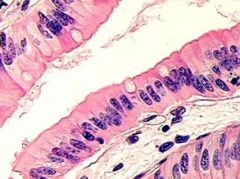
What is this?
|
Small Intestine - Simple Columnar
|
|

What is this?
|
Areolar Connective Tissue
|
|
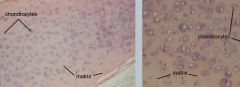
What is this?
|
Hyaline Cartilage Tissue
|
|

What is this?
|
Bone
|
|

What is this?
|
Skeletal muscle
|
|
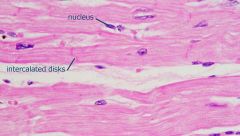
What is this?
|
Cardiac muscle
|
|
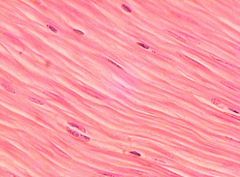
What is this?
|
Smooth muscle
|
|
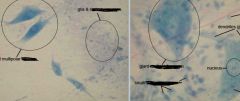
What is this?
|
Nervous Tissue - Neurons
|
|
|
Squamous, cuboidal and columnar are all examples of what?
|
Epithelial Tissues
|
|
|
Areolar, Hyaline and Bone are all examples of what?
|
Connective tissues
|
|
|
Skeletal, cardiac and smooth are all examples of what?
|
Muscle tissues
|
|
|
Cranial ?
Oral ? Thoracic ? Abdominal ? |
Head
Mouth Chest Stomach |
|
|
The digestive system includes...?
|
Mouth, oral cavity, esophagus, stomach, small intestine, large intestine, rectum.
Accessory organs are gall blader, liver and pancreas |
|
|
The oral cavity includes the...?
|
Hard palate, soft palate, pharynx and epiglottis
|
|
|
Function of each organ
Liver ? Gall Bladder ? Spleen ? Stomach ? Esophagus ? Small Intestine? |
Liver: Storage and synthesis, produces bile
Gall bladder: Stores bile Spleen: Destroys, recycles and synthesizes red blood cells Stomach: Mixes nutrients with gastric juices to start digestion Esophagus: connected to stomach Small intestine: final digestion and absorbtion |
|
|
The kidney, ureters, urinary bladder, urethra, penis and vagina make up what?
|
Urogenital system (urinary system)
|
|
|
Function of the kidney?
|
To filter waste from the blood
|
|
|
Function of ureters?
|
Urine exits the kidneys through these tubes
|
|
|
Function of the urethra?
|
Urine exits the bladder through this tube which ends at the urogenital opening
|
|
|
Female pelvic cavity includes...?
|
Ovaries, uterine horns, uterus, vagina
|
|
|
Male pelvic cavity includes...?
|
Scrotal sac, testes, epididymis (where sperm is stored), vas defrens (carries sperm FROM testes), penis
|
|
|
The thymus, thyroid, testes, ovaries and pancreas are part of what system?
|
Endocrine system (long distance chemical signaling - hormones
|
|
|
The thymus gland and thyroid are located where in the body?
|
The neck region
|
|
|
The muscles involved in breathing are...?
|
Diaphragm, intercostals (muscles between the ribs), lungs, trachea, bronchi, bronchioles, alveoli, larynx, epiglottis
|
|
|
What are the upper chambers of the heart called?
|
atria
|
|
|
What are the lower chambers of the heart called?
|
ventricles
|
|
|
What do the ventricles do?
|
Pump blood OUT OF the heart
|
|
|
What does the atria do?
|
Recieves the blood into the heart
|
|
|
What does the pulmonary trunk do?
|
Takes blood from the right ventricle to each lung (after it recieves oxygen, it is carried back to the left atrium)
|
|
|
What is the anterior vena cava?
|
It enters the right atrium. This vein brings deoxygenated blood to the right atrium.
|
|
|
What is the aorta?
|
A major artery that exits the left ventricle and takes oxygenated blood to the rest of the body. It is the largest artery in the body
|
|
|
What is the largest vein in the body?
|
Vena cava
|
|
|
What is the purpose of the right and left jugular veins?
|
Carry deoxygenated blood AWAY from the head and neck
|
|
|
What organ contains the vocal cords?
|
Larynx
|
|
|
What does they thymus gland do?
|
Its the site of white blood cell maturation
|
|
|
What is another term for large intestine. What is its function?
|
Colon: absorbtion of water, sythesis of vitamins and the collection of waste (feces)
|
|
|
What is the purpose of heat shocking bacteria?
|
Neutralized negative charge on DNA. Plasmids are then more easily foced into the bacteria. Makes plasma membrane more fluid
|
|
|
What does HIC stand for and what is it?
|
Hydrophobic Interaction Column (Chromatography): We use this to purify proteins from transformed bacteria. It separates proteins based on their ability to bind to specific chemical groups
|
|
|
What is the pathway to make a bacteria cell glow?
|
Arabinose (sugar) - activates araC gene - which turns on the gfp gene - which creates a glow.
gfp stands for green fluorescent protein) |
|
|
How do you find Celcius?
|
C= 5/9 (F -32)
|
|
|
How do you find Fahrenheit?
|
F=(9/5C) + 32
|
|
|
150 cm = ______km?
|
.00150
|
|
|
4mm + 3.5nm + 3nm = ______m?
|
.0040000065 m
|
|
|
What are the 4 magnifications on a microscope?
|
1. Scanning objective 4X
2. Low power objective 10X 3. High-dry objective 40X 4. Oil immersion 100X |
|
|
What is the magnificaiton of the ocular lens?
|
10X
|
|
|
What is TOTAL magnificaiton when looking through the scanning objective lens?
|
40X (10 x 4)
|
|
|
What do the condenser and iris do?
|
1. Collects and focuses light
2. Controls the amount of light |
|
|
Is the condenser knob on the left or right?
|
Small knob on the left
|
|
|
Are the fine and course adjustment knobs on the left or right?
|
Right
|
|
|
What were the 5 slides we looked at in our first lab?
|
1. Flea (xenospylla)
2. Volvocales 3. Vinegar eels 4. Bone 5. Rannnunculus Root |
|
|
Char tests for what?
What is + What is - |
Organic
Black Clear/White |
|
|
Benedict tests for what?
What is + What is - |
Simple Sugars (Carbs)
Red/Orange Blue |
|
|
Iodine tests for what?
What is + What is - |
Starch (complex sugar)
Blue/Black Yellow/Brown |
|
|
Sudan tests for what?
What is + What is - |
Fats (lipids)
Red / Very Red No color |
|
|
Biuret tests for what?
What is + What is - |
Proteins
Lavender Blue |
|
|
What functional group is this?
O || R-C-H |
aldehyde
|
|
|
What functional group is this?
O || R-C-R |
keytone
|
|
|
What functional group is this?
O || R-C-OH |
carboxyl
|
|
|
What functional group is this?
O || R-N-H-H |
amino
|
|
|
What functional group is this?
R - O - H |
hydroxyl
|
|
|
In a protein standard curve, the more concentration, the more light is ______?
What is the machine called used to measure this? |
absorbed
spectrophotometer |
|
|
When graphing a protien standard curve, what goes on the y axis? the x axis?
|
absorbance
concentration |
|
|
In probing the cell lab, after centrifuging the peas, what were the "layers" in the test tube?
|
pellet - starch grains
supernatant - nuclei, organelles green stuff at top - chloroplasts |
|
|
What do we use to avoid excess cell damage when blending?
|
Cold sucrose buffer
|
|
|
The salivary gland chromosome we studied came from a what?
|
Drosophila larva
|
|
|
The saliary gland chromosome is special. What is it called?
|
A polytene chromosome
|
|
|
What is the enzyme that we used that is extracted from yeast cells?
|
Invertase (or Sucrase)
|
|
|
What three things effect the activity of an enzyme?
|
Concentration, temp and pH
|
|
|
What is RF and how is it calculated?
|
Ratio Fronts: used in paper chromatography
RF=Distance Moved by Pigment divided by Distance from pigment origin to solvent front |
|
|
When chloroplasts are viewed through a spectroscope, which colors are absorbed?
|
Red, Violet and blue have high absorbance....the remaining light (greenish) is what we see.
|

