![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
71 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
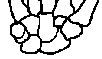
Bones of hand
|
Scared Lovers Try Positions That They Can't Handle
sca phoid tri que trum cap i tate |
s
|
|
|
sartorius*
|
flex thigh, rotate laterally
broad superficial thigh outer hip to inner knee |
|
|
|
tensor fasciae latae*
|
flex, abduct thigh at hip
muscle pulls on white fascia latae which covers the vastus lateralis muscle on lateral part of the thigh. |
|
|
|
gracilis*
|
adduct thigh
superficial inner thigh groin to inner knee |
|
|
|
adductors
|
adduct thigh
humans: brevis, longus, magnus just above and under gracilis. in groin, often a darker color |
|
|
|
rectus femoris*
|
Quad extend foreleg
straight cylinder of muscle under sartorius partially covered by vastus medialis and vastus lateralis along the edges |
|
|
|
vastus lateralis
|
Quad: extend foreleg
lateral to rectus femoris, hidden by fascia latae injection site |
|
|
|
vastus medialis
|
Quad: extend foreleg
big medial thigh muscle runs anterior and parallel to femoral artery & vein |
|
|
|
vastus intermedius
|
Quad: extend foreleg
under rectus femoris and often darker than vastus medialis and vastus lateralis that are on each side |
|
|
|
biceps femoris
|
Hamstring: flex foreleg
huge muscle lateral thigh outer hip to lateral knee fascia latae is connected to lateral margin of the muscle |
|
|
|
semimembranosus
|
Hamstring: flex foreleg
see from both sides, under gracilis larger, broad medial thigh muscle hip to medial side of knee |
|
|
|
semitendinosus
|
Hamstring: flex foreleg
skinny, long thinner medial thigh muscle hip to medial side of knee, superficial to the semimembranosus can see semimem on both sides of semitend |
|
|
|
gluteus medius
|
abducts thigh
large superior muscle in the cat superior dorsal region of hip preferred IM injection site |
|
|
|
gluteus maximus
|
extends thigh
smaller inferior muscle in cat posterior to gluteus medius |
|
|
|
gastrocnemius
|
plantar flexion (extend foot)
|
|
|
|
tibialis anterior
|
dorsiflex foot
(toes closer to shin) anterior muscle parallel to tibia (shin bone). Bone is the medial edge of the muscle. |
|
|
|
rectus abdominis
|
compresses abdomen,
flexes vertebral column middle - cut - stitches most anterior, runs from chest to groin on both sides of the linea alba (white line of connective tissue in the midline of abdomen) |
|
|
|
external abdominal oblique
|
compresses abdomen
very thin, most superficial, sides. fibers on angle from ribs down towards the linea alba |
|
|
|
internal abdominal oblique
|
compresses abdomen
middle layer on sides of abdomen fibers on angle from lateral groin up towards linea alba. underneath external abdominal oblique |
|
|
|
transversus abdominis
|
compresses abdomen
darker, sides of abdomen, fibers run transverse to linea alba and go under rectus abdominis |
|
|
|
masseter
|
elevates jaw
large muscle of the cheek |
|
|
|
digastric
|
depresses jaw
under the chin following the V of the mandible (lower jaw bone) |
|
|
|
sternocleidomastoid
|
turns (rotates) head, both flex head
form a V in the neck from the sternum and clavicles to the mastoid process |
|
|
|
pectoralis major and minor
|
flex and adduct arm
large muscle that runs from the backbone to the axilla (armpit). |
|
|
|
serratus anterior
|
rotates scapula upward and laterally
under fat, axillary region under pectoral muscles & latissimus dorsi. fan shaped muscle with fingers that go to ribs from axilla |
|
|
|
trapezius
|
retracts scapula
back. 3 parts in cat. superficial muscles of back, both sides of backbone from lumbar to neck. |
|
|
|
deltoid
|
abducts arm
on top. 3 parts in cat. shoulder muscle. starts at acromion where trapezius ends.. runs out to upper humerus. preferred IM injection site |
|
|
|
biceps brachii
|
flexes forearm
underneath deltoid. anterior upper arm muscle - pull insertion of pectoralis up to see the cylindrical muscle on the humerus |
|
|
|
triceps brachii
|
extends forearm
posterior lower arm muscle large group posterior and inferior to humerus |
|
|
|
abduct
|
move away
|
|
|
|
adduct
|
move to midline
|
|
|
|
-cepts
|
heads
|
|
|
|
brachii =
|
upper arm
|
|
|
|
dia-
|
through
|
|
|
|
external
|
outside
|
|
|
|
femur
|
thigh bone
|
|
|
|
gastro-
|
belly
|
|
|
|
gracile means
|
slender
|
|
|
|
latissimus means
|
widest
|
|
|
|
rectus means
|
parallel to midline
|
|
|
|
sator means
|
tailor seat, cross
|
|
|
|
serrated means
|
wavy edge
|
|
|
|
tensor means
|
pulls tight
|
|
|
|
vast means
|
great in size
|
|
|
|
alveolar process
|
where teeth go, mandible and maxilla
|
|
|
|
Which bones make up orbit of eye?
|
zygomatic
frontal sphenal maxilla palantine ethmoid lacrimal |
|
|
|
mandibular condyle
|
joint C jaw
articulation point of the mandible with the mandibular fossa of the temporal bone |
|
|
|
fetal skull
|
fontanels: incomplete ossification
anterior posterior anteriolateral posteriolateral |
|
|
|
Atlas C1
|
Atlas - no body, lateral processes have large concave depressions to receive occipital condyles of the skull.
|
|
|
|
Axis C2
|
Dens (odontoid process). pivot point
|
|
|
|
C3 to C7 features
|
smallest, lightest vertebrae
vertebral foramen is triangular spinous process short, often bifurcated (two branches) C7 - not branched. longer Transverse processes have foramen for veterbral arteries |
|
|
|
Thoracic Vertebrae
|
12
Costal facets (articulate with ribs) spinous process long, sharp downward hook. gets less sharp and shorter |
|
|
|
Lumbar Vertebrae
|
5
massive bodies. short thick hatchet shaped spinous processes extending directly back. spinal cord ends at L2, but outer covering/fluid extends beyond (lumbar puncture and "saddle block" for childbirth) |
|
|
|
Sacrum
|
5 fused
|
|
|
|
Sternum
|
parts
manubrium (articulates w clavicle) body (gladiolus) xiphoid process |
|
|
|
Ribs
|
True 1 - 7
False 8 - 12 Floating 11, 12 |
|
|
|
Tubercle - definition
|
1. A small rounded projecting part or outgrowth,
|
|
|
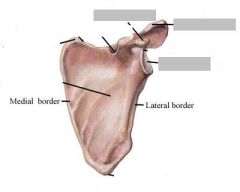
Name the important features of the scapula
|
spine
acromion process coracoid process glenoid cavity |
|
|
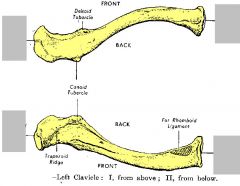
Name the ends
|
sternal (manubrial) end
acromial end |
|
|
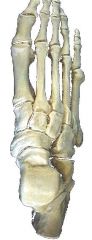
Name tarsal bones
|
"Tiger Cubs Need MILC":
Superior, then clockwise on right foot: Talus Calcaneus Navicular Medial cuneiform Intermediate cuneiform Lateral cuneiform Cuboid |
|
|
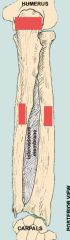
Identify
|
ulna pinky UP thinner
articulates with Humerus at Olecranon (process on Ulna and fossa on Humerus) Styloid process at bottom of Ulna and Radius |
|
|
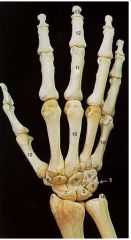
Identify numbers 1 and 14
and all the rest too! |
1. Styloid Process of Radius
14. Styloid Process of Ulna 2. Navicular (Scaphoid) 3. Lunate 4. Triquetral 5. Pisiform 6. Trapezium 7. Trapezoid 8. Capitate 9. Hamate 10. Metacarpal 11. Proximal Phalange 12. Middle Phalange 13. Distal Phalange |
|
|
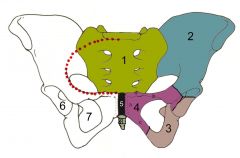
Name the three parts of the Os Coxae
|
(1) sacrum,
(2) ilium, (3) ischium, (4) pubis, (5) pubic symphisis |
|
|
|
What is the difference between the true and false pelvis?
|
If you look at a model of a pelvis (from the side) you will see an arcuate line. Everything superior to the arcuate line is the false pelvis, and everything inferior to the arcuate line is true. The false pelvis is not involved in childbirth in any way, whereas the dimensions of the true pelvis are crucial to an uncomplicated delivery
|
|
|
|
pelvic brim = pelvic inset
|
divides false pelvis from true
begins at sacral promontory & extends lateraly and inferiorly to end at the public symphysis |
|
|
|
false pelvis
|
portion of pelvis superior to pelvic brim.
wide area extending to top of iliac crest |
|
|
|
true pelvis
|
portion of pelvis inferior to pelvic brim
surrounds the pelvic cavity |
|
|
|
pelvic outlet
|
inferior opening of true pelvis,
bordered by coccyx, ischial spines and ischial tuberosities. "baby hole" |
|
|
|
sacral curve
|
male = curved in
female not as much |
|
|
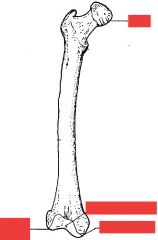
Name the labeled parts.
|
head
medial condyle (on head side) lateral condyle intercondylar fossa |
|
|
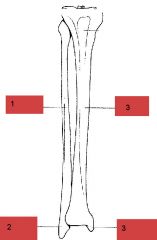
Identify parts
|
1. fibula
2. lateral malleolus 3. tibia 4. medial malleolus (big toe side of course.. medial) |
|

