![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
23 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Formation of the neural groove from the neural plate occurs at how many days of development?
|
18
|
|
|
Formation of the neural groove is induced by what?
|
The notochord
|
|
|
Closing of the neural tube occurs in what direction?
|
Rostral --> caudal
|
|
|
Failure to close the neural tube at the rostral end results in _________; failure to close the neural tube at the caudal end results in ______________.
What nutrient is important in avoiding these birth defects? |
-rostral - anencephaly
-caudal - spina bifida (or less severely, myelomeningecele) -folic acid |
|
|
____________ cells later go on to form Schwann cells, melanocytes, and dorsal root ganglia.
|
Neural crest cells
|
|
|
Name the three primitive brain divisions.
|
-prosencephalon
-mesencephalon -rhombencephalon |
|
|
Name the vesicles that arise from the prosencephalon.
|
prosencephalon --> telencephalon, diencephalon
|
|
|
Name the vesicles that arise from the mesencephalon
|
mesencephalon --> mesencephalon
(stays the same) |
|
|
Name the vesicles that arise from the rhombencephalon.
|
rhombencephalon --> metencephalon, myelencephalon
|
|
|
Name the two flexures that arise as the brain develops and where they occur.
|
cephalic flexure - mesencephalon
cervical flexure - between the rhombencephalon and the spinal cord |
|
|
The most rostral portion of the telencephalon, which persists as the most rostral portion of the ventricular system in the adult, is the __________________.
|
lamina terminalis
|
|
|
The ______________ will develop into the cerebral hemispheres and lateral ventricles.
|
Telencephalon
|
|
|
T/F In the adult, the ventricular system in the brain is associated with the ventricular system of the spinal cord.
|
False - the hollow ventricular system in the spinal cord closes and becomes the central canal (not filled with CSF)
|
|
|
The third ventricle develops from what vesicle?
|
Diencephalon
|
|
|
The pons develops from what vesicle?
|
Metencephalon
|
|
|
The medulla and cranial nerves 8-12 arise from what vesicle?
|
Myelencephalon
-also central canal |
|
|
The cerebral aqueduct develops from what vesicle?
|
Mesencephalon
|
|
|
The thalamus and its associated structures (hypothalamus, etc.) develop from what vesicle?
|
Diencephalon
|
|
|
The fourth ventricle and cerebellum develop from what vesicle?
|
Metencephalon
|
|
|
The sulcus limitans is a groove along the walls of the ventricular system that divides the cranial nerves into _________ and _________ nuclei.
|
Sensory (Alar) and Motor (Basal)
|
|
|
At the third ventricle, the sulcus limitans is also called what?
|
Hypothalamic sulcus (divides thalamus from hypothalamus)
|
|
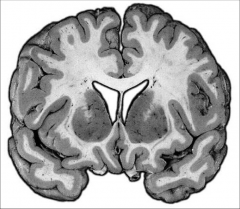
What kind of section is this?
|
Coronal
|
|
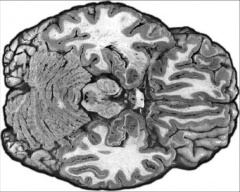
What kind of section is this?
|
Horizontal
|

