![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
76 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Blood cells are produced in the ____ ______. |
bone marrow |
|
|
formation of blood components |
hematopoiesis |
|
|
formation of red blood cells |
erythropoieses |
|
|
Kidneys detect decrease in circulating O2, secrete hormone ______________ that signals the body to produce more blood cells. |
erythropoietin |
|
|
Blood is comprised of __% plasma (hormones, glucose, electrolytes, antibodies, nutrients, etc.) and __% formed elements. |
55% plasma, 45% formed elements |
|
|
regulate colloidal osmotic blood pressure |
albumin |
|
|
involved in immunity, solute transporting, and blood clotting |
globulin |
|
|
involved in blood clotting |
fibrinogen |
|
|
red blood cells; contain protein __________ |
erythrocytes; hemoglobin |
|
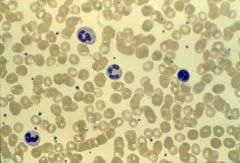
|
blood; plasma; erythrocyte; leukocyte; thrombocyte |
|
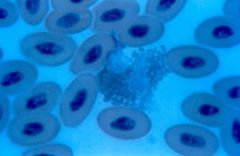
|
erythrocytes; most common |
|
|
squeeze between cells |
diapedesis |
|
|
engulf foreign particles or cellular debris |
phagocytosis |
|
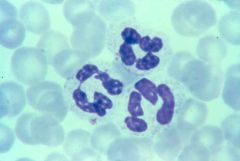
|
neutrophil (multi-lobed) |
|
|
type of granulocyte; first responders, phagocytic |
neutrophil |
|
|
type of granulocyte; allergic reactions and parasitic infections |
eosinophils |
|
|
type of granulocyte; inflammation and allergic reactions; histamine and heparine |
basophil |
|
|
eosinophil (two-lobed) |
|
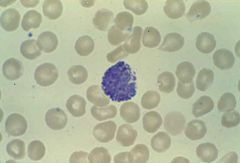
|
basophil (S-shabed) |
|
|
type of agranulocyte; lymphocyte; mature into plasma cells; antibody-mediated immunity |
B-cells |
|
|
type of agranulocyte; lymphocyte; cell-mediated immunity; attack bacteria, virus-infection cells, tumors, tissue transplants, etc. |
T-cells |
|
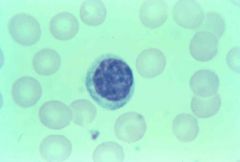
|
lymphocyte (round, dented) |
|
|
agranulocyte; biggest leukocyte; major phagocytic cell; move from blood into tissues and become macrophages |
monocyte |
|
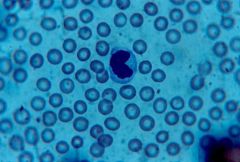
|
monocyte (pacman) |
|
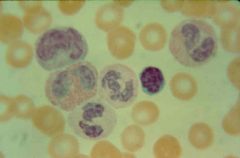
|
leukocytes (monocyte, eosinophil, neutrophil (2), lymphocyte, basophil) |
|
|
formed element involved in blood clotting; consist of small fragments of megakaryocytes (largest bone marrow cell) |
thrombocytes (platelets) |
|
|
The heart is found in region known as the ___________. |
mediastinum |
|
|
layer of heart composed primarily of connective tissue and fat serving as protection for the heart; sometimes considered a continuation of the serous layer of the parietal pericardium |
epicardium (visceral pericardium) |
|
|
filled with pericardial fluid (acts as lubricant) |
pericardial cavity |
|
|
thickest layer of the heart wall; composed primarily of cardiac muscle tissue containing cardiomyocytes involved in heart conduction; intercalated discs in this layer |
myocardium |
|
|
innermost layer that lines all four heart chambers, composed of endothelial cells (specialized squamous epithelium) |
endocardium |
|
|
inflammation of the endocardium layer of the heart |
endocarditis |
|
|
________ carry blood away from the heart. |
Arteries |
|
|
_____ carry blood toward the heart. |
Veins |
|
|
smallest blood vessels where exchange occurs; connect arteries/arterioles and veins/venules |
capillaries |
|
|
oxygenated blood travels through... |
systemic arteries (Aorta) and pulmonary veins |
|
|
deoxygenated travels through... |
systemic veins (Vena cava) and pulmonary arteries |
|
|
three layers of blood vessels |
tunica externa/adventitia (connective tissue), tunica media (smooth muscle tissue; thicker in arteries; elastic fibers in arteries), tunica interna/intima |
|
|
blood vessels that nourish other blood vessels |
vasa vasorum |
|
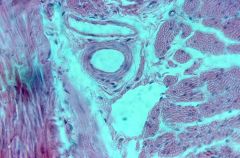
|
veins (collapsed, thin tunica media); arteries (perfect circles, thick tunica media) |
|
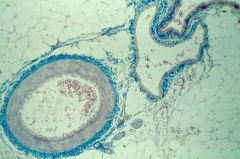
|
artery (round) vein (collapsed) |
|
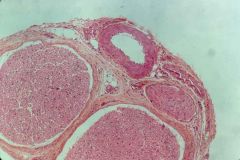
|
nerve (2), artery (round), vein (squished) |
|
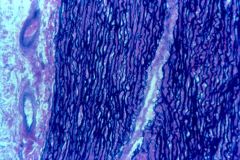
|
elastic tissue of Aorta; vasa vasorum |
|
|
blood vessels that nourish larger blood vessels such as the aorta and vena cava |
vasa vasorum |
|
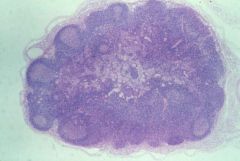
|
lymph node (capsule, germinal center, medulla) |
|
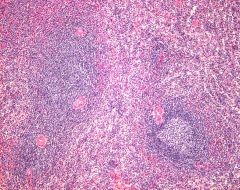
|
spleen (white pulp, red pulp) |
|
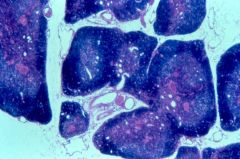
|
thymus (cortex, medulla, capsule) |
|
|
How many lobes make up the right lung? |
3 |
|
|
How many lobes make up the left lung? |
2 |
|
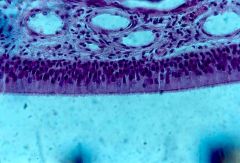
|
pseudostratified ciliated columnar epithelium |
|
|
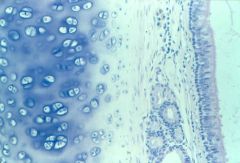
trachea (hyaline cartilage with chondrocytes; pseudostratified ciliated columnar epithelium) |
|
|
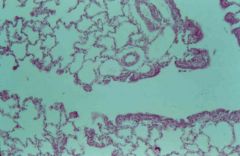
respiratory branchiole, terminal branchiole, alveoli |
|
|
_____ ________ _____ comprise 96% of the alveolar surface area and allow for gas exchange |
type I alveolar cells |
|
|
______ _______ _____ comprise 4% of the alveolar surface area and secrete pulmonary surfactant |
type II alveolar cells |
|
|
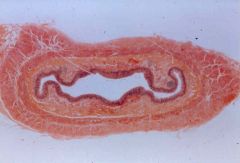
esophagus (mucosa, submucosa, muscularis, adventitia) |
|
|
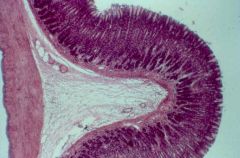
stomach mucosa layer (outer muscularis mucosa; middle lamina propria composed of connective tissue; inner mucous membrane composed of epithelium containing surface mucous cells, chief cells, and parietal cells) |
|
|
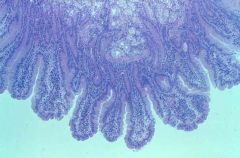
small intestine duodenum (duodenal/Brunner's glands; villi) |
|
|
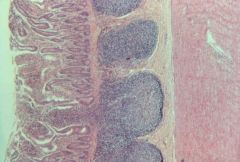
small intestine ileum (villi; Peyer's patches) |
|
|
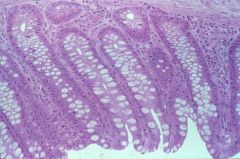
large intestine (lamina propria; globlet cells; mucosa layer) |
|
|
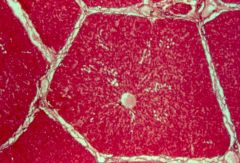
liver (lobule; central vein; hepatocytes--red; sinusoids--white) |
|
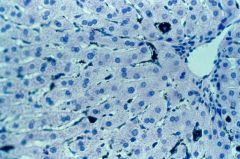
|
liver (central vein; hepatocytes--transparent red; sinusoids--white; Kupffer cells--black) |
|
|
Alpha cells release ________ to ________ blood glucose levels. |
glucagon; increase |
|
|
Beta cells release _______ to ________ blood glucose levels. |
insulin; decrease |
|
|
What is the functional unit of the kidney? |
nephron |
|
|
triangular region formed by both ureters and the urethra |
trigone |
|
|
cluster of capillaries in the nephron |
glomerulus |
|
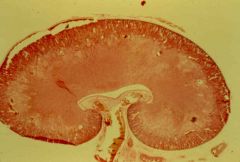
|
kidney (renal cortex; renal medulla) |
|
|
Majority of nephrons are found in the cortex, thus called ________ ________. |
cortical nephrons |
|
|
Few nephrons are found in the medulla, thus called the ______________ ________. |
juxtamedullary nephrons |
|
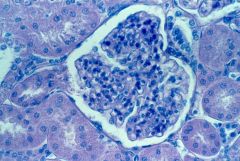
|
glomerulus (urinary space; Bowman's capsule) |
|
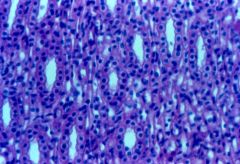
|
kidney tubules |
|
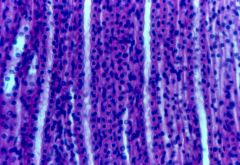
|
kidney tubules |
|
|
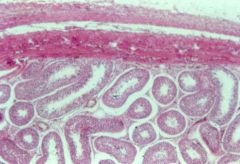
seminiferous tubules in testes (sertoli cells; interstitial cells) |
|
|
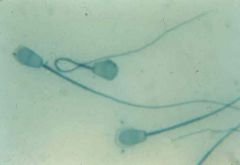
sperm; head (contains DNA and acrosome that contains enzymes to digest exterior covering female gamete); mid-piece of tail (contains mitochondria {ATP} for movement); remainder of tail (flagellum that propels sperm forward) |
|
|
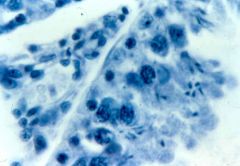
spermatocytes |
|
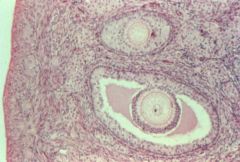
|
oocyte (follicle--whole oval; oocyte--inner circle) |

