![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
20 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
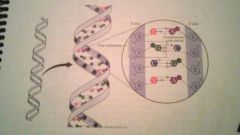
Understand the composition of DNA |
|
|
|
|
Be able to build a simple karyotype |

|
|
|
|
Be able to read a karyotype and to identify: male, female, trisomy 21, Klinefelter syndrome and turner syndrome from chromosome spreads |

T |

|
|
|
Restriction enzymes |
A bacterial enzyme that cuts up foreign DNA at one very specific nucleotide sequence thus protecting bacteria against intruding DNA from phages and other organisms. Used in DNA technology to cut DNA molecules in reproducible ways. |
|
|
|
Evolution |
A measurable change in the allele frequency of a population over time |
|
|
|
Identify vestigial structures on a human |
An organ or structure that has diminished over an organisms evolutionary history due to selection pressures. Lack any real function. Ex. Wisdom teeth, earlobes, ear muscles, tail bone, pelvic griddle, limbs of snakes, goose bumps |
|
|
|
Microevolution |
A change in a populations gene pool over a succession of generations; evolutionary changes in species over relatively brief periods of geologic time |
|
|
|
Macroevolution |
Evolutionary change above the species level including the origin of evolutionary novelty and new taxonmic groups and the impact of mass extinctions on the diversity of life and its subsequent recovery |
|
|
|
Homologous structures |
Similarity in characteristics resulting from shared ancestry. May not have the same function |
|
|
|
Convergent evolution |
The independent evolution of similar structures in unrelated species caused by similar environmental conditions ex. Desert plants |
|
|
|
Energy |
The capacity to do work. Work: any action that moves matter against an opposing force |
|
|
|
Explain why energy transformations are not efficient |
The energy of a system remains constant but the quality of energy is always decreasing |
|
|
|
Logistic growth |
Population growth where exponential growth slows and eventually stops in response to environmental resistance |
|
|
|
Carrying capacity (k) |
The maximum species population that can be realistically supported by a landscape or seascape |
|
|
|
Density dependent |
As populations increases resources become limited ex. Territory, and nesting traits, nutrition, predation, waste, disease |
|
|
|
Density independent |
Natural disasters, severe weather, fire, droughts, floods, earthquakes |
|
|
|
Construct and analyze a graph |
Independent variable plotted on x axis, dependent variable y axis |
|
|
|
Independent variable |
The parameter that the investigator is testing , can be changed as required ex. Behavior- manipulating experiment |
|
|
|
Dependent variable |
The variable that changes due to manipulation of the independent variable. The result measured during an experiment ex. Grades |
|
|
|
Scientific method |
1.observation: must be precise to lead to one question2. questionex. why do rattle snakes come out at night3. hypothesis4. prediction: the result you expect from testing the hypothesis. always if/then statementsex. if vitamin c decreases the risk of catching a cold , then people who take vitamin c supplements will experience fewer colds than people who do not take supplements5. experiment: change one element at a time because some measurable change will happen have a control & experimental group6. results7. conclusion ex. rattle snakes come out at night because their prey is more active at night |
|

