![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
38 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Skeletal muscle
4 |
• Striated
• Long, parallel fibers • Several fused cells make multinucleated fibers • Voluntary contraction |
|
|
2 skeletal muscle groups
How they work together |
1) Flexor = contracts and shortens
2) Extensor = relaxes and elongates They work antagonistically, as one contracts the other relaxes |
|
|
Tendons
What? Made of? Extension of? |
• Connects skeletal muscle to bone
• Fibrous dense connective tissue • Extension of the epimysium (facia) layer which wraps around the muscle |
|
|
Smooth muscle
4 |
• No striations
• Spindle shaped • Found amongst the internal organs • Involuntary peristalsis |
|
|
Cardiac muscle
4 |
• Striated
• Branched • Intercalated disks (gap junctions) separate myocytes • Involuntary contractions |
|
|
Muscle anatomy
4 |
1) Muscle = organ
2) Muscle fiber = cell 3) Myofibril = organelle 4) Sarcomere = contractile unit |
|
|
A bands vs. I bands
|
A bands:
• Thick segment of myofilaments • Made up of horizontal thick myosin proteins, and thin actin proteins projecting in between the myosin I bands: • Thin segment of myofilaments • Made up of the vertical zig-zagging Z line with the horizontal actin proteins attached to it |
|
|
Z line
|
The vertical actin protein disk dividing I bands in half
|
|
|
Sarcomere
|
• Repeating contractile units
• 1 sarcomere = Z line - Z line |
|
|
Myosin structure
2 |
• many golf-club shaped protein filaments twisted together
• has heads which protrude out to walk along the actin |
|
|
Actin structure
2 |
• double helixed proteins
• has myosin binding sites covered by tropomyosin until troponin binds to unveil them |
|
|
Sarcoplasmic reticulum
|
Smooth ER of a myocyte which stores Ca+2
|
|
|
Where is the concentration gradient of Ca+2 in a myocyte?
When and how is it built? |
• Concentration gradient is inside the sarcoplasmic reticulum
• It is built when the muscle fiber is at rest • Ca+2 pumps actively transports Ca+2 inside the SR |
|
|
What is contraction?
2 |
• Myosin heads walk along the actin filaments, pulling in the Z line
• Actin and myosin do not shorten, rather they glide past one another shortening the sarcomeres |
|
|
Mechanism of contraction
5 steps Remember 4 chemicals involved minus ATP |
1) Motor neurons secrete the neurotransmitter acetylcholine
2) ACh ignites an impulse that travels to the sarcoplasmic reticulum 3) Impulse opens Ca+2 channels, allowing Ca+2 to rush out into the cytoplasm 4) Ca+ bind to troponin, causing the tropomyosin to uncover actin's myosin binding sites 5) Mysoin heads can now bind to actin to walk along it |
|
|
ATP's role in contraction
4 |
1) High energy state: ATP bound to myosin & detached from actin
2) Myosin hydrolysizes ATP → ADP + P, thrusting the head forward to bind to the myosin binding site 3) ADP + P is released from head, and head pivots (power stroke), pulling myosin filament along actin 4) ATP binds to head, releasing it from actin |
|

|
Orbicularis oculi
|
|

|
Zygomaticus
|
|

|
Masseter
|
|

|
Orbicularis oris
|
|

|
Platysma
|
|

|
Trapezius
|
|

|
Deltoids
|
|

|
Triceps brachii
|
|
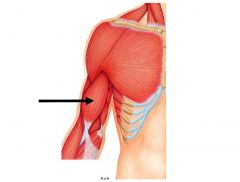
|
Biceps brachii
|
|

|
Pectoralis major
|
|

|
Intercostals
|
|

|
Rectus abdominis
|
|

|
Latissimus dorsi
|
|
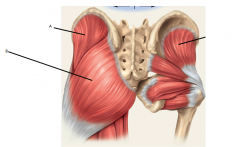
A
|
Gluteus medius
|
|
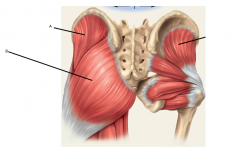
B
|
Gluteus maximus
|
|

|
Sartorius
|
|

|
Rectus femoris
|
|

|
Vastus lateralis
|
|

|
Vastus medialis
|
|

|
Gastrocnemius
|
|

|
Biceps femoris
|
|

|
Calcaneal (Achilles) tendon
|

