![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
62 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Germicide |
Chemicals lethal to pathogens (ie bacteriocidal) |
|
|
Disinfectant |
Chemicals used for killing or inhibiting microbial growth, meant to be used on inanimate surfaces such as floors and table tops |
|
|
Antiseptics |
Appropriate for use only on living tissue such as skin |
|
|
Bacteriostatic |
Inhibits microbial growth but doesn't kill bacteria |
|
|
Bacteriocidal |
Killing of bacteria |
|
|
What are the 5 general groups of anti microbial agents? (Know 2) |
Alcohols aldehydes halogens phenols quaternary ammonium compounds |
|
|
List the characteristics of a good disinfectant. |
Highly effective when dilute Nontoxic Inexpensive Biodegradable Harmless to wood, metal, glass, and human skin |
|
|
What is the purpose of an aniline dye? |
To kill gram positive microbes because they kill them more readily than gram negative microbes. |
|
|
Name some examples of heavy metals that control microbial growth. |
Mercury Silver Copper Zinc |
|
|
Where are antibiotics derived from? |
Bacteria or fungi more specifically streptomycese, bacillus, and penicillum |
|
|
Selective toxicity |
When a chemical kills the microbe but leaves the host tissue alone |
|
|
Endoenzyme |
Used inside the cell ex cytochrome oxidase |
|
|
Exotoxin |
Excreted out of the cell ex amylase and lipase |
|
|
Antibiotic |
Type of chemotherapeutic derived from a bacteria or fungi |
|
|
Broad spectrum |
Effective against a wide range of microorganisms |
|
|
Narrow spectrum |
Effective against few microorganisms |
|
|
What are the ingredients and purpose of growth media? |
There is a carbon source, water, salts, and amino acids. It is used to grow microorganisms |
|
|
All purpose media |
Media that is used to grow most microorganisms that are not too picky |
|
|
Differential media |
Differentiate between the microorganisms growing |
|
|
Selective media |
Only grow specific organisms ex PDA selective for fungi |
|
|
EMB eosin methylene blue |
Differential media used to grow gram negative this is an example of an aniline dye |
|

Front (Term) |
E.coli on EMB |
|
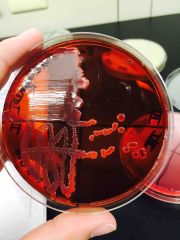
Front (Term) |
E.arogenese on EMB |
|
|
Mannitol salt |
High salt concentrations make it selective for salt. Differentiates between bacteria that can produce acid. Staph aureus grows yellow. Staph epi grows pink |
|
|
Streptococci can cause what kind of diseases |
Strep throat Pneumonia |
|
|
Blood agar |
TSA enriched with Sherpa blood |
|
|
Alpha hemolysis |
Partial breakdown of there's blood cells. Looks like a dark green brown color |
|
|
Gamma hemolysis |
No color change no hemolysys |
|
|
Beta hemolysis |
Complete lysis of the cell wherever there is a colony it is clear |
|
|
Enzyme |
Molecule that speeds up chemical reactions |
|
|
What is the equation for starch hydrolysis? |
Amylase Starch ➡️ glucose + maltose |
|
|
What is the media used for starch hydrolysis? |
Starch agar |
|
|
What is the indicator used in test for amylase? |
Iodine |
|
|
What is the color of a positive result for amylase? |
Yellow color bacteria |
|
|
What is the equation for starch hydrolysis? |
Amylase Starch ➡️ glucose + maltose |
|
|
What is the media used for starch hydrolysis? |
Starch agar |
|
|
What is the indicator used in test for amylase? |
Iodine |
|
|
What is the color of a positive result for amylase? |
Yellow color bacteria |
|
|
What does a positive test look like for lipase? |
There's intensified blue color and a clearing around the bacteria |
|
|
What is the disc used for the cytochrome oxidase test? |
Cytochrome oxidase disk (+) color change (-) none |
|
|
What is the indicator for urea hydrolysis? |
Phenol red |
|
|
What is the specific product from urea hydrolysis that causes color change? |
Ammonia |
|
|
What does nitrite A and Nitrite B test for? |
Nitrites |
|
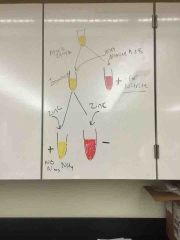
What test is this diagram explaining? |
Nitrate reduction |
|
|
Why do we put the liquid gelatin in an ice bath? |
To see if it stays liquid or turns solid. Liquid (+) solid (-) |
|
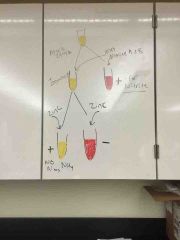
What test is this diagram explaining? |
Nitrate reduction |
|
|
Why do we put the liquid gelatin in an ice bath? |
To see if it stays liquid or turns solid. Liquid (+) solid (-) |
|
|
What are the three parts of an amino acid? |
R group Amino group Carboxylic acid |
|
|
Deaminase |
Removes amine group |
|
|
Decarboxylase |
Removes carboxyl group |
|
|
Desulfhydrase |
Removes sulfhydryl group |
|
|
What is the specific ingredient in the media peptones iron agar that changes color? |
Iron |
|
|
Why do we add a fermentable sugar to lysine Decarboxylase? |
To produce an acid |
|
|
Why do we add mineral oil to the top of lysine Decarboxylase? |
To make an aerobic environmental |
|
|
What are the three main forms of carbohydrates? |
Monosaccharides-glucose Disaccharides-sucrose Polysaccharide- starch |
|
|
Fermentation |
Catabolic reaction that yields an acid and gas and energy |
|
|
What are the three main forms of carbohydrates? |
Monosaccharides-glucose Disaccharides-sucrose Polysaccharide- starch |
|
|
Fermentation |
Catabolic reaction that yields an acid and gas and energy |
|
|
What's the little test tube that is upside down in the fermentation tubes? |
Durham tube |
|
|
What is the indicator in Simmons citrate agar? |
Bromothymol blue |
|
|
What is the indicator in Simmons citrate agar? |
Bromothymol blue |
|
|
What does the Simmons citrate test for? |
Ability for the bacteria to use citrate as its only source of carbon. If it can utilize citrate the media turns dark blue. (Aerobic on top anaerobic on bottom) |

