![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
107 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Anatomical Position
|
viewing the body in a straight position
|
|
|
Biped
|
using 2 legs for walking
|
|
|
Quadruped
|
using 4 legs for walking
|
|
|
Superior
|
above it/ towards the top ex: the head is superior to the neck |
|
|
Inferior
|
below it/ towards the bottom ex: the mouth is inferior to the nose |
|
|
Anterior/Ventral
|
towards the front ex: the lips are anterior to the teeth |
|
|
Posterior/Dorsal
|
towards the back ex: the buttock are posterior to the stomach |
|
|
Medial
|
closer to the mid line ex: the heart is medial to the lungs |
|
|
Lateral
|
away from the mid line ex: the ears are lateral to the nose |
|
|
Ipsilateral
|
in the same side ex: the right arm and right leg are ipsilateral |
|
|
Contralateral
|
different side of the body ex: the right kidney and left kidney are contralteral |
|
|
Superficial |
close to the surface ex: the muscles are superficial to the bones |
|
|
Deep
|
away from the surface/ further into the body ex: The blood vessels are deep to the skin |
|
|
Proximal
|
nearest the point of attachment or origin (when talking about arms/legs) ex: the knee is proximal to the ankle |
|
|
Distal
|
away from the point of attachment (when talking about arms/legs) ex: the fingers are distal to the wrist |
|
|
Parasagittal (Sagital) Plane
|
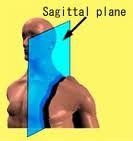
vertical plane that divides the body into left/right sides
|
|
|
Midsagittal Plane
|
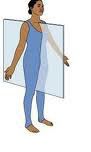
divides the body into equal right and left sides, passes through the midline
|
|
|
Frontal (Coronal) Plane
|
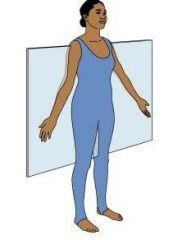
divides body into front and back portions
|
|
|
Transverse Plane
|
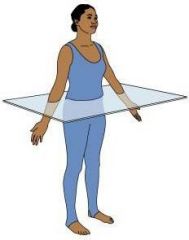
divides body into top and bottom portions
|
|
|
Cephalic
|
relating to the head |
|
|
Cranial
|
skull
|
|
|
Facial
|
face
|
|
|
Frontal
|
forehead
|
|
|
Orbital
|
eye
|
|
|
Octic
|
ear
|
|
|
Buccal
|
cheek
|
|
|
Nasal
|
nose
|
|
|
Oral
|
mouth
|
|
|
Mental
|
chin
|
|
|
Occipital
|
back of head
|
|
|
Cervical
|
neck region |
|
|
Thoracic
|
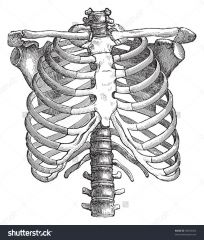
relating to the thorax
|
|
|
Pectoral
|
chest |
|
|
Sternal
|
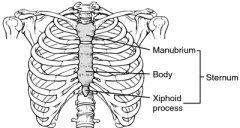
relating to the sternum region of breastbone |
|
|
Abdominal
|
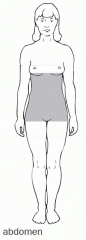
the abs /belly area |
|
|
Umbilical
|
navel/ belly button
|
|
|
Coxal
|
hips |
|
|
Pelvic
|
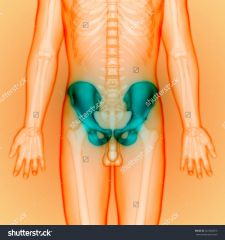
pelvis region
|
|
|
Pubic
|
gential region
|
|
|
Dorsum
|
the back
|
|
|
Scapular
|
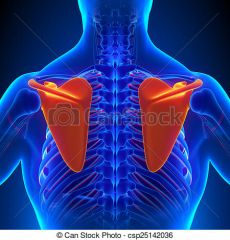
shoulder blade area
|
|
|
Vertebral
|
the spine area
|
|
|
Lumbar
|
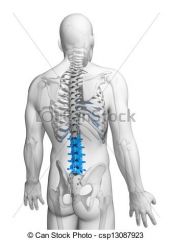
lower back (the area of the back between the ribs and hips) |
|
|
Upper Limb
|
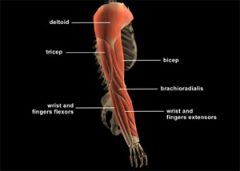
-arm (the region extending from the deltoid (shoulder) region to the hand0 |
|
|
Acromial
|
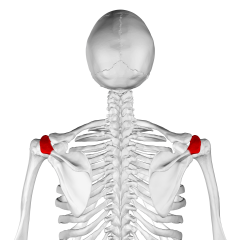
point of shoulder
|
|
|
Axillary
|
armpit
|
|
|
Brachial
|
arm
|
|
|
Antebrachial
|
forearm
|
|
|
Antecubital
|
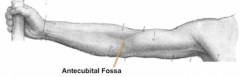
front elbow
|
|
|
Olecranal
|
back of elbow
|
|
|
Carpal
|
wrist
|
|
|
Palmar
|
palm of hand
|
|
|
Digital
|
finger or toes
|
|
|
Lower limb
|
the human leg (limb of the human body, including the foot, thigh and even the hip or gluteal region) |
|
|
Inguinal
|
groin
|
|
|
Gluteal
|
buttocks
|
|
|
Femoral
|

thigh
|
|
|
Patellar
|
front of knee
|
|
|
Popliteral
|
back of knee
|
|
|
Crucal
|
leg
|
|
|
Fibular
|
side of leg
|
|
|
Tarsal
|
ankle
|
|
|
Pedal
|
foot
|
|
|
Plantar
|

sole of foot
|
|
|
Calcaneal
|
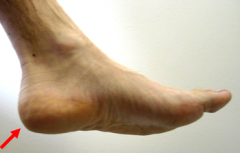
heal of foot
|
|
|
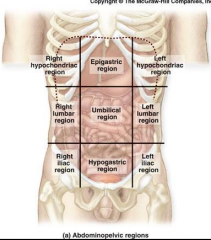
Abdominopelvic Regions
|
|
|
|
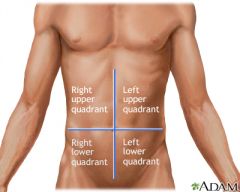
Abdominal Quadrants
|
|
|
|
Body Cavities
|
any space in the body that contains orgams
|
|
|
Dorsal Cavity
|
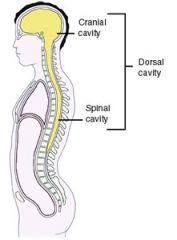
located near the dorsal surface of the body and has two subdivision: Cranial cavity and Vertebral cavity
|
|
|
Cranial Cavity |
contains the brain
|
|
|
Vertebral
|
any of the bones or segments composing the spinal column
|
|
|
Vertebral Cavity
|
contain spinal cord and the beginnings of spinal nerves. |
|
|
Thoracic Cavity
|
-chest cavity -contains pleural and pericardial cavities and mediastinum |
|
|
Pleural Cavities
|
space that lies between the pleura, the two thin membranes that line and surround the lungs
|
|
|
Parietal Layer
|
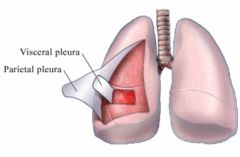
outer layer, thin lining of the walls of the thoracic and abdominopelvic cavity
|
|
|
Visceral Layer
|
inner layer, lining that covers the organs within the cavity
|
|
|
Pleural Fluid
|
provides lubrication as the lungs expand and contract during respiration
|
|
|
Mediastinum
|
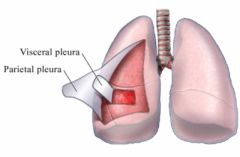
-the space in thoracic cavity between lungs. -contains all of the chest organs except the lungs |
|
|
Pericardial Cavity
|
encloses the heart
|
|
|
Abdominopelvic Cavity
|
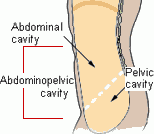
a body cavity that consists of the abdominal cavity and the pelvic cavity
|
|
|
Peritoneal Cavity
|
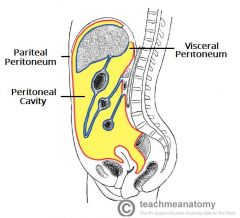
the potential space between the parietal and the visceral peritoneum.
|
|
|
Retroperitoneal Space
|
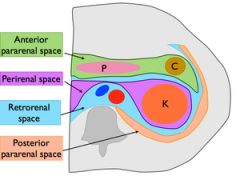
the space between the peritoneum and the posterior abdominal wall
|
|
|
Kidneys
|
either of a pair of bean-shaped organs in the back part of the abdominal cavity that form and excrete urine, regulate fluid and electrolyte balance, and act as endocrine glands.
|
|
|
Pelvic
|
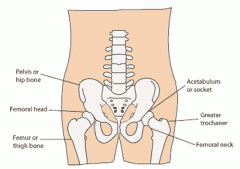
The basin-shaped structure in vertebrate animals that joins the spine and lower or hind limbs
|
|
|
Appendicular Skeleton
|
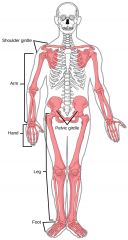
|
|
|
Axial Skeleton
|
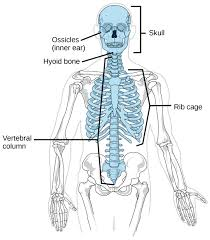
|
|
|
Foramen
|
a hole through a bone, usually round (foramen magnum of the skull) |
|
|
Fossa
|
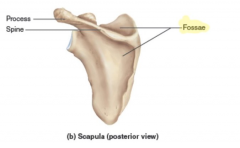
a shallow, broad, or elongated basin
|
|
|
Groove or Sulcus
|
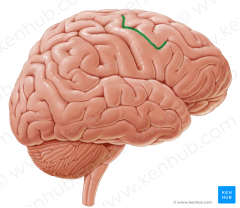
a groove for a tendon, nerve, or blood vessel
|
|
|
Meatus
|
a passage or opening leading to the interior of the body.
|
|
|
Fissure
|
a slit through a bone (orbital fissures behind the eye) |
|
|
Sinus
|
an air-filled space in a bone (frontal sinus of the forehead) |
|
|
Condyle
|
a rounded knob that articulates with another bone (occipital condyles of the skull) |
|
|
Epicondyle
|
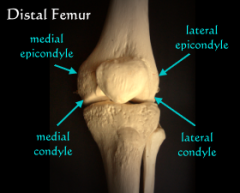
an expanded region superior to a condyle
|
|
|
Tuberosity
|
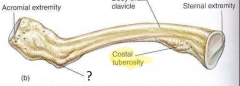
an elevation or protuberance, especially of a bone.
|
|
|
Tubercle
|
a small, rounded process
|
|
|
Trochanter
|
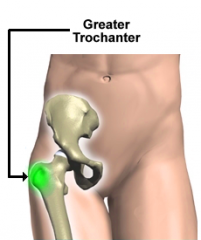
anatomical part of the femur connecting to the hip bone
|
|
|
Head (bones)
|
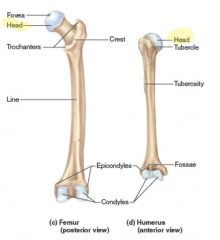
the prominent expanded end of a bone, sometimes rounded
|
|
|
Process
|
is a projection or outgrowth of tissue from a larger body
|
|
|
Line
|
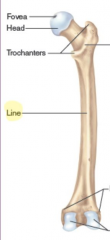
A slightly raised, elongated ridge
|
|
|
Crest
|
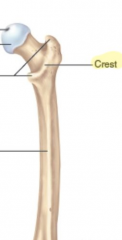
A narrow ridge
|
|
|
Spine or spinous process
|
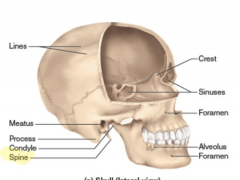
A sharp, slender, or narrow process
|
|
|
Facet
|
A smooth, flat, slightly concave or convex articular surface
|
|
|
Epiphysis
|
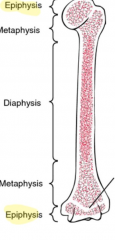
The end segment of a long bone
|
|
|
Ramus
|
a branch, such as a branch of a blood vessel or nerve
|
|
|
Dorsal Cavity
|
include Cranial cavity and Vertebral
|
|
|
Ventral Cavity
|
includes Thoracic cavity and Abdominopelvic cavity
|

