![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
23 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
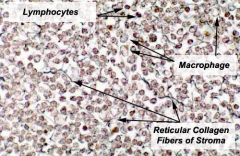
|
-Not sharply delineated.
-No special organization -Composition: Reticular stroma plus free cells (e.g. macrophages, lymphocytes, and plasma cells). |
|
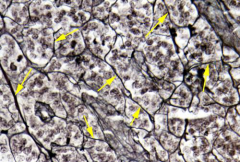
|
Reticular fiber network found in diffuse lymphoid tissue.
-Contains Type III collagen fibers. -Difficult to see normally, needs special silver stain |
|
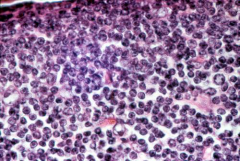
|
Diffuse lymph tissue
|
|
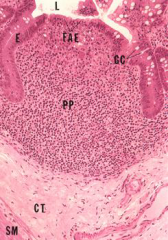
|
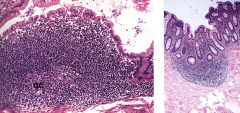
Dense aggregations or individual solitary spherical masses.
-Always surrounded by diffuse lymphoid tissue. -Primary nodule: -Homogeneous in appearance -Mainly B-lymphocytes -Secondary nodule: -Contains a germinal center -Forms in response to an antigenic response -Contains lymphoblasts and proliferating B-lymphocytes -Transitory structure |
|
|
Pyer's patch
|
|
|
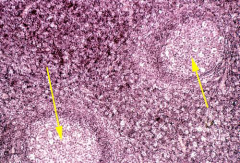
Secondary lymph nodule
|
|
|
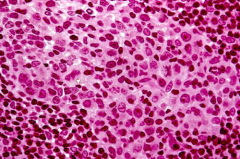
Secondary Nodule
-Stains paler because the cells are larger and not as densely packed. -Cells migrate from the germinal centers (in secondary nodules) into the surrounding tissue and eventually into the vascular and circulatory system |
|
|
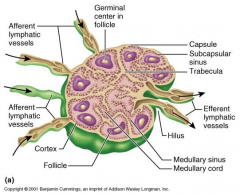
Lymph node overview
-General characteristics -Ovoid and encapsulated lymphoid organs -Lymph flows through the organs and is filtered -Histological organization -Dense, collagenous capsule -Trabeculae project into node -Cells held in a reticular meshwork -Lymph nodes have a distinct cortex and medulla -Numerous lymph sinuses are present |
|

|
Lymph Node:
Note- Inner medulla and outer cortex Cortex is composed of the primary and secondary lymph nodules. This is the site of production of B lymphocytes Medulla is composed of medullary cords, reticular fibers and medullary sinuses |
|
|
Lymph Node Cortex
|
Outer dense mass of lymphoid cells.
-Superficial Cortex -Contains primary and secondary nodules (nodular cortex) -Internodular cortex -Lies between nodules -Tertiary Cortex -Lies between the medulla and the remaining part of the cortex -T-lymphocytes found in these cotical regions |
|
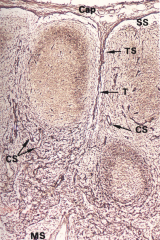
|
Reticular framework of lymph node
|
|

|
Superficial cortex (with primary and secondary nodules)
|
|
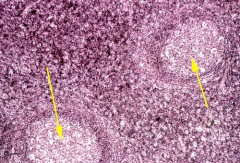
|
Germinal centers in the superficial cortex
|
|
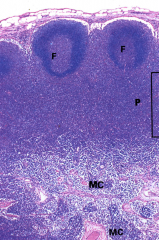
|
Regions of the cortex. Includes Superficial (with primary and secondary nodules), internodular cortex, and tertiary cortex.
Also contains the medulla *note: white= lymph |
|
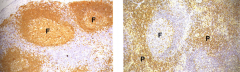
|
Left= Secondary germinal center and site of B cell development
Right= Internodular and tertiary cortex. Sites of T cell accumulation |
|
|
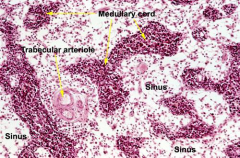
Lymph node medulla:
Lies central to the cortex and extends to the hilus -Composed of medullary cords, reticular fibers, and medullary sinuses -Medullary cords are branching portions of the reticular tissue, extensions of the tertiary cortex, and contain: -Lymphocytes, macrophages, and plasma cells -No plasma cells are normally found in the lymph |
|
|
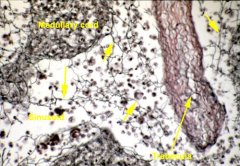
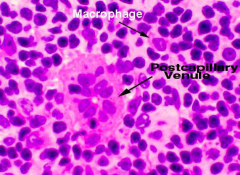
Macrophages are the black dots. They sit on the reticular mesh and help to break down pathogens and unwanted materials
|
|
|
Lymph Node Sinuses
|
-Transport lymph through then node
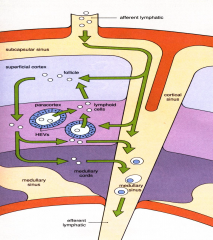
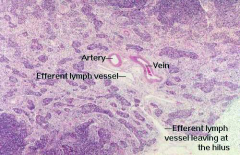
-Lined by reticular/endothelial cellsthat extend cytoplasmic processes across the sinus lumen -Pathway for lymph: 1. Afferent lymphatic vessels- Pierce capsule and empty into the SUBCAPSULAR SINUSES 2. Cortical sinuses- run radially from the subcapsular through the cortex 3. Medullary sinuses 4. Efferent lymphatic vessels- convergence at the hilus |
|
|
Functional compartments of the lymph node
|
|
|
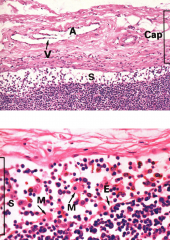
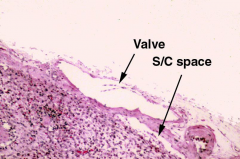
Lymph node capsule and subcapsular sinus
Note: two different images. Note: valve (V) in the afferent valve |
|
|
Capsule and subcapsular sinus
|
|
|
Hilus of lymph node
|
|
|
Postcapillary venules- High Endothelia Venules
-Located in the TERTIARY CORTEX of the lymph node -cuboidal endotheial lining -T lymphocytes use these vessels to pass from the blood into the lymph node -Site that B-lymphocytes exit |

