![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
20 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What are the key features of the TCA cycle? |
Definition: oxidation of acetyl CoAto CO2 and water • Location: mitochondrial matrix • Tissues: all tissues with mitochondria(not red blood cells or whitemuscle fibres) • Functions: energy trapping,biosynthesis of intermediates |
|
|
What happens in the TCA cycle overall? |
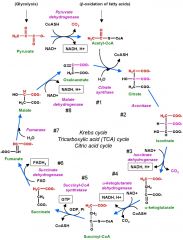
|
|
|
What happens in the Conversion of Pyruvate to Acetyl CoA(the link reaction)? |
CH3 CO COOH + CoASH ----> CH3 CO S CoA +CO2 Pyruvate dehydrogenase + NAD+ + NADH + H+ |
|
|
What does the coenzyme A do? |
Coenzyme A forms thioesterbonds with carboxylic acids |
|
|
What type of reaction is the first step? |
Condensation reaction Citrate synthase |
|
|
What type of reaction is the second step? |
Isomerisation Aconitase |
|
|
What happens in the 3rd step? |
First loss of CO2 Isocitratedehydrogenase |
|
|
What happens in the 4th step? |
Second loss of CO2 α-Ketoglutarate dehydrogenase |
|
|
What happens in the 5th step? |
Trapping thioester bond energyas GTP Succinyl-CoA synthetase |
|
|
What happens in the 6th step? |
Conversion of succinateto fumarate Succinate dehydrogenase |
|
|
What happens in the 7th step? |
Conversion of fumarateto malate Fumarase |
|
|
What happens in the 8th step? |
Conversion of malateto oxaloacetate Malate dehydrogenase |
|
|
How is ATP generated in the Electron transport chain? |
The re-oxidation of NADH to NAD+ and FADH2toFAD via the Electron Transport Chain results insynthesis of ATP from ADP and Pi (OxidativePhosphorylation) |
|
|
What are the energy yields of TCA cycle? |
• 3 enzyme reactions produce NADH and H+ • 1 enzyme reaction produces FADH 2 • 1 enzyme reaction produces GTP |
|
|
What enzymes are involved in the 3 irreversible steps? |
3 enzyme steps are highly exergonic& irreversible: • citrate synthase • isocitrate dehydrogenase • α-ketoglutarate dehydrogenase |
|
|
What is the feedback inhibition of these key step enzymes? |
Rate of TCA cycle regulated by feedback inhibition of key enzymes • citrate synthase ATP, NADH, Succinyl-CoA inhibit. ADP activates • isocitrate dehydrogenase ADP activates. ATP, NADH inhibit • α-ketoglutarate dehydrogenase NADH , Succinyl-CoAinhibit |
|
|
What is the Biosynthetic role of TCA cycle? |
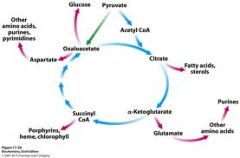
|
|
|
What is Anaplerotic ‘topping up’ of TCA cycle |
Replenishing substrates in the cycle from Pyruvate. Malate - Malicenzyme Oxaloacetate - Pyruvatecarboxylase |
|
|
What does Pyruvate carboxylase reaction also allow? |
Pyruvate carboxylase reaction also allowsregeneration of glucose from pyruvate |
|
|
What can pyruvate not directly form? |
Phosphoenolpyruvate Oxaloacetate ----> Phosphoenol pyruvate PEP carboxykinase |

