![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
35 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What are individual cells part of? |
Individual cells are part of a complex community ofinteracting tissue and respond to a wide array ofextracellular signals |
|
|
What are cell signals needed for? |
Cell differentiation Cell Growth Cell Death Cell Division Cell movement |
|
|
What are the different types of signal? |
Divide Secrete/release Grow Differentiate Move Mobilise/store energy Die |
|
|
What sort of signal? |
Hormones and Growth Factors (development, woundhealing) - Oestradiol, Testosterone, Epidermal Growth Factor Metabolic Regulators - Insulin, Adrenaline, Glucagon Neurotransmitters – Acetylcholine, Glutamate Inflammatory mediators - Prostaglandins, Cytokines |
|
|
What are the different methods for signal action? |
Endocrine Paracrine Neuronal Contact dependent |
|
|
What happens when a signal binds to a receptor? |
Binding of a signal to a receptor generates abiological response within target cell |
|
|
What signals to receptors bind? |
Receptors bind signals with high selectivity and highaffinity Receptors have to be turned off (time delay) |
|
|
What are examples of intracellular signals? |
e.g. Steroid hormones -OestradiolTestosterone |
|
|
What are ion channel membrane receptors? |
Ion Channels flow of ions across the membranechanges membrane potentiale.g. Nicotinic acetycholine receptor |
|
|
What are enzymatic signal receptors? |
Enzymatic protein kinasese.g. EGF receptor |
|
|
What are G-protein-coupled receptors? |
G-protein -coupled receptors (GPCR) G protein activates enzyme or ionchannele.g. Adrenaline receptor |
|
|
What ions do ion channel membrane receptors respond to? |
Na+, K+, Ca2+ |
|
|
What are proteins phosphorylated on in enzymatic membrane receptors? |
Proteins are phosphorylated on serine, threonineand tyrosine amino acids |
|
|
What are G-protein coupled receptors? |
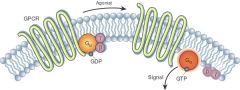
G-protein-coupled receptor: B-adrenergic receptor |
|
|
What do receptors induce? |
Receptors can induce production ofsecond messengers Signal = first messenger |
|
|
What are some examples of second messengers? |
cyclic AMP IP3/DAG Ca2+ nitricoxide cyclic GMP |
|
|
What are second messengers generally produced by? |
Second messengers are generally producedby the activation of effector enzymes |
|
|
what does ADENYLYL CYCLASE produce? |
adenosine 3’:5’-cyclicmonophosphate (cAMP) |
|
|
What does PHOSPHOLIPASE C produce? |
inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate (IP3) 1,2-diacylglycerol (DAG) |
|
|
What are G-proteins? |
Guanine nucleotide binding proteins(G-proteins) |
|
|
What happens when GTP binds to G proteins? |
Dissociates when GTP binds Free active Ga subunit activates effector enzymes Complex re-associates when GTP hydrolysed toGDP by a GTPase activity |
|
|
What happens in GPCR SIGNALLING TO EFFECTOR ENZYMES? |
1. Signal (e.g. adrenaline) binds to receptor 2. G-protein (GDP bound) associates withreceptor 3. GTP/GDP exchange on G-protein (GTP bound) 4. G-proteins dissociates into a (GTP bound) and By subunits 5. a subunit (with GTP bound) activates effectorenzyme 6. Effector enzyme produces 2nd messenger 7. GTP hydrolysed to GDP, G-protein complexreassociates, signalling ends |
|
|
What does cAMP look like? |
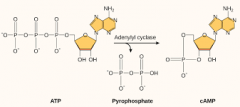
|
|
|
What happens in the Activation of protein kinase A by cAMP? |
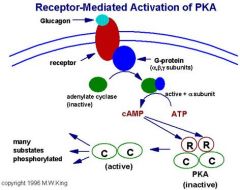
|
|
|
Where are proteins phosphorylated? |
phosphorylation of proteinson serine and threonineamino acids |
|
|
What do cAMP and PKA regulate? |
cAMP and PKA regulate metabolism “Fight or Flight” Adrenaline in muscle: B-adrenergic receptor |
|
|
what happens in the RECEPTOR ACTIVATION OF PHOSPHOLIPASE C? |
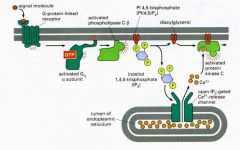
|
|
|
Why is Ca2+ an important signal? |
Concentration gradient of Ca2+ makes it an important signale.g. stimulates secretion of neurotransmitters in the brain |
|
|
What is PKC activated by? |
Protein kinase C is activated by DAG and Ca2+ |
|
|
What does PKC do? |
Protein kinase C phosphorylates proteins PKC phosphorylates different proteins to PKAe.g. proteins involved in neurotransmitter secretion (brain) |
|
|
How do different G-protein coupled receptors cause different responses? |
Different G-protein coupled receptors signal throughdifferent G-proteins to different responses |
|
|
What is the G-protein involved in B-adrenergic receptors and what is the effector enzyme? |
Gs Adenylylcyclase increasescAMP |
|
|
What is the G-protein involved inProstaglandin receptors and what is the effector enzyme? |
Adenylylcyclase decreases cAMP |
|
|
What is the G-protein involved in a1-adrenergic receptors and what is the effector enzyme? |
Gq Phospholipase C IP3(releaseof Ca2+ fromstores), DAG |
|
|
what is a summary of cell signalling? |
Binding of extracellular signalling molecules to cell surfacereceptors activates intracellular signalling pathways. G-PROTEIN COUPLED RECEPTORSe.g. Adrenaline receptors • activate adenylyl cyclase, phospholipase C • generate cAMP, IP3 DAG and Ca2+ as 2ndmessengers • Activate protein kinase A and protein kinase C |

