![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
23 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
How does structure dictate function? |
-the greater the surface area available for diffusion/transport (FLOW) , the greater the conductance |
|
|
What increases surface area? |
-folds increase surface area and therefore conductance |
|
|
What are the sources of substrate? |
-Exogenous: Gastrointestinal System -endogenous: liver and adipose tissue |
|
|
Functions of the Liver |
1.Filtration and storage of blood 2.Metabolism of CHO, Fat, and Protein 3.Formation of Bile 4.Storage of vitamins and iron 5.Formation of coagulation factors |
|
|
Why Liver Carbohydrate Metabolism ? |
-are large glycogen stores important for maintenance of blood glucose can store and release glucose when needed - very important during exercise |
|
|
Steps of Glycogenolysis |
glycogen breakdown 1.Glucose removed by Glycogen Phosphorylase(PHOS) 2.G-6-P converted to Glucose byG-6-phosphatase (removal of Pi) 3.Glucose released into circulation |
|
|
Gluconeogenesis |
-formation of glucose from protein and glycerol -importance for maintenance of blood glucose during fasting conditions |
|
|
Steps of Gluconeogenesis |
sythesis of glucose 1.Amino acids/lactate/pyruvate converted toG-6-P by PEPCKand reverse glycolysis 2.G-6-P converted to Glucose by G-6-phosphatase (removal of Pi ) 3.Glucose released into circulation |
|
|
Liver Fatty Acid Metabolism |
•Synthesisof cholesterol and phospholipids –Phospholipids contain FFA •Shippedto other organs and used to synthesize membranes •FFAalso a source of substrate for energy production |
|
|
Why is liver fatty acid metabolism important ? |
•Synthesisof fat from protein and carbohydrate –Almost all of the TG synthesis from CHOoccurs in the liver –Once formed TG are transported to adiposetissue and stored –Can also be utilized by other tissue formetabolism |
|
|
What are the dangers of fructose ? |
-small intestine can only absorb a limited amount of glucose per hour -however, can absorb fructose at the same time -unlike glucose, fructose is almost exclusively converted to fat in the liver |
|
|
Cirrhosis |
-replacement of liver tissue with fibrous tissue leading to lose of liver function -alcoholism, hepatitis , fatty liver disease |
|
|
Where is glucose provided from during exercise ? |
by the liver via glycogenolysis andgluconeogenesis |
|
|
Sources of Substrate? |
GI Tract - digestion and absorption of fat and CHO Liver –Triglyceride Storage –Glycogenolysis –Gluconeogenesis –Fatty Acid Synthesis |
|
|
What are adipose tissues? |
-very simple cells made up of 80-95% triglyerides -function to store fat and release it when needed |
|
|
Re-esterification |
occurs when FA-CoA and Glycerol combine to form triglycerides ( mechanism that suggest that blood flow plays a role in regulation of FFA release ) |
|
|
What are two insulin- contained receptors ? |
FAT CD36 and GLUT 4 |
|
|
uses of adipose tissue |
•Adiposetissue stores large amounts of TGs •TGsare broken down to form FFA by lipases •FFAthen enter the blood and are taken up and metabolized by muscle and otheractive tissue |
|
|
Lipolysis |
is the breakdown of lipids and involves hydrolysis of triglycerides into glycerol and free fatty acids |
|
|
Adipose Tissue Lipases |
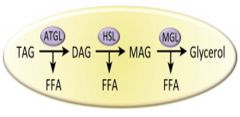
adipose-enriched protein with triglyceride-specific lipase activity |
|
|
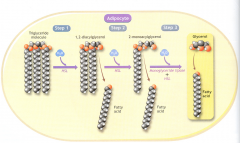
Skeletal Muscle Lipases |
|
|
|
What is an important source of substrate for exercise ? |
FFA |
|
|
What is the 3 step process in the hydrolysis of TG? |
•Adipose triacylglyceridelipase (ATGL) »Cleaves TG •Hormone sensitive lipase »Cleaves DG •Monoacylglyceride lipse »Cleaves MG |

