![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
24 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Describe Genu Recurvatum
|
Hyperextension of the knee
Can be due to Equinus, Neurological disease Weak Quads Hyperpronation |
|
|
What causes the hyperextension of the knee in Genu Recurvatum?
|
if the tibia cannot move forward (equinus), then the upper body because of momentum continues forward causing hyperextension.
If the knee cannot flex (weak hamstrings or tight quads) hyperextension occurs. |
|
|
What is the cause of External vs internally rotated recurvatum?
|
External-severe,
due to equinus Internal- usually mild due to Hyperpronated foot |
|
|
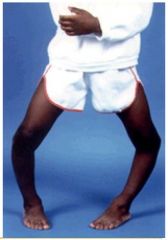
To what age is genu varum normal?
|
Normal up to age 3.
|
|
|
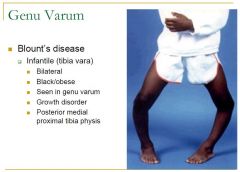
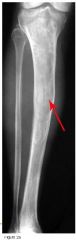
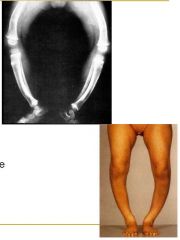
What can be some causes of Genu Varum?
|
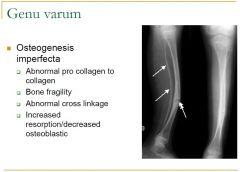
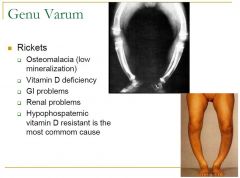
Blounts
Ricketts Trauma Osteogenesis imperfecta Metaphysal chondrodysplasia |
|
|
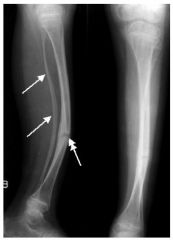
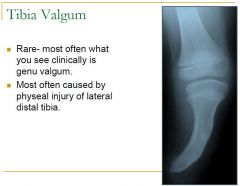
What is an osteochondroma?
|
the most common type of bone tumor,
Has a cartilaginous cap |
|
|
What is metaphyseal condrodysplasia?
|
An inherited disorder that causes bowing of limbs
|
|
|
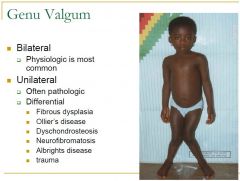
Genu Valgum Bilateral vs unilateral
|
Bilateral- physiologic, most common
Unilateral- often pathologic with many differential diagnoses. |
|
|
during what period is Genu valgum normal?
|
Physiologically normal from 4-8.
By 9 years of age slight valgum or neutral is normal |
|
|
What is the source of physiologically normal genu valgum
|
(4-9yrs)
Medial femoral condyle is longer |
|
|
Describe Tibial varum
|
Frontal plane deformity of the distal tibia in regards to proximal tibia
Adult normal is 2-3 degrees. greater than 5 and the STJ must pronate to get foot flat on the ground. |
|
|
What is pseudolack of malleolar torsion?
|
Tibia looks like it did not undergo normal external rotation.
It is a soft tissue problem at the knee (laxity) Presents as intoeing usually. |
|
|
What is Internal Tibial Torsion?
|
True lack of normal ontogeny.
Most common cause of intoeing. |
|
|
What are statistical deformities that accompany Internal tibial Torsion?
|
Seen in 2nd year
M=F 1/3 will have met adductus 2/3 will be bilateral |
|
|
What is the Q angle?
|
Quadriceps angle formed by the measurement of the ASIS to the center of the patella and the tibial tuberosity ot the center of the patella.
|
|
|
What are the normal values for q angle?
|
male 0-15 degrees
Female 0-20 degrees |
|
|
What increases with increased Q angle?
|
The higher the Q angle the more lateral the pull on the patella.
|
|
|
|
|
|

|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
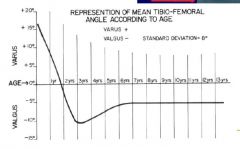
What is the normal pattern for genu valgum/varum in development?
|
|

