![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
60 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Acetic acid
|
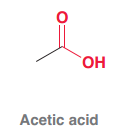
|
|
|
Butanoic acid
|
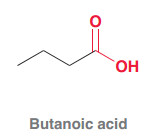
|
|
|
Lactic Acid
|
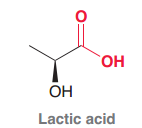
|
|
|
Formic acid
|
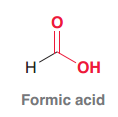
|
|
|
Butyric acid
|
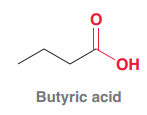
|
|
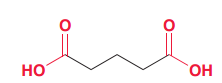
Name following compound?
|
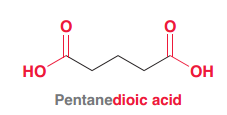
|
|
|
Oxalic acid
|
![[memorize: ~oskol =>just two aceticacid group attached to each other]](https://images.cram.com/images/upload-flashcards/1028804/2376835_m.png)
[memorize: ~oskol =>just two aceticacid group attached to each other]
|
|
|
Malonic acid
|
![[memorize: ~mal => 2 be 1 malidan]](https://images.cram.com/images/upload-flashcards/1028804/2376838_m.png)
[memorize: ~mal => 2 be 1 malidan]
|
|
|
Succinic acid
|
![[Memorize: suski ke docharkhe savar mishe]](https://images.cram.com/images/upload-flashcards/1028804/2376841_m.png)
[Memorize: suski ke docharkhe savar mishe]
|
|
|
Write down Henderson-Hasselbalch equation to calculate pH of buffered solutions?
|
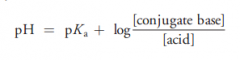
|
|
|
If an acide dissolved in a buffered solution, when the pH of the buffere solution is equal to pKa of the acide, what is the ratio of the acid and its conjugate base?why?
|
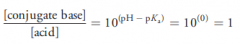
An acid and its conjugate base will be present in approximately equal amounts (due to Henderson-Hasselbalch equation for calculation of pH of a buffer)
|
|
|
carboxylic acids will exist primarily as …… (caroxylic acid / carboxylate salts) at physiological pH. Why?
|
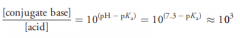
carboxylate salts (because according to Henderson-Hasselbalch equation concentration of conjugate would be 1000 times more than acid. Notice Pka of most of carboxylic acids is between 4 and 5):
|
|
|
How to convert alkyl halides to carboxylic acids with one more carbon?
|
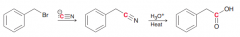
1.SN2 reaction with CN- /2.Acidic hydrolysis of CN group
|
|
|
How we can make carboxylic acids from grignard reagents?
|
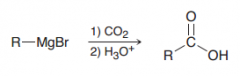
Reacting with CO2
|
|
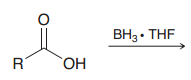
|
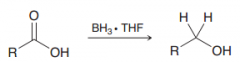
Borane can selectively reduce carboxylic acids to alcohols
|
|

|
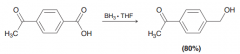
borane reduces selectively a carboxylic acid moiety in the presence of another carbonyl group
|
|
|
Name four major groups of carboxylic acid derivatives?
|
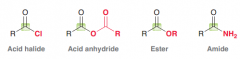
Acid halides, Acid anhydrides, Esters, Amides
|
|
|
What is the result of acidic hydrolysis of carboxylic acid derivatives? a.acide chlorides b. acid anhydrides c.esters d.amides
|
All will be converted to their corresponding carboxylic acid
|
|
|
Acid halide?
|
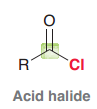
|
|
|
Acid anhydride
|
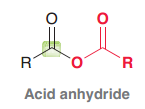
|
|
|
Ester
|
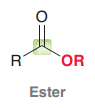
|
|
|
Amide
|
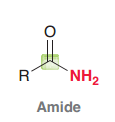
|
|
|
Nitrile
|

|
|
|
Are nitriles considered as carboxylic acid derivatives? Why?
|
Yes. Because like carboxylic acids the central carbon has three bonds to more electronegative elements therefore has the same oxidation state as carboxylic acid
|
|
|
Succinic anhydride
|
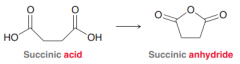
|
|
|
Acetamide
|
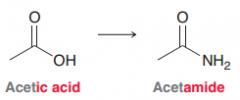
Amide made from acetic acid
|
|
|
Benzamide
|
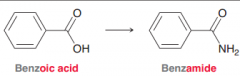
|
|
|
N-Methyl acetamide
|
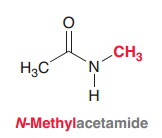
|
|
|
Benzonitrile
|
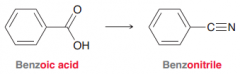
A nitrile derivated from benzoicacid
|
|
|
Rank acid halides, acid anhydrides, esters and amides according to reactivity toward nucelophiles?
|
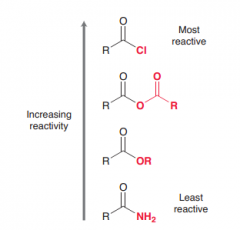
Acid halides > ancid anhydride > Esters > Amides (due to ability to contribute to stabilize positive charge by resonance)
|
|
|
Discuss the possibiblity of the conversion of four major carcboxylic acid derivates to each other by a simple acyl substitution?
|
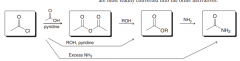
the more reactive carboxylic acid derivatives can be converted to the less reactive derivative by a simple acyl subsitution . (Acid chlorides can be converted to acid anhydrides, esters and amides / acid anhydrides can be convereted to esters and amides/ Esters can be converted to amindes )
|
|
|
What is the hybridization of nitrogen in amides? Why? What geometry they adapt?
|
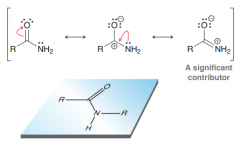
Sp2 (not sp3! As expected because in resonance structure The p orbital on the carbon atom effectively overlaps with
a p orbital on the nitrogen atom) =>trigonal planar |
|
|
Define nucleophilic acyl substitution?
|
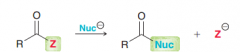
Where z is a good leaving group (not H and R)
|
|
|
Explain when nucleophilic attack on C=O leads to and addition and when to a substitution?
|
When a nucleophile attacks a carbonyl group to form a tetrahedral intermediate, the carbonyl group
will always be re-formed, if possible, but H– and C– are never expelled as leaving groups |
|
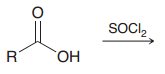
|
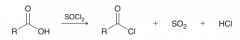
Formation of acid chlorides
|
|

|
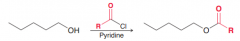
Name: Acylation of OH group or Alcoholysis of Acid chlorides or (acyl substitution)
|
|
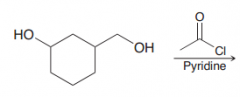
|
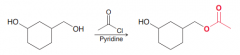
Name: Acylation of OH group (acyl substitution) is sensitive to steric hindrance so primary is preferred over secondary
|
|
|
What is the result of Aminolysis of Acid Chlorides?
|
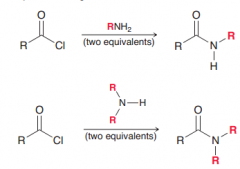
formation of Amides
|
|
|
LiAlH4 is a very strong hydride reducing reagent. Propose a hydride reducing reagent which is moderate (for exmaple reduces acid chlorides to aldehyes not all the way down to alcohol?
|
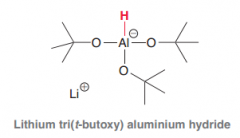
tri(t-butoxy) aluminum hydride (bulky and just one mole of hydride exists. Unlike LiAlH4 which has four hydrides)
|
|
|
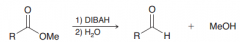
What is DIBAH? What is good for?
|
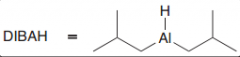
DIBAH = diisobutylaluminiumhydride / it's a moderate reducing reagentso it just able do acyl substitution on carboxylic acid derivtives to give aldehydes (unlike LiAlH4 which goes all the way down to an alcohol)
|
|

|
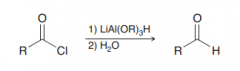
Acyl substation by LiAl(OR)3H (which is a mild hydride reducing reagent so it won't recduce the C=O all the way down to an alcohol. It stops at aldehyde)
|
|
|
What's Gilman reagent? What is used for?
|
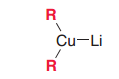
A lithium dialkyl cuprate. It provide carbon nuclephiles with mild reactivity which can perform substitution on C=O but not addtion.
|
|
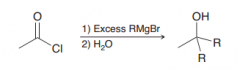
|
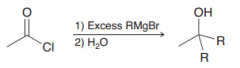
two Nuclephilic attack of the carbon nucleophile of Grignard reagent (1.acyl substitution and then addition 2.protonation)
|
|
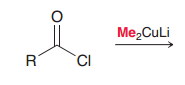
|
Reaction of C=O with Gilman reagent. (carbon nucleophile of Gilman reagent is not as strong as carbon nucleophile of Grignard reagent so it is just able to do acyl subsitution but not addition)
|
|

|
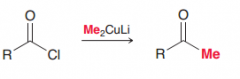
Acyl substitution. (the more reactive carboxylic acid derivatives can be converted to the less reactive derivative by a simple acyl subsitution . e.g. Esters can be made from acid anydrides)
|
|
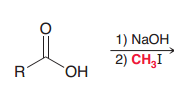
|
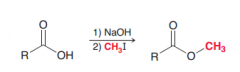
1. Deprotonatin 2.Simple SN2 reaction
|
|
|
Define Fischer esterification?
|
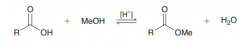
Carboxylic acids are converted into esters when treated with an alcohol in the presence of an acid catalyst. This process is called the Fischer esterification
|
|
|
Define saponification?
|
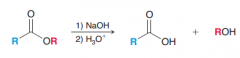
Esters can be converted into carboxylic acids by treatment with sodium hydroxide followed by an acid.
|
|
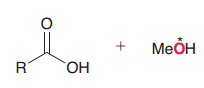
In the following Fischer esterification explain wehere the 18O would be in the product?
|
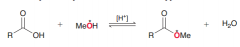
Since RO attackes, 18O would be in the ester and carboxylic acid OH will turn to water
|
|
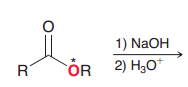
Explain place of 18O in the products in the following saponification reaction?
|
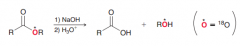
Since OH attacks to make tetrahderal and then RO kicks out, 18O with be in ROH
|
|
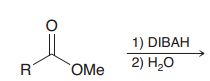
|
DIBAH = moderate hydride reducing reagent (1.just one acyl substitution / 2.protonation)
|
|
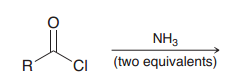
|
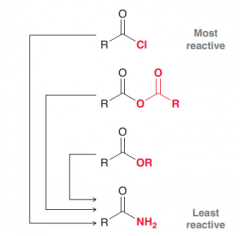
Acyl substittion (Amides can be prepared from any of the other 3 carboxylic acid derivatives because it is the least reactive one)
|
|
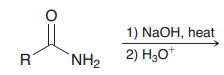
|
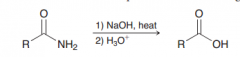
Basic hydrolysis of amides (which like acidic hydrolysis yields carboxylic acids)
|
|

|
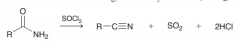
Preparation of nitriles from amids
|
|
|
What would be the result of acidic (H3O+) or basic (1.NaOH, H2O 2.H3O+) hydrolysis of nitriles?
|
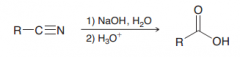
Carboxylic acids (e.g. the following basic reaction)
|
|
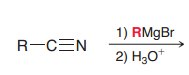
|
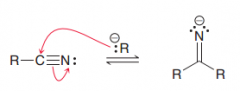
1. Creation of imine (by a nucleophililic attack) 2.acidic hydrolysis of imines
|
|

|
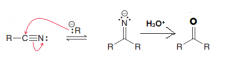
1. Creation of imine (by a nucleophililic attack) 2.acidic hydrolysis of imines
|
|
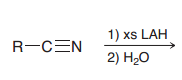
|
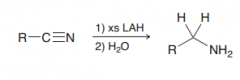
1.two successive Hydride attack 2.protonation (of nitrogen)
|
|
|
Explain C-C bond forming reactions of carboxylic acid derivatives?
|
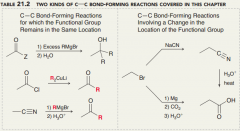
a. Making C-C connection b. makind C-C connection with an extra carbon
|
|
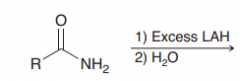
|
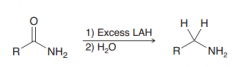
Amides in the presence of LAlH4 are reduced to CH2 (against expectation of hydride attack on C=O)
|

