![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
35 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What does "laser" stand for?
|
LASER = light amplification by stimulated emission of radiation
|
|
|
What is the process of spontaneous emission?
|
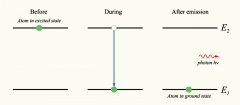
photons being emitted after high energy electrons decay to their lower energy "ground state"
most of these spontaneously emitted photons are absorbed and decay, however, photons emitted in the direction of the long axis of the resonant cavity are retained as they bounce between the two mirrors of the laser. |
|
|
What is the process of stimulated emission?
|
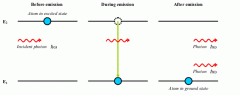
When photons encounter an atom in the excited state, they stimulate an excited electron to decay to its ground state, and emit another photon of the SAME wavelength in the SAME direction.
This amplifies the light. |
|
|
What is the process of population inversion?
|
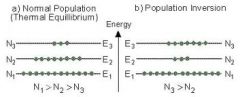
When more than half of the atoms in the active medium reach the high-energy state, population inversion occurs.
This is a necessary condition for a laser to start working. |
|
|
What are properties of laser light?
|
Monochromatic
Unidirectional Uniform in phase and polarization Spreads over distances, and can be focused with lenses Once laser light exits the main resonance chamber, it has to be delivered to tissue via optical fibers or waveguides. |
|
|
How does tissue interact with laser light?
|
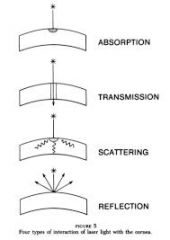
tissue interacts ONLY with laser light that is ABSORBED, not reflected, transmitted, or scattered
|
|
|
Visible and infrared (IR) lasers used in ENT work by heating tissues, photodissociation of bonds, or both?
|
heating tissues only; laser is absorbed and converted to heat
|
|
|
What is thermal relaxation time?
|
time needed for tissue to dissipate HALF of its heat.
|
|
|
What are the layers of laser wounds?
|
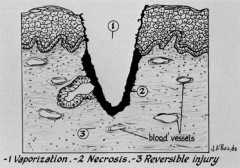
Tissue vaporization
Necrosis Thermal conductivity and repair (reversible damage) |
|
|
What is done to minimize thermal injury?
|
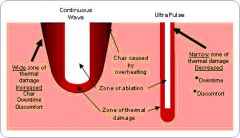
High laser energy is delivered in short pulses and by allowing time for heat to diffuse between pulses
|
|
|
What are the laser parameters that are under surgeon's control?
|
Power
Spot size Exposure time |
|
|
What is the argon laser used for?
|

Argon (514 nm - blue green) - transmits easily through clear tissues.
Light is absorbed by hemoglobin and pigment tissues. Used for photocoagulation of pigmented lesions, port-wine stains, hemangiomas and telangiectasias, middle ear and STAPES surgery. |
|
|
What is the copper vapor laser used for?
|
Copper vapor (511 nm--green, 578 nm--yellow)
The green 511 nm laser is best absorbed by melanin and is used to treat superficial pigmented lesions, cafe au lait spots, nevi and freckles. The yellow 578 nm variety is better absorbed by hemoglobin and is used for vascular lesions. |
|
|
What is the KTP laser used for?
|
KTP = potassium titanyl phosphate, 532nm - green
Absorbed by hemoglobin even better than argon gas. Used for pigmented dermal lesions, port-wine stains, middle ear, and stapes surgery. Light can easily be delivered through a flexible fiberoptic bronchoscope for management of tracheobronchial lesions. KTP laser has been used in endoscopic sinus surgery and management of sinonasal polyps. Major advantage of the KTP laser in sinonasal surgery is excellent HEMOSTASIS! |
|
|
What is the tunable dye laser used for?
|
Tunable dye laser (585 nm--yellow) - dye is chosen for best absorption by hemoglobin.
Used for treatment of vascular lesions such as hemangiomas and port-wine stains. |
|
|
What is the ruby laser used for?
|
Ruby laser - 694 nm--red - absorbed by melanin
This laser was used for hair and tattoo removal, works best in patients with light skin complexion |
|
|
What is the alexandrite laser used for?
|
Alexandrite laser - 755nm--red; absorbed by melanin
Frequently used for hair and tattoo removal in pts with a range of Fitzpatrick skin types |
|
|
What is the Nd:YAG laser used for?
|
Nd:YAG = neodymium yttrium aluminum garnet, 1.06μm--near IR
Produces a layer of tissue coagulation and necrosis 4mm deep, but precise control is NOT possible This laser allows good control of hemorrhage Used for palliation of obstructive esophageal and tracheobronchial lesions, photocoagulation of vascular lesions, and lymphatic malformations. Nd:YAG laser CAN be transmitted through optical fibers, allowing easy delivery via flexible endoscopes |
|
|
What is the Er:YAG laser used for?
|
Erbium yttrium aluminum garnet - 2.94μm--near IR
This laser wavelength is near the peak of water absorption, resulting in very shallow tissue penetration. It produces a clean incision with minimal thermal damage to adjacent tissue. Because of shallow penetration, hemostasis is difficult. Used for facial skin resurfacing and epidermal lesions. |
|
|
What is the CO2 laser used for?
|

CO2 laser -- 10.6μm - IR - this wavelength is invisible and needs a coaxial helium-neon (He-Ne) red laser as an aiming beam.
**CO2 laser is strongly absorbed by tissues with high water content. Tissue penetration is shallow. Advantages include precision and good hemostasis of small vessels. This wavelength cannot be delivered via optical fiber, however specialized flexible waveguides (OmniGuide; image) have been developed that allow delivery of this infrared wavelength directly to the tissues through a handpiece. The CO2 laser is the most widely used laser in ENT. |
|
|
What are the semiconductor (diode) laser used for?
|
Semiconductor (diode) lasers are available in several wavelengths.
Advantage = compact size (ie..think of the laser used to read CD's/DVD's) Used in variety of ENT procedures. |
|
|
Lasers targeting hemoglobin and vascular lesions generally have short wavelengths of less than _________
|
700nm
|
|
|
List which lasers are used in the middle ear and stapes surgery.
|
Argon
KTP CO2 (less popular now) |
|
|
What are the properties of lasers used for facial skin resurfacing?
|
Operate in the infrared range (Er:YAG - 2.94μm, CO2 - 10.6μm)
Well absorbed by water Shallow tissue penetration |
|
|
What's the difference between CO2 and Er:YAG lasers in skin resurfacing?
|
CO2 laser removes 50-100μm of surface tissue in one pass
- allows for "bloodless" skin resurfacing because small blood vessels in target skin are coagulated. - skin reepithelializes within 2 weeks Er:YAG is superbly absorbed by water, resulting in very shallow tissue penetration depth. Energy is absorbed in the epithelium, therefore this lase is used for skin with mild to moderate signs of aging, predominantly in the epidermis. Removes 25-30μm of surface tissue. Some bleeding occurs with this laser, as the light is unable to coagulate the small vessels within the targe skin. Skin reepithelializes in 5-7 days. |
|
|
Which two lasers are best for tattoo removal?
|
Ruby
Alexandrite |
|
|
What are some preop considerations for laser skin rejuvenation?
|
herpes prophylaxis started 24hrs prior to procedure and continues until 10th POD.
pseudomonas coverage with ciprofloxacin |
|
|
List the complications of laser skin resurfacing
|
prolonged erythema
scarring hyperpigmentation (Fitpatrick skin types III and greater have a higher risk of pigmentary changes) |
|
|
What are contraindications of laser skin resurfacing?
|
Isotretinoin (accutane) in the past 1-2yrs, as this could impair re-epithelialization
Scleroderma active acne Hx of facial burns H&N radiation therapy |
|
|
What are some anesthesia precautions that are important while using lasers in the OR?
|
Reducing partial pressure of O2 in the inhaled gas mixture to a minimum when lasing in the airway
Wavelengths-specific endotracheal tubes Nitrous oxide should be avoided durnig laser surgery (may use halothane, enflurane, and isoflurane) |
|
|
What is radiofrequecy surgery? Explain radiofrequency energy.
|
Radiofrequency energy is delivered to tissue where particles are IONIZED and a layer of plasma develops.
The high-energy plasma particles are capable of causing bond dissociation in tissue at relatively low temps (40-70*C). This allows tissue removal, tissue shrinkage, or vessel coagulation without significant thermal damage |
|
|
When was radiofrequency ablation tonsillectomy introduced?
|
Radiofreq ablation tonsillectomy = coblation, was introduced in 2001.
|
|
|
A 2008 meta-analysis found that radiofrequency surgery at the tongue base and palate in OSA pts results in ___% reduction in long-term (>24 months) respiratory distress index (RDI).
|
45%
|
|
|
Where is the neurovascular bundle in relation to the foramen cecum?
|
2.7cm deep and 1.6cm lateral to foramen cecum
|
|
|
In general, lasers with longer wavelengths have shorter or deeper tissue penetration?
What laser is an exception to this rule? |
Longer wavelength = deeper penetration
Exception is CO2 laser (10.6 μm) |

