![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
31 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
How can marketers trigger consumer motives |
Inducing need recognitions |
|
|
|
Maslow Hierarchy of needs |
1) psychological 2) safety 3)Social 4) Egotistic 5) self actualization |
|
|
|
Marketing implications |
Ads must link the product appeals to specific needs |
|
|
|
Utilitarian vs. Hedonic Motives |
Rational vs. Emotional motives to purchases. Utilitarian buys to achieve Hedonic buys to satisfy |
|
|
|
Motivational conflicts |
As a form of goal seeking behavior, motivation usually involves 3 forms of conflicts 1) approach-approach conflict Choice of 2 desirable alt. 2) approach-avoidance conflict Products we want have negative effects 3) avoidance-avoidance conflict Choice between 2 unwanted alt. |
|
|
|
Consumer Involvment |
Degree of personal relevance a consumer finds a value from a given consumption act
Types: product Shopping Situational: feelings a customer feels in a situation when he thinks of a product Enduring: feelings felt toward a product category that are persistent over time Emotional |
|
|
|
CAT |
How we feel after what just happened
Appraisals 1) anticipation- focuses on future 2) agency- responsibility for events 3) equity- how fair some events are 4) outcome appraisal- how something turned out Advertisers can induce these emotions through ads to affect their attitude towards a product |
|
|
|
Moods |
Less intense than emotions they are always changing. Consumers can be aware of them |
|
|
|
Mood congruent judement |
Value of target is influenced in a consistant way by ones mood Negative moods will make negative evaluations Positive mood will seek variety increasing willingness to try new things |
|
|
|
Freudian Theory |
Childhood experience determines personality Structure of personality 1) ID - Primitive and impulsive drives 2) superego - societies moral and ethics 3) Ego- balance of Id and superego In marketing, make ego over superego win. Stimulate ID, SuperEgo |
|
|
|
Karen Horney |
Characterized behavior by 3 orientations 1) Compliant Individuals - move towards others, desire to be loved wanted and appreciated 2) aggressive individuals - against others, need for power 3) Detached Individuals - move away from others, introverted |
|
|
|
Motivation Research |
Underlying unconscious motives that influence customer behavior. Helps identity influences that customer may not be aware of. What motives people to purchase? Woman buy more physical appearance as they age |
|
|
|
Trait Approach |
Measures personality in terms of traits Value consciousness - bargain hunters, coupon clippers Materialism - possessive, envious Innovativeness Compliant Process Need for cognition - humor, sex Competitive- social comparison Generalized self confidence - conformable in making decisions Self consciousness - self image Optimum stimulation level - people have greater desire to explore environment. Impulsiveness - likely to buy a product they do not need |
|
|
|
5 factor model - big 5 personality trait |
1) openness/creativity - creative 2) conscientiousness- efficient carless 3) extroversion - outgoing 4) agreeableness - friendly compassionate 5) neuroticism/stability - sensitive nervous |
|
|
|
Brand personality dimension |
Human characteristics associated with a brand. Opp. To build brand relationship with consumers. |
|
|
|
Lifestyles |
How consumers live and spend their time and money. Values on family, work, leisure, religion, education. |
|
|
|
Psychographics and AIO |
The way consumer lifestyles are measures AIO - Activities Interests Opinions Activities: Work, hobbies, social events Interests: Achievement, reaction, community, family, food Opinions: business, social issues, politics, education |
|
|
|
VALS |
Divides us adult consumers into 8 groups, firs ton the basis of motivations and then on the basis of resources to which they have access. |
|
|
|
PRISM |
Potential Ratings Index by Zip Market Based on premises that people with similar backgrounds and means to tend to live close to one another and emulate others behaviors and lifestyles 66 segments |
|
|
|
Self Image |
Consumers self concept plays a significant role in predicting and explaining behavior Actual self Social self Ideal self Ideal social self |
|
|
|
Forms of self image |
1) actual self - try to protect their personal identity 2) ideal self - motivates behavior through self esteem motive 3) social self - influences behavior through consistency motive 4) ideal social self - Influences behavior through social approval motive |
|
|
|
Extended self, Self Esteem, Self Congruency, Symbolic Consumption |
Extend self: Various possessions that help the consumer form perceptions about himself Self Esteem - positive about oneselces Self congruency - does the store match your self concept? Theory: Proposes that much of the consumers behavior can be explained by the match between self concept and the image of typical users of a focal product Symbolic consumption- consumers buy and use goods and services not just for their utkity but for what they mean |
|
|
|
Consumer Attitudes |
Not all attitudes are equal 1) compliance - formed to gain reward or avoid punishment 2) identification - formed to conform with others 3) internalization - has to become part of a persons value system rhatcis hard to schange once formed |
|
|
|
ABC attitude approach |
Affect - I really like my Honda civic Behavior - I always buy Honda Products Cognition - My Honda civic gets good gas mileage |
|
|
|
Functions of consumer attitudes |
Utilitarian Knowledge Value expressive Ego defensive |
|
|
|
Fishbein Model |
ATO strategy for attitude change Suggest changes based on diagnosis of brand strengths and weaknesses on relevant product attributes 1) product involvement 2) increase the importance 3) add an new attribute 4)decrease the importance of a weak attribute 5) decrease belief ratings for competitive brands |
|
|
|
Elaboration Likelihood model (ELM) |
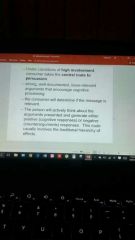
Once a consumer receives message he will being to process it.
|

|
|
|
Balance Theory |
Considers relations among elements a person might perceive as belonging together. Each contain A person and his perceptions An attitude object Some other person or object Either positive or negative Altered to make them consistent Balance theory accounts for the widespread use of celebrities in advertising Unbalanced triad: 1) Jane likes Larry 2) Larry wears and earring 3) Jane does not like men wearing earnings Solution: 1)Jane does not like Larry 2) Jane tries to negate the unit relation between Larry and earrings. (He's doing it for fashion) 3) Jane attitude towards earrings become. Postitive. |
|
|
|
Social Judgement Theory |
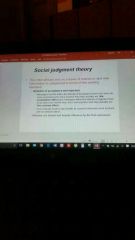
|

|
|
|
One vs Two Sided argument |
Ads that have One sided messages - only positive messages Two sided messages - give positive and negative info and more credible |
|
|
|
Source Effects |

Credibility Attractiveness Likeability Meaningfulness |
|

