![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
14 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
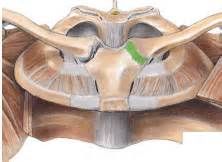
Sternoclavicular
Location: clavicle to sternum Function: provides stability to the joint , its considered the joint capsule |
|
|
|
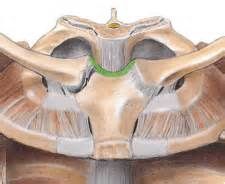
Interclavicular
Location: top of manubrium, connects the superior sternal ends of the clavicle Function: limits the amount of clavicular depression |
|
|
|
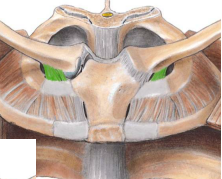
Costoclavicular
Location: short, flat, rhomboid shaped that connects the inferior surface of the clavicle to the superior surface of the costal cartilage of the first rib. Function: limits clavicular elevation |
|
|
|
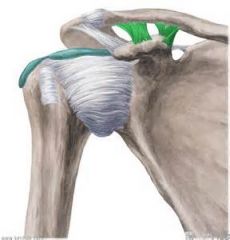
Coracoclavicular comprised of the : trapezoid & conoid
Location: superior border of the coracoid process to the inferior border of clavicle Function: not directly on jt but provides stability of the jt |
|
|
|
Coracoacromial
Location: from tip of coracoid process to acromian Function: forms arch of the head of humerus |
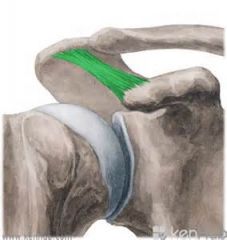
|
|
|
Superior Glenohumeral
Location: froms jt capsule Function: restricts ER jt in neutral abduction |
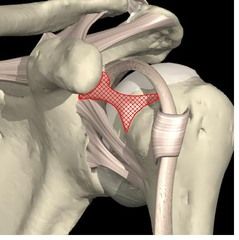
|
|
|
Middle Glenohumeral
Location: forms jt capsule Function: restricts ER @ 45 degrees of abduction |
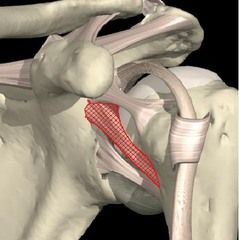
|
|
|
Inferior Glenohumeral
Location: forms jt capsule Function: restricts ER @ 90 degrees of abduction |
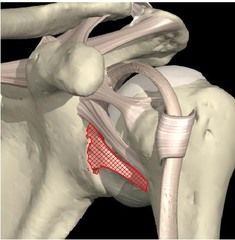
|
|
|
Coracohumeral
Location: stretches from coracoid process to greater tubercle Function: provides stability to the joint |
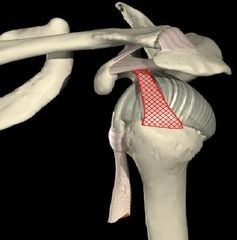
|
|
|
Transverse
Location: covers the bicipital groove Function: keeps the long head of the bicep brachii in the bicipital groove |
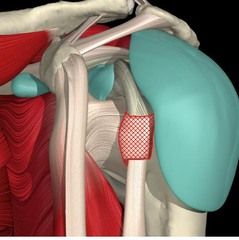
|
|
|
Axillary pouch or axillary recess
Location: inferior side of the glenohumeral jt Function: allows for abduction -if immobilization occurs, the plates will adhere to themselves and will theres no opening. will only get rolling of the shoulder, no motion, restricted abduction |
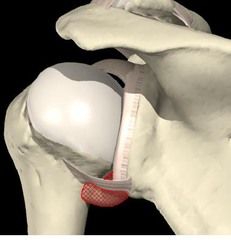
|
|
|
scapulohumeral rhythm
|
-the first 30 degrees of shoulder joint motion is pure shoulder joint motion
-after the first 30 degrees, every 2 degrees of shoulder flexion or abduction must be accompanied by 1 degree of upward rot. of the scapula (2:1 ratio) |
|
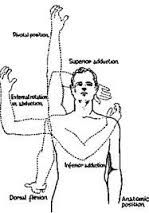
codmans paradox
|
normal shoulder motions used to not place any stress on the humerus. The point is to not stress the humerus
|
|
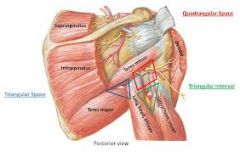
quadrangular space
|
emerges the axillary nerve. impingement can cause lack of lift from the deltoids. hypertrophy of tight fascia can restrict this nerve
Borders: Muscles superior: teres minor inferior: teres major medial: long head of triceps lateral: neck of the humerus Artery: circumflex humeral artery, Nerve: axillary |

