![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
143 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
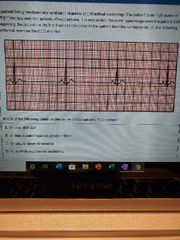
When using a flow-inflating resuscitation bag during mechanical ventilation of a neonate, the FiO2 received by the neonate is determined by: A. FiO2 of gas delivered to the bag B. The size of O2 reservoir C. The oxygen flow rate D. How much the bag is compressed |
A |
|
|
A |
|
|
C |
|
|
C(a-v)O2 formula |
[(Hbx1.34xSaO2) + (PaO2x0.003)] - CvO2 |
|
|
Normal C(a-v)O2 |
4-5% |
|
|
Shunt shortcut |
5% + 5% for every 100 mmHg A-a |
|
|
Water seal spirometer |
|
|
D |
|
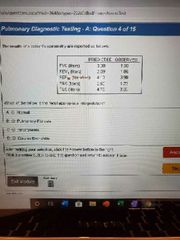
|
B. |
|
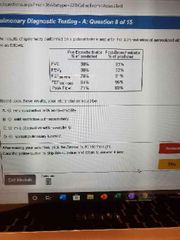
|
D |
|
|
Which of the following structures are visualized in a patient with mallampati class 2? A. Soft palate, uvula, fauces, and pillars B. Soft palate, uvula, fauces C. Soft palate and base of uvula D. Hard palate only |
B |
|
|
While monitoring the pressure wave form during insertion of a Swan-Ganz catheter, the RT notes the presence of a dicrotic notch. This indicates that the tip of the catheter is inside the: A. R atrium B. R ventricle C. Pulmonary artery D. Pulmonary capillary |
C |
|
|
Which of the following sxn catheters would be most appropriate for a patient with a 7.5 ETT? A. 8 B. 10 C. 12 D. 14 |
B. 10 |
|
|
While manually ventilating a 29 week gestational age newborn, the RT notices that the flow-inflating resuscitation bag is completely full prior to squeezing the bag. The RT should: A. Close the flow control valve B. Add a P manometer C. Change to self-inflating bag D. Decrease flow to bag |
D. Decrease flow |
|
|
Which of the following OI would indicate the need for ECMO in newborn? A. 8 B. 16 C. 32 D. 44 |
D. 44 |
|

|
C. Venous admixture |
|

|
B |
|

|
A. Reduce PEEP |
|

|
C. |
|

|
B. |
|

|
B |
|
|
The RT is performing an apnea test for determining brain death on a 29 yo man who suffered a closed head injury. After disconnecting the ventilator, the RT should: A. Monitor etCO2 B. Obtain an ABG C. initiate PS D. Administer 100% O2 |
D |
|
|
Which of the following advanced directives describes the treatment a patient would want if he became terminally ill, but has not specifically appointed someone else to make the medical decision? A. DNR B. Patient bill of rights C. Notarized living will D. Durable power of attorney for health care |
C |
|
|
A patient is in the ICU after undergoing an aortic valve replacement. A pulmonary artery catheter has been inserted and the RT is asked to assess proper placement. Where should the catheter appear on the CXR? A. at the level of the aortic arch B. In the RLL field C. At the level of the 10th rib D. In the right ventricle |
B |
|

|
C |
|
|
The RT provides manual resuscitation with a self inflating bag with the flowmeter set to flush during resuscitation in the ICU. The therapist notices that the patient valve is stuck in the open position. The therapist's initial response should be to: A. Decrease flow to bag B. Use another form of ventilation C. Obtain a larger self inflating bag D. Attach a reservoir to the bag |
A |
|
|
A responsive infant presents to the ED with a severe AW obstruction. After the RT delivers back blows and chest thrusts, the infant becomes unresponsive. After placing the infant on a firm surface, the RT should: A. Initiate chest compressions B. Check for brachial pulse C. Perform blind finger sweep D. Look for foreign object in patient's mouth |
A |
|
|
A 22 yo female admitted to ED with narcotic OD has been intubated for AW protection. IV access is not available. The Dr. Orders NARCAN via ETT. Following administration, the RT should A. Hyperventilate pt for 30 secs B. Administer 50 mL of normal saline via ETT C. Perform cardioversion D. Sxn or via ETT |
A |
|
|
All of the following strategies are likely to decrease the likelihood of damage to the tracheal mucosa except: A. Maintaining cuff pressures between 20-25 mmHg B. Using minimal leak technique for inflation C. Using a low-residual, low-compliance cuff D. Monitoring intracuff pressures |
C. |
|
|
Static compliance equation |
Vt/plateau - PEEP |
|
|
Which of the following patients would most likely benefit from PSV? A. An intubated patient with an absent respiratory drive B. A pt on SIMV with a mandatory rate of 12 and total rate of 24 C. A pt with acute lung injury D. A patient who requires short-term post-op vent support |
B |
|
|
A pr receiving mechanical ventilation has developed a temp of 99.9 F with prudent secretions over the last 12 hours. The RT has also noted a steady increase on PIP. What initial rec should be to address the changes? A. Initiate bronchial hygiene therapy B. Obtain a sputum gram stain C. Admister IPV D. Insert CASS tube |
B |
|
|
Which of the following may be obtained from FVC maneuver during bedside pulmonary function testing? 1. FEV1 2. PEFR 3. FRC 4. RV A. 1&2 B. 1&3 C. 2&4 D. 3 &4 |
A. FEV1 and PEFR |
|
|
The RT provides education for a pt who is being discharged home on aerosol therapy. The most important reason for the pt to follow the recommended cleaning procedures using a vinegar/water solution is that this solution will: A. Sterilize the equipment B. Retard bacterial growth C. Kill all microorganisms and spores D. Extend equipment life |
B. |
|
|
A pt who complains of dyspnea is noted to have a dry, non-productive cough. On physical exam, breath sounds are diminished on the right, tactile fremitus is decreased and there is dullness to percussion over the right lower lobe. The RT should suspect that the pt is suffering from: A. PNA B. PE C. Pleural effusion D. Bronchiolitis |
C |
|
|
Which of the following sxn catheters would be appropriate for a pt with a size 8.0 ETT? A. 8 B. 10 C. 12 D. 14 |
C |
|
|
How to determine sxn catheter size |
(ETT/2) x3 size down if needed |
|
|
At 1 min post-delivery, a newborn has blue extremities, HR 90, RR 20, weak cry, cough reflex present, some flexion of extremities. At 5 min, infant is completely pink, HR 140, RR 40, cough reflex, active, strong cry. What APGAR's should be assigned? |
6 & 10 |
|
|
Following thoracotomy, a pt on VC has a chest tube in left pleural space. While inspecting the chest drainage system, the RT notes bubbling in the water seal chamber during inspiration. The therapist should report this as: A. A persistent bronchopleural fistula B. A resolved PTX C. Back pressure from sxn catheter D. Normal function of the water seal chamber |
A |
|
|
19 yo brought to ED after taking a handful of pills. The pt is obtunded but making regular, sonorous respiratory efforts. Auscultation reveals coarse rhonchi bilaterally. Which should be done first to assess the pt? A. Obtain a sputum specimen B. Obtain an ABG C. Measure peak expiratory flow D. Determine GCS |
B |
|
|
All of the following conditions can be treated with HBO except: A. Carbon monoxide poisoning B. Decompression sickness C. Anaerobic infections D. PHTN |
D |
|
|
A 16 yo w/CF attends high school. Which of the following bronchial hygiene therapies would be most appropriate? A. IPV B. Dornase Alpha C. Vibratory/ oscillatory PEP D. PD and manual percussion |
C. |
|
|
After assisting with BAL and lung biopsy on a mechanically ventilated pt, the RT notes the activation of a high pressure alarm. PIP has increased from 32 to 45 after the procedure. Possible causes include: 1. Bronchospasm 2. PTX 3. Pulmonary hemorrhage A. 1 &2 B. 1 &3 C. 2 & 3 D. 1, 2, & 3 |
D |
|
|
Posterior basal segment, lower lobes PD position |
Head down, prone, pillow under hips |
|
|
Normal PAP |
25/8 mean 14 |
|
|
BNP levels |
>300: mild >600: moderate >900: severe |
|
|
Following blunt chest trauma, a 35 yo is orally intubated and continuous mechanical ventilation is initiated. Physical assessment of neck and chest reveal a midline trachea and significant reduction in thoracic expansion of the left chest. There are diminished breath sounds in the left lung compared to the right lung. These findings most likely indicate: A. Flail chest on right thorax B. Right tension PTX C. endobronchial intubation D. SubQ emphysema |
C. |
|
|
The RT performs the quality control procedures for the blood gas analyzer in the NICU and notices a single data pt is 3 standard deviations from the mean value for the pH electrode. The therapist should: A. Perform another control run B. Contact the QC supervisor C. Recalibrate the electrode D. Replace the electrode |
A |
|
|
A capnograph used for continous monitoring of a pt on mechanical ventilation should be recalibrated every A. 2 hours B. 4 hours C. 8 hours D. 24 hours |
C. 8 hours |
|
|
A sudden decrease in etCO2 occurs in a mechanically ventilated pt. A repeat analysis yields the same result. Which of the following might account for this? A. The ventilator circuit has become disconnected B. There is a leak around the ETT C. There is an increase in alveolar dead space D. The CO2 absorber is exhausted |
A. |
|
|
Dynamic inflation is a major concern when using VC in patients with which condition? A. Post-traumatic chest trauma B. Community-acquried PNA C. Spinal cord injury D. Chronic bronchitis |
D |
|
|
A post-op thoracic surge pt is having difficulty developing an effective cough. The RT could recommend all of the following except: A. Coordinating coughing with pain meds B. Performing serial coughs C. Applying pressure to patient's abdomen during exhalation D. "Splinting" the incision area |
C. |
|
|
Which of the following should the RT consider when preparing for helo transport of a pt receiving mechanical ventilation? 1. Select a ventilator that uses demand valves rather than a reservoir IMV system 2. Calculate O2 cylinder duration of flow 3. Selecting a vent that incorporates an internal air compressor A. 1 & 2 B. 2 & 3 C. 3 D. 1, 2, & 3 |
A |
|
|
A 65 yo F pt with advanced emphysema comes to ED and is placed in 6L NC. On inspection, patient us drowsy and less responsive since O2 therapy was initiated an hour ago. pH 7.33, PaCO2 64, PaO2 85, HCO3 35. Which should the RT recommend? A. Leave pt on cannula and continue to monitor B. Change to 24% VM and repeat ABG C. Change to simple O2 mask and repeat ABG D. Prepare pt for endotracheal intubation |
B. |
|
|
Normal PT |
12-15 seconds |
|
|
While administering 3.5 mg of albuterol to a pt with asthma in the ICU , the RT notes the pt HR increases from 120 to 150. What us the appropriate modification for the next tx for this pt? A. Reduce Albuterol dose B. DC tx C. Change to 3 puffs if beclamethasone D. Change to 0.63 mg Levalbuterol |
A |
|
|
During review of the medical record prior to obtaining ABG, the RT notes that the patient has a platelet count of 115,000. What should the therapist do? 1. Perform ABG as normal 2. Refuse to perform ABG 3. Hold pressure on the puncture site for a longer time after collecting sample 4. Recommend ABG only if absolutely necessary A. 2, 4 B. 1, 3 C. 3, 4 D. 2 |
A |
|
|
The RT assists with elective intubation of a pt with myasthenia Gravis. While providing manual ventilation, the self inflating bag becomes difficult to compress. Which if the following should the therapist do first? A. Check inlet valve B. Check patient valve C. Replace bag D. Check for excessive flow |
C |
|
|
The RT notices the low pressure alarm sounding from ventilator. Pressure manometer reads 6 cmH2O during inspiration. The therapist's first action should be to: A. Look for kink in circuit B. Change modes of ventilation C. Check exhalation valve D. Sxn patient. |
C |
|
|
Which of the following airway clearance techniques uses a pneumatic device to deliver compressed gas mini bursts at sub-tidal volumes to the airway at frequencies of 100 to 250/min? A. IPV B. Autogenic drainage C. High frequency chest wall compression device D. Positive expiration pressure breathing |
A |
|
|
A pt who has significant decreases in airflow during sleep but does not have a complete cessation of breathing is having what type of episodes? A. OSA B. Dyspnea C. Hypopnea D. Central sleep apnea |
C |
|
|
A 68 yo pt with advanced emphysema is receiving O2 by 1L NC. The Dr. ha ordered the SpO2 be maintained at 90%. pH 7.34, PaCO2 65, PaO2 65, PaO2 55, HCO3 35. What should the therapist recommend first? A. Initiate NIPPV B. Titration O2 flow to NC C. Change to simple mask D. Change to NRM |
B |
|
|
A 44 yo pt who suffered a CVA has been moved from neuro ICU to step-down unit. He becomes diaphoretic and SpO2 drops from 95% to 88% on 32% trach collar. His HR is 115, RR 42, diminished breath sounds. The RT is unsuccessful in attempting to pass a 12 Fr catheter. The RT should: A. Increase sxn pressure to 120 B. Change to 10 Fr C. Replace trach tube D. Orally intubate the pt |
C |
|
|
A 13 yo pt in ED complains of dyspnea, and a loose, productive cough. The pt has a RR 33, bilateral wheezing. What tx should the RT initiate? A. Levalbuterol B. O2 C. Slameterol D. PEP |
B |
|
|
After performing spirometry on a pt in the pulmonary clinic, the RT notes that both the inspiratory and expiratory flow portion of the flow-volume loop is flattened. The RT should interpret this as: A. Normal B. Obstructive C. Restrictive D. Large airway obstruction |
D |
|
|
A chronic hypercapnic pt enters the ER complaining of SOB. The pt is coughing up inspissated, pale, yellow secretions. Which do you recommend? A. Sputum culture and sensitivity B. 2L NC C. A-P and lateral CXR D. ABG |
B |
|
|
While receiving PD and percussion to her RLL, a 44 yo pt suddenly vomits and aspirates. The RT should immediately: A. Place pt in Fowler's position B. Encourage pt to take deep breaths C. Sxn the pt D. Administer acetlcysteine by SVN |
C. |
|
|
An air Flowmaster and an O2 flowmeter are being used to deliver 40% O2 via NRM. A total flow of 12 LPM is required to prevent bag from deflating. How many liters of each should the RT use? A. 2 air, 6 O2 B. 4 air, 8 O2 C. 6 air, 6 O2 D. 9 air, 3 O2 |
D |
|
|
A 3 day post op laryngectomy pt is receiving 50% with a cool aerosol via trach collar. The secretions being sectioned are thick and difficult to aspirated. The RT should recommend: A. Increase frequency of sxn B. Instill 2mL normal saline prior to sxn C. Decrease O2 to 45% D. Add a heating element to aerosol |
D |
|
|
A 26 week gestational age infant requires intensive monitoring and care in the NICU. Which device is most appropriate? A. Radiant warmer B. Isolette C. Croupette D. Bassinet |
A |
|
|
The RT calibrates a spirometer and checks the volume with a 3 L super syringe. The volumes recorded are: 2.85, 2.8, and 2.8. Based on the info obtained which of the following is a correct statement? A. Another syringe needs to be used B. Spirometer is accurate C. The plunger was advanced too slowly D. Spirometer may have a leak |
D. |
|
|
A 43 yo F pt undergoes a total abdominal hysterectomy. The pt arrives in PACU obtained with minimal response to painful stimulus. What tx should the RT recommend? A. Initiate assisted ventilation B. Insert oropharyngeal airway C. Obtain positron emission tomography D. Initiate noninvasive capnography |
B. |
|
|
A 44 week infant delivered via c section gasping, grunting, tachycardic, and tachypneic. At one minute APGAR 4, 5 minutes score is 5. Infant most likely suffering from: A. TTN B. MAS C. BPD D. apnea of prematurity |
B |
|
|
While instructing a pt prior to a VC maneuver, the RT should direct the pt to: A. Exhale to RV and inhale to IC B. Inhale to TLC then exhale to RV C. exhale normally then inhale to TLC D. inhale normally then exhale to FRC |
B |
|
|
A pt with end-stage pulmonary fibrosis receives O2 at 2L/min via TTO2. The pt complains of increased WOB and SOB. The RT should: A. Manually ventilate the pt with resuscitation bag B. Increase flow to TTO2 to 6L C. Evaluate SpO2 with pulse ox D. Flush TTO2 with saline |
D. |
|
|
Symptoms of MAS |
Cyanosis/stained with meconium Grunting, retraction, nasal flaring, gasping with tachypnea Wheeze, rhonchi, crackles, expiration grunting Tachycardia, tachypnea, HTN |
|
|
During bedside monitoring, the RT notices a dampened waveform on A line graphic. To restore graphic to normal, the RT should: A. Verify position of transducer B. Check transducer dome for air bubbles C. Flush with heparin D. Attempt to draw blood from A line |
D. |
|
|
An optimal PEEP study is initiated for a pt receiving mechanical ventilation. The RT initiates PEEP of 10 for 20 minutes with no adverse effects. The PEEP is increased to 15 and the patient's HR rises significantly with severe fall in BP. Based upon the above information, the RT should conclude that the pt is suffering from: A. Peripheral vasoconstriction B. Hypovolemia C. Increased venous return D. Increased SVR |
B |
|
|
The RT is in charge of transporting a pt with multiple trauma to a regional trauma center in a fixed wing aircraft. Which of the following should the RT be most concerned with during transport? A. Tissue oxygenation B. PTX C. PE D. Humidification of inspired gas |
A |
|
|
A balloon-tipped, flow-directed catheter is positioned in the pulmonary artery with the balloon deflated. Which of the following pressures will be measured by the distal lumen? A. CVP B. PAP C. PCWP D. MAP |
B |
|

|
A |
|
|
The RT receives an order to administer bronchodilator therapy with Albuterol. To reduce chance of cross contamination, the RT should: A. Select an MDI B. Use a DPI C. replace SVN every 24 hours D. Wipe surface if neb with alcohol every evening |
A |
|
|
Which if the following is a false statement about self-inflating resuscitation devices? A. A reservoir is utilized to increase delivered O2 concentration B. The RT can sense changes in the patient's lung compliance and Raw C. A compressed gas is necessary for the device to operate D. Excessive gas flow may cause the valve to malfunction |
C. |
|
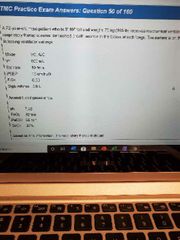
A. Maintain current settings B. Increase set rate to 12 C. Decrease Vt to 500 D. Increase sigh volume to 1 L |
D |
|
|
What is a sigh breath? |
A periodic hyperinflation during PSV |
|
|
The FRC measured by body plethysmography is 30% larger than that measured by helium dilution. This difference is best explained by: A. Maldistribution of ventilation B. Increased diffusion capacity C. Trapped thoracic gas D. Reduced lung compliance |
C. |
|
|
Which of the following would produce the greatest humidity output for a pt? A. Bubble humidifier B. Wick-type humidifier C. Large reservoir neb D. Ultrasonic neb |
D |
|
|
An SBT has been initiated for a 64 yo, intubated, post-op patient. O2 is being administered by T piece at 50% via heated air entrainment neb at 12 LPM and a temp of 37. The RT notices that the aerosol must disappears from reservoir outlet during the patient's inspiration. The RT should consider all of the following except: A. Lengthening the reservoir tubing B. Adding an additional neb C. Increasing flow to 15 LPM D. Increasing temp to 39 |
D |
|
|
Normal spontaneous Vt |
5-8 mls/kg |
|
|
The RT reviews a patient's medical record prior to performing bedside assessment to determine readiness for weaning from ventilatory assistance. The pt weighs 60 kg. The RT should expect the pt to be able to achieve a spontaneous Vt of: A. 200-355 mL B. 300-480 C. 400 - 620 D. 600 - 720 |
B |
|
|
After completing O2 rounds, the RT must clean flowmeters that were removed from rooms where no patients were receiving O2 therapy. Which of the following methods is most appropriate for disinfection of the flowmeters? A. Steam autoclave B. Soak in acid gluteraldehyde C. Wash in Pasteurmatic D. Wipe with alcohol |
D |
|
|
A 4 yo girl is admitted to the ED with persistent dry coughing. CXR results reveal normal inspiration with R lung remaining expanded on expiration. Which of the following should the RT recommend at this time? A. Endobronchial intubation B. ABG C. Bronchoscopic exam D. Lateral neck radiograph |
C |
|
|
A ballon-tipped, flow-directed catheter is positioned in the pulmonary artery with the balloon inflated. Which of the following pressured will be measured by the distal lumen? A. CVP B. PAP C. PCWP D. MAP |
C |
|
|
A pt has been intubated with a nasotracheal tube and is being manually ventilated. As the RT ventilated the pt, he notices that there is no chest movement, minimal breath sounds, and air escaping from moth when bag is squeezed. A CXR confirms correct placement. What is most likely the cause? A. The tube is in the esophagus B. The pt had developed a tracheosphageal fistula C. The cuff ruptured during intubation D. The cuff herniated over the end of the tube |
C |
|
|
Oropharyngeal airway indications |
Unconscious Support base of tongue Bite block Facilitate oral sxn |
|
|
A pt receives 40% via 8L VM. While performing O2 rounds, the RT notes the flowmeter setting has been changed to 12 L. How would this affect accuracy of the device? A. FiO2 will remain unchanged B. FiO2 will decrease to 35% C. Air entrainment factor will decrease D. FiO2 will increase to 50% |
A |
|

A. RVEDP B. left atrial filling P C. SVR D. Cardiac output |
C |
|
|
Normal CI |
2.5-4 |
|
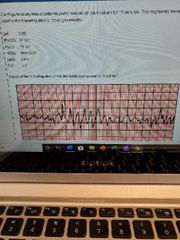
A. Increase minute vent B. Administer sodium bicarbonate C. Decrease FiO2 D. Administer lidocaine |
B |
|
|
PCV would be least appropriate for a pt with: A. Kyphosis B. Muscular dystrophy C. ARDS D. Drug OD |
C |
|
|
A pt involved in an MVA several days ago sustained a long bone fracture and remain is traction. The pt suddenly complains of chest pain and develops tachypnea and tachycardia. The RT should: A. Administer O2 B. Recommend heparin C. Recommend streptokinase D. Request CXR |
A |
|
|
A 48 yo woman is admitted to the CCU for chest pain, dizziness, and nausea. Her BP is 60/40, RR 20, cardiac monitor shows sinus rhythm at 50 bpm with frequent multifocal PVC. The RT should recommend: A. Lidocaine B. Nitroglycerin C. Atropine D. Amiodarone |
C |
|
|
Which statements is true concerning PEP therapy? A. It applies EPAP using one way expiratory valve and a one way flow resistor B. It is used for 5 - 10 minute intervals every hour C. The inspiratory flow resistor prevents pressures from rising above 0 D. It may help improve secretion expectoration, decrease hyperinflation, and improve airway maintenance |
D |
|
|
A 44 yo undergoes polymnography and has an AHI of 25. This value should be reported as: A. Normal B. Mild C. Moderate D. Severe |
C |
|
|
Mild AHI |
5-15 |
|
|
Moderate AHI |
16-30 |
|
|
Severe AHI |
>30 |
|
|
AHI calc |

|
|
|
Which if the following would NOT cause a capnography reading to change from 36 to 30? A. Tachypnea B. Hyperventilation C. PE D. ETT in right mainstem bronchus |
D |
|
|
A patients cardiac output is increased and his shunt is 20%. The RT should inform the DR this pt has: A. An elevated shunt B. Reduced CI C. Increased PVR D. Normal lung mechanics |
A |
|
|
A pt is suspected of having developed a PE. Which if the following tests should the RT recommend to confirm the dx? A. A-a B. C(a-v)O2 C. Vd/Vt D. P50 |
C |
|
|
During mechanical ventilation, a pt initiates a breath and then the ventilator controls the remaining variables for that breath. This describes a/an: A. Spontaneous breath B. Assisted breath C. Mandatory breath D. Supported breath |
B |
|
|
A 1600 g neonates receives O2 by oxyhood at an FiO2 of 60%. The flowmeter is set at 5LPM. while analyzing the O2, the RT notices varying FiO2 readings at different locations inside the oxyhood. The RT should: A. Recalibrate the analyzer B. Increase flow to oxyhood C. Place the neonate in an isolated at 60% D. Check the water level of the humidifier |
B. |
|
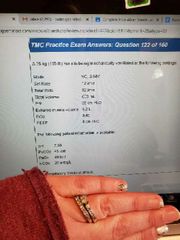
A. Decrease PEEP B. increase set rate to 14 C. Add PS D. initiate PCV |
C |
|
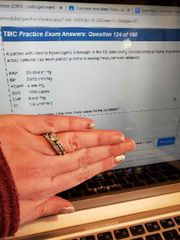
A. Hypovolemia B. Drug OD C. Cor Pulmonale D. High FiO2 vasodilation |
A |
|
|
All of the following are true statements about spacers and holding chambers, except: A. Do not require pt cooperation with their breathing pattern. B. Improve efficiency of MDI C. Can be used for drug delivery by MDI to intubated and mechanically ventilated patients D. If a pt exhales immediately following activation of the inhaler, they will clear the medication from the device and waste the dose |
A |
|
|
During cardioversion, the defibrillator will deliver the synchronized electrical shock on the: A. P wave B. Q wave C. R wave D. T wave |
C |
|
|
During online sxn, 100% O2 is supplied via ventilator. The RT observes several PVC on ECG monitor. The RT should: A. Decrease sxn time per pass B. Use smaller sxn catheter C. Increase oxygenation time D. Decrease sxn pressure |
A |
|
|
A 2 yo child recently diagnosed with laryngotracheobronchitis requires administration of 40% O2. What is the most appropriate method for delivering O2? A. Oxyhood connected to blender B. Cool aerosol mask C. VM D. Croup tent |
B |
|
|
Indirect calorimetry is performed on a 65 yo pt to evaluate his nutritional status. It is determined that the patient's RQ is 1.0. This would indicate that the patient's diet consists mostly of: A. Fats B. Proteins C. Sugars D. Carbs |
D |
|
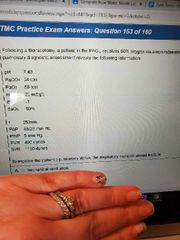
A. Mechanical ventilation B. CPAP C. NO therapy D. Heliox therapy |
B |
|
|
All of the following statements regarding an oxygen concentrator are correct except that it: A. Provides unlimited supply of O2 B. Increases alveolar oxygen tension C. Provides 100% O2 at high flow rates D. Removes nitrogen from room air |
C |
|
|
An RT enters a patient's room during O2 rounds. The patient has end-stage emphysema and appears to be sleeping. The pt doesn't respond to questions and his pulse is 20 bpm. The RT should immediately: A. Confirm DNR B. Go get help C. Begin rescue ventilation D. Begin chest compressions |
A |
|
|
While attempting to calibrate a polarographic O2 analyzer, the RT notes that the analyzer reads 21% at room air and 64% when exposed to 100%. The most appropriate action at this time would be to: A. Reset the zero pt B. Replace the battery C. Replace the fuel cell D. Add electrolyte solution |
B |
|
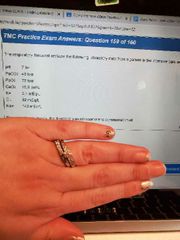
A. KCL B. Bicarbonate C. NaCl D. O2 |
A. |
|
|
Normal shunt |
3-5% |
|
|
Normal K+ |
3.5-4.5 |
|
|
Normal Cl- |
90-100 |
|
|
Super syringe calibration must be how accurate? |
Within 3.5% (2.9-3.1) |
|
|
Upper lobe apical segment |
Sitting up Leaning forward |
|
|
Upper lobe anterior segment |
Head flat, pt supine, pillow under knees |
|
|
Upper lobe superior segment |
Leaning forward in a chair |
|
|
Right middle lobe lateral and medial segments |
L side Head down Pillow behind back |
|
|
Left upper lobe superior and inferior lingual segments |
R side Pillow behind back Head down |
|
|
Lower lobes lateral segment of left lung |
R side Pillow between knees Head down |
|
|
Lateral lobes lateral basal segment right lung |
L side Pillow between knees Head down |
|
|
Lower lobes posterior basal segment |
Prone, pillow under hips, head down |
|
|
Lower lobes, superior segment |
Prone, head flat, pillow under hips |
|
|
Lower lobes anterior segment |
Supine, pillow under hips, head down |
|
|
Shunt equation (long) |
A-a(300)/(A-a x 300) + C(a-v)O2 |
|
|
An adult pt required PPV for 6 weeks bc of ARDS. 2 days following extubation, the pt develops stridor. The RT should assess the pt for evidence of: A. Vocal cord polyps B. Bronchospasm C. Mucosal ulceration D. Tracheostenosis |
D |
|
|
A pt is admitted to the ED following a 911 call for respiratory arrest. The paramedics inserted a Combitube. The RT's first responsibility for airway management should be to: A. Insert King supraglottic airway B. Assess current tube position C. Replace combitube with ETT D. extubate pt |
C |
|
|
A conscious pt is having difficulty clearing secretions and the RT decides to insert a nasopharyngeal airway to facilitate nasotracheal suctioning. Which of the following should the therapist utilize to properly insert the airway? A. Head tilt, chin lift B. Rotate 180 degrees prior to insertion C. Modified jaw thrust D. Insert along the anatomic shape |
D |

