![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
11 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Clinical KID syndrome
|
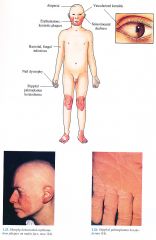
|
|
|
Inheritance
|
Autosornal dominant and recessive transmission reported; GJB2 gene on I 3q1 1 12
|
|
|
Prenatal
|
Mutation analysis if defect known
|
|
|
Incidence
|
Approximately 30 cases reported; M=F
|
|
|
Age at Presentation
|
Birth
|
|
|
Pathogenesis
|
Mutations in GJB2, the gene encoding for connexin 26, a gap junction protein responsible for intercellular communications in the epidermis and cochlea, produces phenotype
|
|
|
Clinical
|
Skin
Generalized mild hyperkeratosis with follicular plugging; Erythematous, keratotic plaques on face, extremities > trunk; Palmoplantar keratoderma with stippled surface; Recurrent bacterial and fungal infections Squamous cell carcinoma of skin, tongue not rare Hair Alopecia in scalp, eyelashes, eyebrows Nails Dystrophic ENT: Nonprogressive sensorineural deafness Eyes Progressive bilateral vascularized keratitis secondary blindness may occur |
|
|
D/Dx
|
Keratosis follicularis spinulosa decalvans
|
|
|
Lab
|
Audiologic testing
Skin cultures |
|
|
Management
|
Referral to dermatologist antibiotics, systemic antifungals, topical emollients, keratolytics; oral retinoids may exacerbate corneal neovascularization
Referral to ophthalmologist topical cyclosporine has helped keratitis Referral to otolaryngologist |
|
|
Prognosis
|
Dependent on degree of hearing loss and blindness, may have severe sensory handicap; otherwise normal life span
|

