![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
66 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
what is the chemical formula for a carbohydrate? |
Carbo means carbon and hydrate pertains to water therefore the chemical formula is Cn(H20) n or (CH20)n where n stands for a number An example would be C2(H20) n=2 |
|
|
What is the primary function of carbohydrates? |
To provide energy. ATP is a stored form of glucose in fat tissue (aka adipose tissue) and in muscle tissue (ATP in muscle is for rapid needs) |
|
|
Carbohydrates are chains of _____(_a_)______ each bonded to _____(b)__ and ____(c)____groups |
a) Carbons b) H c) OH |
|
|
How is energy stored in carbohydrates? |
In strong C-C and C=0 covalent bonds (single and double covalent bonds) |
|
|
Each gram of carbon yields about__________ calories of energy |
4 |
|
|
How are carbohydrates "tags" to address proteins? |
The 'identity tags' (antigens) on the surface of all cells are made from carbohydrates joined to proteins. These molecules are essential for cells to recognise each other and to keep the different parts of your body working together.
|
|
|
1. What is the most basic carbohydrate? 2. Name its chemical formula (aka structural formula) 3. Give 3 examples |
1. monosaccharides 2. structural formula C6H12O6 3. glucose, fructose (sugar found in fruits, galactose |
|
|
What is one structural component of RNA? |
Ribose which is a pentose monosaccharide (5 carbons make a pentagon). RNA is important in transcription. Chains of ribose sugars make up the structural component of RNA |
|
|
What is the structural component of DNA? |
Deoxyribose which is a monosaccharide. It is called deoxyribose because it looks like ribose with one oxygen molecule missing. |
|
|
1. What is a disaccharide? |
1. Disaccharides are two simple sugars linked together by covalent bonds. An example would be sucrose (table sugar) which is fructose and glucose joined together by a covalent bond |
|
|
Name 3 disaccharides? |
a. sucrose (table sugar)= fructose +glucose Sucrose is a natural sugar found in sugar cane and sugar beets. 2b. lactose= galactose+glucose Lactose is found in milk 3c. maltose= glucose+glucose with an alpha bond least common and found in germinating grains |
|
|
What are sugar chains of 3 to 20 monosaccharides called? |
Oligosaccharides |
|
|
What are sugar chains of hundreds or thousands of monosaccharides called? |
Polysaccharides |
|
|
Name 3 polysaccharides |
1. Starch 2. glycogen 3. fiber |
|
|
What is glycogen and where is it stored in the human body? |
It is a polysaccharide and represents the main storage form of glucose in the body. Glycogen is stored in muscle and the liver |
|
|
What is starch? |
It is how plants store carbohydrates. They store them as starch. The molecule has lots of branches. |
|
|
What is cellulose? |
Cellulose makes plant cell walls strong. Humans ingest it as "dietary fiber" The molecule is not branched. It is linear. |
|
|
What is Fiber? |
It is a polymer of glucose that the body can't digest |
|
|
What contains the highest amount of fiber? |
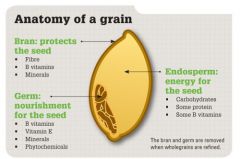
If you look at a piece of grain, the germ (little white pre- plant inside) and the bran (seed coat) of the seed |
|
|
What are the 3 main classes of fiber? |
1. functional fiber (pectin) adds texture to food 2. Dietary fiber- found in bran of oats , wheat, cellulose, fruits and veggies 3. Total fiber = functional +dietary |
|
|
What two things does soluble fiber do? |
1. Slows glucose absorption 2. Lowers plasma cholesterol |
|
|
What is soluble fiber and how does it lower cholesterol? |
Soluble fiber dissolves and thickens in water.
Soluble fiber is probably best known for its cholesterol lowering effect. Soluble fiber binds with bile acids. Bile acids are made from the cholesterol that is stored in our blood, so more of your body’s cholesterol is used up in replenishing the bile acids. |
|
|
How does soluble fiber control diabetes? |
Soluble fiber also helps to stabilize blood sugar and control diabetes, by slowing the absorption of carbohydrates and reducing the rise of blood sugar after a meal. |
|
|
Do we digest fiber? |
No. It just passes through digestive tract. Some people see it as a scrub brush cleaning our intestines. Soluble fiber also provides a feeling of fullness, so it can potentially help with weight loss. |
|
|
What are two good sources of soluble fiber? |
1. oats (like oatmeal) 2. barley |
|
|
What is insoluble fiber and what does it do? |
Insoluble fiber does not absorb or dissolve in water. It passes through our digestive system in close to its original form.
It helps stimulate the release of mucus in the Large intestine. The mucus acts as a protective barrier for the lining of the intestine. |
|
|
What is a type of food that contains insoluble fiber? |
Wheat bran |
|
|
What is the Glycemic Index? |
The Glycemic Index is a numerical Index that ranks carbohydrates based on their rate of glycemic response (i.e. their conversion to glucose within the human body). Glycemic Index uses a scale of 0 to 100, with higher values given to foods that cause the most rapid rise in blood sugar.
|
|
|
Foods that are digested quickly have a ________ GI |
Higher GI (glycemic index) |
|
|
What has the highest GI? |
Glucose |
|
|
What is a Glycemic load? |
The glycemic load accounts for the quantity of carbohydrates in food. |
|
|
What is the formula to calculate glycemic load? |
(grams of carbohydrate x GI)/100 |
|
|
If a food had a glycemic load of greater than 20, what would that mean? |
It would mean that it was high in carbohydrates that may raise your blood sugar. Figuring out the glycemic load of a food can help you craft a menu that won’t put your blood sugar on a roller coaster. If the food was greater than 20, you would want to pare it with a food with a lower glycemic load or choose a food with a lower Glycemic load. |
|
|
What would it mean if the GL was less than 10? Can I eat a lot of this type of food? |
It would mean that it was low in carbohydrates that may raise your blood sugar. No. It is not healthy to eat a ton of certain amount of food with a low GI. Peanuts have a low GI and eating a lot can make you sick. |
|
|
What are "Sugar Alcohols"? |
Sugar alcohols are one type of reduced-calorie sweetener. You can find them in ice creams, cookies, puddings, candies and chewing gum that is labeled as "sugar-free" or "no sugar added." Sugar alcohols provide fewer calories than sugar and have less of an effect on blood glucose (blood sugar) than other carbohydrates.
|
|
|
Name 3 advantages to sugar alcohols |
1. less calories than glucose 2. Don't rot your teeth 3. Diabetic patients can sweeten their food |
|
|
Are sugar alcohols sweeter than glucose? Name 3 examples of sugar alcohols. |
Nope. 1. Mannitol 2. Glycerol 3. Sorbitol |
|
|
Name one of the major biological macromolecules |
Proteins |
|
|
What is a protein? |
A large complex molecule (macromolecule) consisting of amino acids linked in sequences by covalent bonds |
|
|
What is an amino acid? |
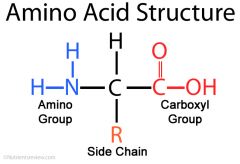
AA's have a central carbon that is bonded to 4 other groups and are classified by their side chains (R) as either polar or non polar etc |
|
|
How many amino acids are there? |
There are 20 amino acids 9 essential 11 non essential |
|
|
What are essential amino acids and how many of them are there? |
1. Essential amino acids are ones that are body can't synthesize. 2. The are 9 essential amino acids |
|
|
What is a non essential amino acid? |
An amino acid that can be made by humans and so is not essential to the human diet. There are 11 nonessential amino acids: alanine, arginine, asparagine, aspartic acid, cysteine, glutamic acid, glutamine, glycine, proline, serine, and tyrosine.
|
|
|
What is transamination? |
Transamination (or aminotransfer) is a chemical reaction that replaces an amine functional group with another amine.
To make nonessential amino acids the body takes essential amino acids and changes them into nonessential by transamination |
|
|
How does the body make nonessential amino acids? |
To make nonessential amino acids the body takes essential amino acids and changes them into nonessential by transamination
|
|
|
What are complete proteins and give two examples? |
Complete proteins have all essential amino acids in them. 1. meat 2. soy |
|
|
What is the primary structure of a protein? |
It is linked amino acids with peptide bonds that form a polypeptide chain. Think of this like a necklace made with different stones laid out perfectly straight without any kinks. Each stone is an amino acid and the gold links are peptide bonds. |
|
|
What is the secondary structure of a protein? |
A polypeptide chain that folds on itself with various different interactions. Think of this as a necklace that has kinks and folds while on your vanity. |
|
|
What is the tertiary structure of a protein? |
A polypeptide chain the is folded and then folds again. Think of this as a necklace that has kinks and folds on your vanity that you now put in a bag. |
|
|
What is a quartenary protein? |
A couple of polypeptide chains that act together to function. Not all proteins work together as a team but when they do we say it is a quaternary protein. Think of this as a couple of necklaces in a bag. You take out the mess and you wear it around your neck even though it is just a knot of two necklaces. It looks good on your neck. |
|
|
What is the significance of actin and myosin? |
Muscles are composed of two major protein filaments: a thick filament composed of the protein myosin and a thin filament composed of the protein actin. Muscle contraction occurs when these filaments slide over one another in a series of repetitive events.
|
|
|
What is the function of protein is muscles? |
Proteins regulate the contraction of actin and myosin in both voluntary and involuntary muscles. |
|
|
What are voluntary and involuntary muscles? |
voluntary = you can control = skeletal muscles, eg. Biceps.
involuntary = you can't control = smooth (eg. gut) and cardiac (heart) muscles. |
|
|
What are motor proteins? |
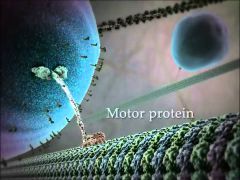
Motor proteins can take molecules on one side of a membrane to the other side or simply help in the process |
|
|
What type of molecule can take hydrophobic (water hating) substances through our circulation? |
Motor Proteins |
|
|
What are cytoskeletal proteins? |
Cytoskeletal proteins give structure (a skeleton) to cell and organelles and are involved in transport within the cell. They seem like train tracks. |
|
|
What type of proteins speed up chemical reactions? |
Enzymes bind chemicals that can react and in doing so lower the activation energy thus speeding up the reaction rate. Let's say you ate a piece of meat. Proteases would go to work and help break down the peptide bonds between the amino acids. |
|
|
What is edema? |
a condition characterized by an excess of watery fluid collecting in the cavities or tissues of the body.
|
|
|
What maintains blood fluid balance? |
Proteins maintain blood fluid balance by regulating the amount of protein in the plasma. |
|
|
What are surface proteins? |
Cell surface receptors (membrane receptors, transmembrane receptors) are specialized integral membrane proteins which communicate signals between the cell and the outside world.
|
|
|
What are antibodies? |
Antibodies are Proteins that bind to particular surface features (antigens) on invading pathogens and cells that are misbehaving |
|
|
Do proteins regulate growth, maintenance and repair? |
Yes |
|
|
How do we maintain pH? |
We maintain it by producing a buffer through proteins. |
|
|
Are proteins normally used as an energy source? |
No. But if you are starving some glycogenic amino acids can be converted to glucose by glycogenesis. |
|
|
What is a normal blood glucose level for a human? |
Normal blood glucose level are less than 140 |
|
|
What is the level of blood glucose in your body if you are diabetic? |
Blood glucose is 200 and up for a diabetic |

