![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
90 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
1. List the expression that represents the general format for using scientific notation.
|

|
|
|
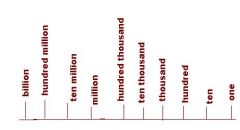
List each of the place values for a 10-digit number.
|
|
|
|
Explain the rule for expressing extremely large numbers in scientific notation.
|
Knowing the place value of each digit is important
|
|
|
Explain the rule governing the expression of extremely small numbers in scientific notation.
|
Depiction of the place value of each digit in the decimal number
|
|
|
Define exponent.
|
A number designating the power to which another number is to be raised
|
|
|
Explain how exponents are manipulated during multiplication.
|
Multiplication: when multiplying numbers containing exponents, the exponents ( power of 10) are added and the coefficients are multiplied.
|
|
|
Explain how exponents are manipulated during division.
|
Division: when dividing numbers containing exponents, the exponents are subtracted and the coefficients are divided.
|
|
|
Explain how exponents are manipulated during addition.
|
Addition: when adding numbers containing exponents, the exponents must be equal before the coefficients are added.
|
|
|
Explain how exponents are manipulated during subtraction.
|
Subtraction: when subtracting numbers with exponents, the exponents must be equal before the coefficients are subtracted.
|
|
|
Distinguish between precision and accuracy.
|
Precision: how close a measurement can be reproduced.
Accuracy: how much the measured value agrees with the actual value. |
|
|
What is the significance of the last digit of any measures value?
|
The last digit is an estimate.
|
|
|
Are all zeros significant figures? Explain.
|
Not all zeros are significant. A zero that is used to indicate the location of a decimal point is not significant. For example, the value 0.003kg contains one significant digit, i.e., 3. The zeros are used only to locate the decimal point.
|
|
|
State the rules that govern the process of determining significant figures.
|
• None zero digits are always significant.
• All final zeros following the decimal point are significant. • Zeros between nonzero significant digits are always significant. • Zeros used exclusively for placing the decimal point are not significant. • All digits preceding the power of 10 in scientific notation are significant. |
|
|
Explain how the number of significant figures determines when performing mathematical operations involving measures values.
|
The result of any calculation with measurements can never be more precise than the least precise measurement.
|
|
|
Differentiate between random and systematic errors.
|
Random errors are unavoidable. However, they can be minimized by exercising care during measurements and obtaining an average.
Systemic errors are caused by faulty measuring devices it cannot be minimized by taking repeated measurements and obtaining an average |
|
|
Define parallax.
|
Parallax: is the apparent shift in the position of an object when it is viewed from different angles.
|
|
|
How can the problem of parallax be overcome?
|
View at eye level to obtain the most accurate reading.
|
|
|
How do the units of the ratio relate to each other?
|
A ratio must be comprised of quantities having the same units.
|
|
|
What does the colon (punctuation mark) represent in a ratio? i.e :
|
It means "is to" or division or fraction.
|
|
|
Why is the physiologic measurement compliance not a true ratio?
|
Is not a true ratio because the units of the value in the numerator are not the same units as the units of the denominator. Compliance is not a true ratio.
|
|
|
Name the two components of a ratio.
|
Numerator and Denominator
|
|
|
How can unlike units be manipulated for a ratio to occur?
|
Convert to the same unit, ratio will exist.
|
|
|
Define proportion.
|
A proportion is a statement indicating that two ratios are equal.
|
|
|
Name the component parts of a proportion.
|
Extremes and means.
|
|
|
Using the letters of factors l, f, b, and w, illustrate the four formats by which proportions can be represented.
|
l /f=b/w
l:f =b:w lf =bw l:f :: b:w |
|
|
Name the ideal gas laws the can be solved using the proportion method.
|
Charles’ Law (direct proportion) and Boyle’s Law (inverse proportion)
|
|
|
What is the meaning of the symbol ∝?
|
∝ this symbol means proportional to
|
|
|
What does Direct proportion mean?
|
Direct proportion - Consider 2 things which are related to each other. And if one thing is increasing the second thing which is related to that thing is also increasing and similarly if one thing is decreasing and the second thing which is related to the first is also decreasing that will be called the direct proportion. For example if you purchase 5 eggs for 5 dollars and if you keep increasing the number of eggs the cost will be automatically increase so this is the example of direct proportion. I mean there is the direct proportion between the number of eggs and their cost.
|
|
|
Explain the term Inverse proportion.
|
Inverse Proportion - if something is increasing while the other thing that is related to it is decreasing it will be called inverse proportion. For example if you're driving a car and the car speed is increasing while the distance is decreasing to your destination. That proportion will be called the inverse proportion
|
|
|
What does the % sign indicate?
|
Basically, a percent is a ratio, i.e., some portion of 100 (numerator) over 100 (denominator). For example, 15% represents 15 parts of 100, or 15/100.
|
|
|
List the three types of percent problems.
|
I. Finding the percent of a number
II. Determining what percent of one number is of another. III. Calculating the number when the percent of is known. |
|
|
Define the term content and list the units that can be used express it.
|
Content – is defined as the actual weight of water present in a given volume of air expressed in terms of either grams per cubic meter (g/m3) or milligrams per liter (mg/L).
|
|
|
Define the term capacity, and list the units that can be used to express it..
|
Capacity – describes the maximum amount of of water that air can hold at a given temperature. Capacity is usually expressed in either g/m3 or mg/L.
|
|
|
Define the term humidity deficit.
|
Humidity deficit – insufficient amount of water vapor in the air.
Humidity deficit is dependent on the humidity of inspired air. A higher humidity content in the inspired air gives a lower humidity deficit. 43.9mg/L represents the maximum humidity capacity at body temperature. |
|
|
Why is a ratio solution not a true percent solution?
|
A ratio solution, although it can be expressed as a percentage, it is not a true percent solution. For example., Given : 1/200 solution of Isuprel. The solution contains 1g of solute per 200 ml of solvent. Consequently, this fraction expresses gram per millimeter. The units do not cancel, demonstrating that this drug concentration is not a true percent.
|
|
|
What two expressions are commonly written as percents but are not actually true percentages?
|
Percent Relative humidity and percent body humidity
|
|
|
Why can PAO2 be substituted for by the end-pulmonary capillary oxygen tension in the shunt equation?
|
PAO2 = PCO2
|
|
|
What factors are required to calculate the % shunt using the shunt equation?
|
• PaCO2; used in the alveolar air equation to calculate PAO2 , which substitutes for the end pulmonary capillary oxygen tension. The PB , PH2O , and FIO2 are also used in the alveolar equation.
• PaO2; used to determine the dissolved arterial O2 in terms of vol %. • [Hb]; used to determine hemoglobin’s oxygen-carrying capacity. |
|
|
What is meant by a dimension?
|
Dimension – A unit used to qualify a numerical value.
|
|
|
What is a conversion factor?
|
Conversion factor- a fraction having unlike units in the numerator and denominator.
|
|
|
Why does a true ratio render a dimensionless quantity?
|
A dimensionless value is a numerical value that has no units. For a true ratio to exist, like entities must be compared, i.e., sec/sec (I/E) or ml/ml (VD/VT). The numerical result of such a relationship is termed a dimensionless number because the units cancel.
|
|
|
List the rules governing the use of a dimension in addition and subtraction.
|
Dimensions in Addition and Subtraction
• To add or subtract numbers, the numbers must have the same dimensions. One could not for example, add 10 vol% to 15 g%. the result would be meaningless. • Numbers with unlike units may be added or subtracted only if the units can be converted to the same dimension. |
|
|
List the rules governing the use of a dimension in multiplication, and division.
|
Dimensions in Multiplication and Division
• Like entities, as well as unlike entities, can be multiplied or divided. The units can also be dealt with mathematically in the same fashion as the quantities. |
|
|
What is the factor-units method?
|
Factor-Units Method - The method is based on quantities that can be defined as equalities. Therefore, from any equality two fractions can be formed, each equal to one. For example, In terms of measured quantities:
1 min = 60sec, then 1min/ 60 secs = 1 and 60sec/1min = 1 |
|
|
List the exponential form for the following SI prefixes: (a) nano-, (b) centi-, (c) mega-, (d) kilo-, and (e) micro-.
|
a) Nano = 10 power of -9
b) Centi = 10 power of -2 c) Mega = 10 power of 6 d) Kilo = 10 power of 3 e) Micro = 10 power of -6 |
|
|
List three elements of logarithmic expression.
|
• The logarithm
• The base • A number |
|
|
Define two synonyms of the word logarithm.
|
Exponent- a number designating the power to which another number is to be raised.
Power- the product obtained by multiplying a quantity by itself one or more times: The third power of 2 is 8. |
|
|
What are the two methods by which logarithm can be expressed?
|
Exponetial form: 10 power of 2 = 100
Logarithmic form: log10 100 =2 |
|
|
What are the two element parts of a logarithm?
|
Characteristic and Mantissa
|
|
|
How can you obtain a positive characteristic.
|
Positive characteristic:
• If the number is equal to or greater than 1, count the number of digits to the left of the decimal point and subtract 1. The remainder is the characteristic of the logarithm. Count the number of decimal places (x) the decimal point must be moved to the left to obtain a number between 1 and 9, inclusively. Formula for determining a positive characteristic: (x - 1) = positive characteristics. |
|
|
How can you obtain a negative characteristic.
|
Negative characteristic:
• if the number is less than 1 (i.e., a purely decimal number), count the number of places (n) the decimal point must be moved to the right to obtain a number between 1 and 9. Formula for determining a negative characteristic: (10 – n) – 10 = negative characteristic |
|
|
Which part of a logarithm does the log table represent?
|
The mantissa of a logarithm is obtained from a log table.
|
|
|
Define the term antilog.
|
The process of determining the logarithm (exponent or power) when the number is known. The opposite process of finding the logarithm.
|
|
|
Define the term variable.
|
Variable – a symbol used to represent one or more numbers.
|
|
|
What is the algebraic expression that contains a variable called?
|
Variable expression.
|
|
|
Explain how the solution to an algebraic expression is found.
|
To find the solution to an algebraic expression, a numerical value must be given to substitute for the variable.
|
|
|
What is a numerical expression?
|
Once a number is inserted into an algebraic expression for each variable, the expression is called a numerical expression.
|
|
|
Write an algebraic expression (a) with one variable, (b) with two variables, and (c) with three variables.
|
a) 10 + y
b) a + c c) a + b + c |
|
|
State the two rules the govern the addition of real numbers
|
I. Two real numbers with the same sign
• Add the absolute values and give the total the same sign as the numbers. For example, -5 + (-3) = -8 II. Two real numbers with different signs • Determine the absolute values. • Subtract the smaller absolute value from the larger one. • Give the result the same sign as the larger absolute value. For example, -30 + 25 = -5 |
|
|
Describe what is meant by additive inverse.
|
When subtracting real numbers, a term synonymous with opposite is used, namely, additive inverse. The additive inverse of a real number is that a real number’s opposite absolute value. For example,
The additive inverse of -12 is +12. |
|
|
State the rule that governs the multiplication of real numbers.
|
I. Numbers with the same signs
• The product of two numbers that have the same sign is positive. For example, 10 x 3 = 30 or (-10) (-3) = 30 II. Numbers with opposite signs • The product of two numbers that have opposite signs will be negative. For example, (15) (-3) = -45 |
|
|
1atm = _______torr
|
760 torr
|
|
|
760mmHg = _______atm
|
1 atm
|
|
|
List the various equivalents of 1 atm.
|
760 torr
760 mm Hg 1034 cm H2O 33 ft. H2O 14.7 psi 29.9 in. Hg 101.33 kPa 1.014 x dynes/cm2 |
|
|
Convert
9.21 x 106 mmHg= ______________________cm H2O |
1.25 cm H2O
|
|
|
Convert
429 ft H2O= ___________________________atm |
13 atm
|
|
|
Convert
380 torr= __________________________ft H2O |
16.5 ft.H2O
|
|
|
Convert
80 in, Hg = _________________________cmHg |
203 cm Hg
|
|
|
Convert
563 kPa = __________________________________atm |
5.6 atm
|
|
|
List the subatomic particles located inside an atom’s nucleus
|
Protons and neutrons
|
|
|
Define the terms (a) atomic mass and (b) atomic number
|
a) Atomic mass – sum of protons and neutrons within the nucleus of an atom.
b) Atomic number –the number of protons within nucleus. |
|
|
List the atomic number and the atomic mass for the three forms of oxygen atoms found in nature.
|
1) Form A – mass of 16amu: atomic number of 8
2) Form B – mass of 17amu: atomic number of 8 3) Form C – mass of 18amu: atomic number of 8 |
|
|
How should 0.0000008 be expressed in proper scientific notation?
|
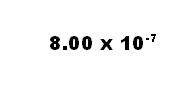
|
|
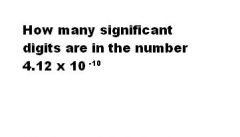
|
3
|
|
|
What is the air:oxygen ratio for an air entrainment mask delivering 24% O2?
|
25:1
|
|
|
Given the following, compute the pressure generated to overcome airway resistance during mechanical ventilation.
PIP 55cm H2O PEEP 10cm H2O P plateau 25cm H2O |
20cm H2O
|
|
|
If a solution undergoes a pH change from 6 to 7, by what fold does [H] of the solution change?
|
10-fold
|
|
|
You are running a ventilator with (4) H cylinders, the tank currently on the ventilators has 1200 PSIG and the others are new. The flow required to maintain pressure with the ventilator is 15 LPM. How much time do you have before you will be required to change the current tank?
|
4 hrs and 11 mins
|
|
|
What is the opposite value of -4?
|
+4
|
|
|
Two numbers whose products is unity are called________.
|
Reciprocals
|
|
|
Which of the following paired terms represent reciprocals?
1. compliance and elastance. 2. conductance and resistance 3. series resistance and parallel resistance. 4. mean airway pressure and peak inspiratory pressure. |
1 and 2
|
|
|
What is the reciprocal of 0?
|
zero has no reciprocal.
|
|
|
The poin ton the number line equivalent to zero is called the _____.
|
origin
|
|
|
Calculate the inspiratory time (TI) for a mechanically ventilated patient with a (TI) of 30% and a total cycle time (TCT) 4 seconds.
|
1.2
|
|
|
Calculate the oxygen content of arterial blood for a patient who has 18 vol% (ml/dl) hemoglobin concentration and a 65% SpO2.
|
15.68 vol% (ml/dl)
|
|
|
Calculate Praw when PIP 40cmH2O and Pplateau is 33cmH2O.
|
7cm H2O
|
|
|
Calculate the FRC given the following data;
TLC = 4000ml VC = 2500ml ERV = 800ml |
700ml
|
|
|
What is the IBW for a 5' 4" 63 year old woman?
|
125 lbs
|
|
|
Calculate the alveolar pressure of oxygen at a barometric pressure of 635mmHg at normal body temperature and a PaCO2 of 38torr.
|
76mmHg
|
|
|
The ability of an object to return to its original shape is called________
|
Elastance
|

