![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
4 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back

|
Phase 0
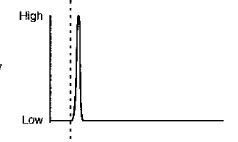
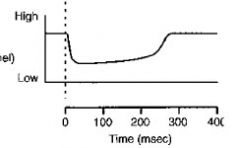
• Fast channels open, i gNa' Sodium influx then causes depolarization. • The channels open and dose quickly, and they have dosed by the time the main part of the plateau phase is entered. Phase 1 This slight repolarization is due to a transient potassium current and the dosing of the sodium channels. Originally it was thought that CI was involved, though we now know that is not the case. Subendocardial fibers lack a phase 1. ~MEDICAL 41 Section II: Excitable Tissue 42 ~MED1CAl Phase 2 • L-type Ca2+ channels are open, gCa t permitting a calcium influx. Voltage-gated potassium channels, the iKI, are closed; gK -1. compared with resting membrane. Potassium efflux continues through the ungated potassium channels and possibly other channels. • If voltage-gated potassium channels did not close during depolarization, early repolarization would occur, preventing the full development of the plateau phase. • The development of the plateau phase is dependent on the closing of voltage-gated potassium channels. • Calcium channel antagonists shorten the plateau. • Potassium channel antagonists lengthen the plateau. Phase 3 L-type Ca2+ channels close,gCa -1.; this eliminates any influx through these channels. Voltage-gatedpotassium channels, the delayed rectifier iK, then the iK j are opening, gK T. Becausewe are a long way from the potassium equilibrium potential and conductance to potassium is increasing, a large potassium efflux begins, and the cell quickly repolarizes. If the voltage-gated potassium channels did not open, the cell would still repolarize but more slowly,because of closure of calcium channels and potassium efflux through the ungated potassium channels. Phase 4 gK high; voltage-gated and ungated potassium channels open. The delayed rectifiers, iK, gradually close but are responsible for the relative refractory period during early phase 4. |
|
|
Na" Permeability
(fast channel) |
|

|
Ca2+ Permeability
(slow channel |
|
|
K+Permeability : /
(vottage-gated channel |

