![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
24 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Name the 3 physical forms matter can exist in
|
Gas, Liquid, Solid
|
|
|
1 atm = ___ mm Hg
|
1 atm = 760 mm Hg
|
|
|
X mm Hg = ___ torr
|
X mm Hg = X torr (same amount)
|
|
|
Define Standard Temperature and Pressure (STP) Conditions
|
STP = 273.15 K (0 deg. C), 1 atm
|
|
|
Define Standard State Conditions
|
Standard state conditions = 298K or 25 deg. C, 1 atm
|
|
|
Boyle's Law
|
Pressure exerted by a gas held at a constant temperature varies inversely with the volume of the gas. If the volume is halved, the pressure is doubled; and if the volume is doubled, the pressure is halved. Given the inverse relationship between pressure and volume, the product of pressure (P) and volume (V) is a constant (k) for a given mass of confined gas as long as the temperature is constant. Stated as a formula, thus is: PV = k
P1V1 = P2V2 |
|
|
Give the Gay-Lussac (Charles' Law)
|
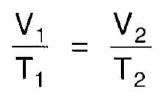
|
|
|
Ideal Gas Law
|
PV=nRT P (atm), V (L), n (mol), R = 0.0821 L-atm/K-mol, T (K)
|
|
|
What is the principle behind Dalton's law of partial pressures?
|
When two or more gases are found in one vessel without chemical interaction,
each gas will behave independently of the other(s). Therefore, the pressure exerted by each gas in the mixture will be equal to the pressure that gas would exert if it were the only one in the container. |
|
|
What is the definition of partial pressure?
|
Partial pressure is the pressure exerted by a specific gas with a mixture of gases.
|
|
|
What is the equation for Dalton's law of partial pressures?
|
PT= Pa+Pb+Pc....
|
|
|
What is the relationship between the amount of moles of a gas and it's pressure?
|
they are directly related. If you can determine the amount of moles of a gas and the moles of the whole system, and given the total pressure, you can determine the partial pressures.
|
|
|
What is the purpose of the Van der Walls equation of state?
|
to make up for diviations from PV=nRT made by pressure and temperature.
|
|
|
What is the idea behind the kenetic molecular theory of gases?
|
Essentially, the theory posits that pressure is due not to static repulsion between molecules, as was Isaac Newton's conjecture, but due to collisions between molecules moving at different velocities.
|
|
|
What are the five assumptions of the kinetic molecular theory?
|

|
|
|
What is the average kinetic energy of a gas proportional to?
|
The absolute temperature of the gas.
|
|
|
What is the equation used to relate the average kinetic energy and absolute temperature?
|
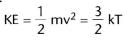
k is the boltzmann constant
|
|
|
What equation is used to determine the average speeds of all the gas particles in a sample?
|
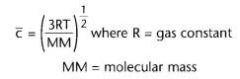
|
|
|
Please give the equation used to determine the rate of effusion and diffusion:
|
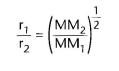
|
|
|
Please define effusion:
|
Effusion is the flow of gas particles under pressure from one compartment
to another through a small opening. |
|
|
Differentiate STP and Standard Conditions
|
STP (273 K, 1 atm) used for gas law calculations
Standard State (298 K, 1 atm) used for measuring standard enthalpy, entropy, free energy, changes, and voltage |
|
|
1 atm = __ torr = __ mm Hg = __ kPa
|
1 atm = 760 torr = 760 mm Hg = 101 kPa
|
|
|
Characteristics of an Ideal Gas
|
An ideal gas has molecules that (1) have no intermolecular forces, (2) occupy no volume.
|
|
|
Under isobaric conditions, what is the relationship between volume and temperature?
|
At constant pressure, volume is directly proportional to temperature (V1/T1 = V2/T2)
|

